ASTM B559-12(2023)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Nickel-Coated, Copper-Clad Steel Wire for Electronic Application
Standard Specification for Nickel-Coated, Copper-Clad Steel Wire for Electronic Application
ABSTRACT
This specification covers nickel-coated, round, copper-clad steel wire for electronic applications. The nickel-coated wire shall consist of the basis wire coated with nickel. Tensile strength and elongation of the nickel-coated wire shall conform to the specified requirements for the applicable size and class of copper-clad steel wire. The electrical resistivity shall not exceed the values specified. Continuity, adherence, and mass of the coating shall be determined. Necessary joints in the wire and rod prior to final coating and drawing shall be made.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers nickel-coated, round, copper-clad steel wire for electronic application.
1.2 Nickel coatings in mass percentages of the total mass of the coated wire are as follows: 2 %, 4 %, 7 %, 10 %, and 27 %. Nickel-coated wire having different minimum mass percentages of nickel may be obtained by mutual agreement between the manufacturer and the purchaser. For information purposes, the thickness of coating in microinches provided by the percentages listed above is shown in Table 1.
1.3 Four classes of nickel-coated, copper-clad steel wire are covered as follows:
1.3.1 Class N30HS—Nominal 30 % conductivity, hard drawn.
1.3.2 Class N30A—Nominal 30 % conductivity, annealed.
1.3.3 Class N40HS—Nominal 40 % conductivity, hard drawn.
1.3.4 Class N40A—Nominal 40 % conductivity, annealed.
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.4.1 Exception—The SI values for resistivity are to be regarded as standard.
1.5 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the test method described in this specification. This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.(Warning—Consideration should be given to toxicity and flammability when selecting solvent cleaners.)
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: B559 − 12 (Reapproved 2023)
Standard Specification for
Nickel-Coated, Copper-Clad Steel Wire for Electronic
Application
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B559; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope 1.6 This international standard was developed in accor-
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
1.1 This specification covers nickel-coated, round, copper-
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
clad steel wire for electronic application.
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
1.2 Nickel coatings in mass percentages of the total mass of
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
the coated wire are as follows: 2 %, 4 %, 7 %, 10 %, and 27 %.
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Nickel-coated wire having different minimum mass percent-
ages of nickel may be obtained by mutual agreement between
2. Referenced Documents
the manufacturer and the purchaser. For information purposes,
2.1 The following documents of the issue in effect on date
the thickness of coating in microinches provided by the
of material purchase form a part of this specification to the
percentages listed above is shown in Table 1.
extent referenced herein:
1.3 Four classes of nickel-coated, copper-clad steel wire are
2.2 ASTM Standards:
covered as follows:
B193 Test Method for Resistivity of Electrical Conductor
1.3.1 Class N30HS—Nominal 30 % conductivity, hard
Materials
drawn.
B258 Specification for Standard Nominal Diameters and
1.3.2 Class N30A—Nominal 30 % conductivity, annealed.
Cross-Sectional Areas of AWG Sizes of Solid Round
1.3.3 Class N40HS—Nominal 40 % conductivity, hard
Wires Used as Electrical Conductors
drawn.
B452 Specification for Copper-Clad Steel Wire for Elec-
1.3.4 Class N40A—Nominal 40 % conductivity, annealed.
tronic Application
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
E75 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Copper-Nickel
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
and Copper-Nickel-Zinc Alloys (Withdrawn 2010)
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
2.3 American Chemical Society:
and are not considered standard.
Standard Reagents Tests
1.4.1 Exception—The SI values for resistivity are to be
2.4 NIST Standard:
regarded as standard.
NBS Handbook 100 Copper Wire Tables
1.5 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the
3. Terminology
test method described in this specification. This standard does
not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any,
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this
standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environ-
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
mental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
limitations prior to use.(Warning—Consideration should be
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
given to toxicity and flammability when selecting solvent
the ASTM website.
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
cleaners.)
www.astm.org.
ACS Reagent Chemicals, Specifications and Procedures for Reagents and
Standard-Grade Reference Materials, American Chemical Society, Washington,
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B01 on DC. For suggestions on the testing of reagents not listed by the American Chemical
Electrical Conductors and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee B01.06 on Society, see Analar Standards for Laboratory Chemicals, BDH Ltd., Poole, Dorset,
Bi-Metallic Conductors. U.K., and the United States Pharmacopeia and National Formulary, U.S. Pharma-
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2023. Published October 2023. Originally copeial Convention, Inc. (USPC), Rockville, MD.
approved in 1972. Last previous edition approved in 2017 as B559 – 12 (2017). Available from National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), 100
DOI: 10.1520/B0559-12R23. Bureau Dr., Stop 1070, Gaithersburg, MD 20899-1070, http://www.nist.gov.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
B559 − 12 (2023)
TABLE 1 Nickel Mass Percent and Thickness of Coating
Thickness of Nickel,μ in.
