ASTM D4282-02(2010)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determination of Free Cyanide in Water and Wastewater by Microdiffusion
Standard Test Method for Determination of Free Cyanide in Water and Wastewater by Microdiffusion
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This test method is useful in distinguishing between the potentially available free cyanide (total cyanide) and the free cyanide actually present.
This test method provides a convenient technique for making on-site free cyanide determinations.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of free cyanides in waters and wastewaters. Free cyanide is here defined as the cyanide which diffuses as cyanide (HCN), at room temperature, from a solution at pH 6.
1.2 This test method does not include complexes that resist dissociation, such as hexacyanoferrates and gold cyanide, nor does it include thiocyanate and cyanohydrin.
1.3 This test method may be applied to water and wastewater samples containing free cyanide from 10 to 150 μg/L. Greater concentrations may be determined by appropriate dilution.
1.4 This test method has been fully validated by collaborative testing as specified by Practice D2777.