Diameter Cross-Sectional Area at 20 °C
(for information only)
2 2
in. mm cmil in. mm 2.0 % 4.0 % 7.0 % 10.0 % 27.0 %
0.0720 1.829 5 180 0.00407 2.63 334 637 1 181 1 703 4 892
0.0641 1.628 4 110 0.00323 2.08 298 566 1 050 1 514 4 349
0.0571 1.450 3 260 0.00256 1.65 266 505 936 1 350 3 880
0.0508 1.290 2 580 0.00203 1.31 236 450 833 1 200 3 452
0.0453 1.151 2 050 0.00161 1.04 211 401 743 1 071 3 077
0.0403 1.024 1 620 0.00128 0.823 202 357 661 953 2 738
0.0359 0.912 1 290 0.00101 0.653 167 318 589 849 2 439
0.0320 0.813 1 020 0.000804 0.519 149 283 525 757 2 174
0.0285 0.724 812 0.000638 0.412 133 252 467 686 1 937
0.0253 0.643 640 0.000503 0.324 118 224 415 598 1 719
0.0226 0.574 511 0.000401 0.259 105 200 371 535 1 536
0.0201 0.511 404 0.000317 0.205 94 178 330 475 1 366
0.0179 0.455 320 0.000252 0.162 83 158 294 423 1 216
0.0159 0.404 253 0.000199 0.128 74 141 261 376 1 080
0.0142 0.361 202 0.000158 0.102 66 126 233 336 965
0.0126 0.320 159 0.000125 0.0804 59 112 207 298 856
0.0113 0.287 128 0.000100 0.0647 53 100 185 267 768
0.0100 0.254 100 0.0000785 0.0507 47 89 164 237 680
0.0089 0.226 79.2 0.0000622 0.0401 41 80 146 211 605
0.0080 0.203 64.0 0.0000503 0.0324 . 71 131 189 544
0.0071 0.180 50.4 0.0000396 0.0255 . 63 116 168 482
0.0063 0.160 39.7 0.0000312 0.0201 . 56 103 149 428
0.0056 0.142 31.4 0.0000246 0.0159 . 50 92 132 381
0.0050 0.127 25.0 0.0000196 0.0127 . 44 82 118 340
0.0045 0.114 20.2 0.0000159 0.0103 . 40 74 106 306
0.0040 0.102 16.0 0.0000126 0.00811 . . 66 95 272
0.0035 0.089 12.2 0.00000962 0.00621 . . 57 83 238
0.0031 0.079 9.61 0.00000755 0.00487 . . 51 73 211
3.1.1 lot—any amount of wire of one class and size pre- 5. Materials and Manufacture
sented for acceptance at one time, such amount, however, not
5.1 The basis material shall consist of copper-clad steel wire
to exceed 10 000 lb (4500 kg) (Note 1).
conforming to the product description, quality and specifica-
tion requirements of Specification B452.
NOTE 1—A lot should comprise material taken from a product regularly
meeting the requirements of this specification. Inspection of individual
5.2 The nickel-coated wire shall consist of the basis wire
lots of less than 500 lb (230 kg) of wire cannot be justified economically.
coated with nickel (Note 2). The quality of the nickel-coated
For small lots of 500 lb (230 kg) or less, the purchaser may agree to the
wire shall be such that the finished product meets the properties
manufacturers’ regular inspection of the product as a whole as evidence of
acceptability of such small lots. and requirements in this specification.
3.1.2 sample—a quantity of production units (coils, reels,
NOTE 2—Nickel on copper-clad steel wire provides a protective coating
for a prevention of oxidation of the copper either during fabrication or
etc.) selected at random from the lot for the purpose of
service.
determining conformance of the lot to the requirements of this
specification.
6. General Requirements
3.1.3 specimen—a length of wire removed for test purposes
6.1 Tensile strength and elongation of the nickel-coated
from any individual production unit of the sample.
wire shall conform to the requirements of Specification B452
for the applicable size and class of copper-clad steel wire.
4. Ordering Information
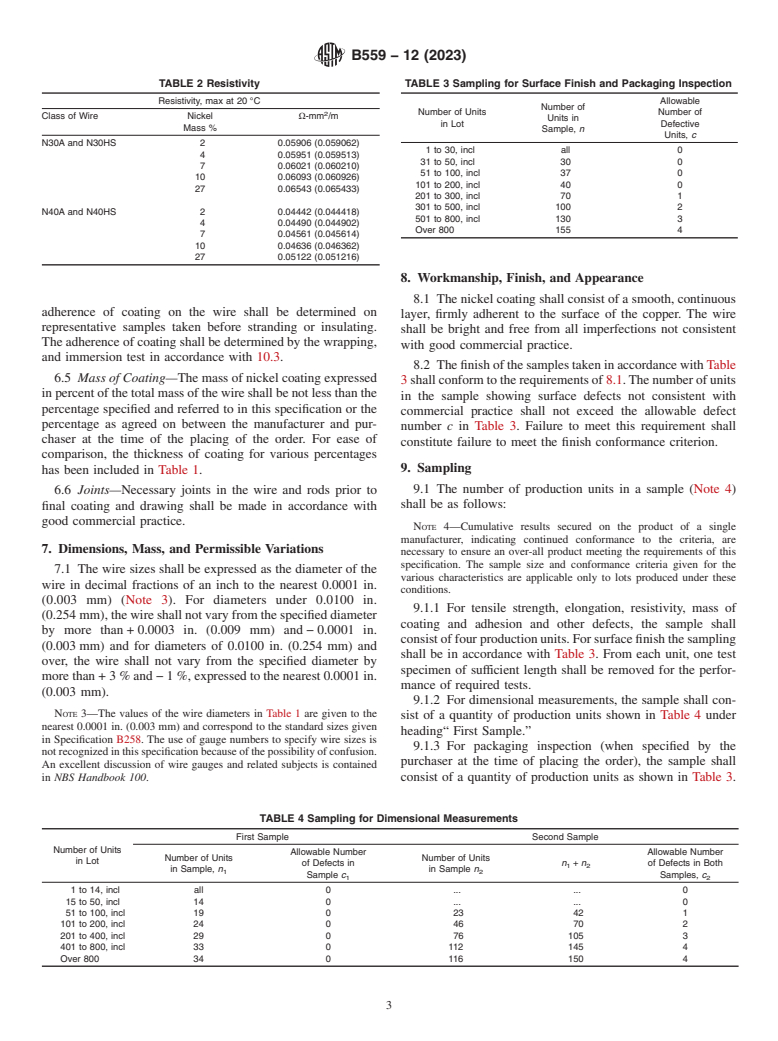
6.2 Resistivity—The electrical resistivity at a temperature of
4.1 Orders for material under this specification shall include
20 °C shall not exceed the values prescribed in Table 2
the following information:
(Explanatory Note 1).
4.1.1 Quantity of each size.
6.3 Continuity of Coating—The nickel coating shall be
4.1.2 Wire size (see Section 7 and Table 1).
continuous. The continuity of the coating shall be determined
4.1.3 Class of basis wire (see 1.3).
on representative samples taken before stranding or insulating
4.1.4 Mass percentage of nickel coating (see 1.2 and Table
and shall be determined by the sodium polysulfide test, in
1).
accordance with 10.2. Wire whose coating weight corresponds
4.1.5 Package size (see 14.2 and Section 14). Packaging to a thickness less than 50 μ in. (0.00005 in.) (1.3 μm) shall not
be subject to this test.
inspection, if required (see 9.1.3).
4.1.6 Special package marking, if required.
6.4 Adherence of Coating—The nickel coating shall be
4.1.7 Place of inspection (see 13.1). firmly adhered to the surface of the copper-clad steel wire. The
B559 − 12 (2023)
TABLE 2 Resistivity TABLE 3 Sampling for Surface Finish and Packaging Inspection
Resistivity, max at 20 °C Allowable
Number of
Number of Units Number of
Class of Wire Nickel Ω-mm /m
Units in
in Lot Defective
Mass %
Sample, n
Units, c
N30A and N30HS 2 0.05906 (0.059062)
1 to 30, incl all 0
4 0.05951 (0.059513)
31 to 50, incl 30 0
7 0.06021 (0.060210)
51 to 100, incl 37 0
10 0.06093 (0.060926)
101 to 200, incl 40 0
27 0.06543 (0.065433)
201 to 300, incl 70 1
301 to 500, incl 100 2
N40A and N40HS 2 0.04442 (0.044418)
501 to 800, incl 130 3
4 0.04490 (0.044902)
Over 800 155 4
7 0.04561 (0.045614)
10 0.04636 (0.046362)
27 0.05122 (0.051216)
8. Workmanship, Finish, and Appearance
8.1 The nickel coating shall consist of a smooth, continuous
adherence of coating on the wire shall be determined on
layer, firmly adherent to the surface of the copper. The wire
representative samples taken before stranding or insulating.
shall be bright and free from all imperfections not consistent
The adherence of coating shall be determined by the wrapping,
with good commercial practice.
and immersion test in accordance with 10.3.
8.2 The finish of the samples taken in accordance with Table
6.5 Mass of Coating—The mass of nickel coating expressed
3 shall conform to the requirements of 8.1. The number of units
in percent of the total mass of the wire shall be not less than the
in the sample showing surface defects not consistent with
percentage specified and referred to in this specification or the
commercial practice shall not exceed the allowable defect
percentage as agreed on between the manufacturer and pur-
number c in Table 3. Failure to meet this requirement shall
chaser at the time of the placing of the order. For ease of
constitute failure to meet the finish conformance criterion.
comparison, the thickness of coating for various percentages
9. Sampling
has been included in Table 1.
9.1 The number of production units in a sample (Note 4)
6.6 Joints—Necessary joints in the wire and rods prior to
shall be as follows:
final coating and drawing shall be made in accordance with
good commercial practice.
NOTE 4—Cumulative results secured on the product of a single
manufacturer, indicating continued conformance to the criteria, are
7. Dimensions, Mass, and Permissible Variations
necessary to ensure an over-all product meeting the requirements of this
specification. The sample size and conformance criteria given for the
7.1 The wire sizes shall be expressed as the diameter of the
various characteristics are applicable only to lots produced under these
wire in decimal fractions of an inch to the nearest 0.0001 in.
conditions.
(0.003 mm) (Note 3). For diameters under 0.0100 in.
9.1.1 For tensile strength, elongation, resistivity, mass of
(0.254 mm), the wire shall not vary from the specified diameter
coating and adhesion and other defects, the sample shall
by more than + 0.0003 in. (0.009 mm) and − 0.0001 in.
consist of four production units. For surface finish the sampling
(0.003 mm) and for diameters of 0.0100 in. (0.254 mm) and
shall be in accordance with Table 3. From each unit, one test
over, the wire shall not vary from the specified diameter by
specimen of sufficient length shall be removed for the perfor-
more than + 3 % and − 1 %, expressed to the nearest 0.0001 in.
mance of required tests.
(0.003 mm).
9.1.2 For dimensional measurements, the sample shall con-
NOTE 3—The values of the wire diameters in Table 1 are given to the
sist of a quantity of production units shown in Table 4 under
nearest 0.0001 in. (0.003 mm) and correspond to the standard sizes given
heading“ First Sample.”
in Specification B258. The use of gauge numbers to specify wire sizes is
9.1.3 For packaging inspection (when specified by the
not recognized in this specification because of the possibility of confusion.
purchaser at the time of placing the order), the sample shall
An excellent discussion of wire gauges and related subjects is contained
in NBS Handbook 100. consist of a quantity of production units as shown in Table 3.
TABLE 4 Sampling for Dimensional Measurements
First Sample Second Sample
Number of Units
Allowable Number Allowable Number
Number of Units Number of Units
in Lot
of Defects in n + n of Defects in Both
1 2
in Sample, n in Sample n
1 2
Sample c Samples, c
1 2
1 to 14, incl all 0 . . 0
15 to 50, incl 14 0 . . 0
51 to 100, incl 19 0 23 42 1
101 to 200, incl 24 0 46 70 2
201 to 400, incl 29 0 76 105 3
401 to 800, incl 33 0 112 145 4
Over 800 34 0 116 150 4
B559 − 12 (2023)
10. Test Methods the surface to be subjected to test. Wire sizes 0.005 in.
(0.13 mm) and smaller may be cleaned after wrapping around
10.1 Tensile Properties—For tensile strength, elongation,
the mandrel.
resistivity, dimensional measurement, and the quality of the
10.3.2 Procedure:
basis wire, the latest issue of Specification B452 shall apply
10.3.2.1 Wrapping—Wrap the test specimen slowly in a
and the tests shall be performed on the nickel-coated wire
suitable manner in an open helix around a wire of its own
(Explanatory Note 2).
diameter. Take care not to stretch the specimen during the
10.2 Continuity of Coating:
wrapping operation. The spacing of the consecutive turns shall
10.2.1 Specimens:
be approximately equal to the diameter of the wire. For wire
10.2.1.1 Length of Specimens—Test specimens shal
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.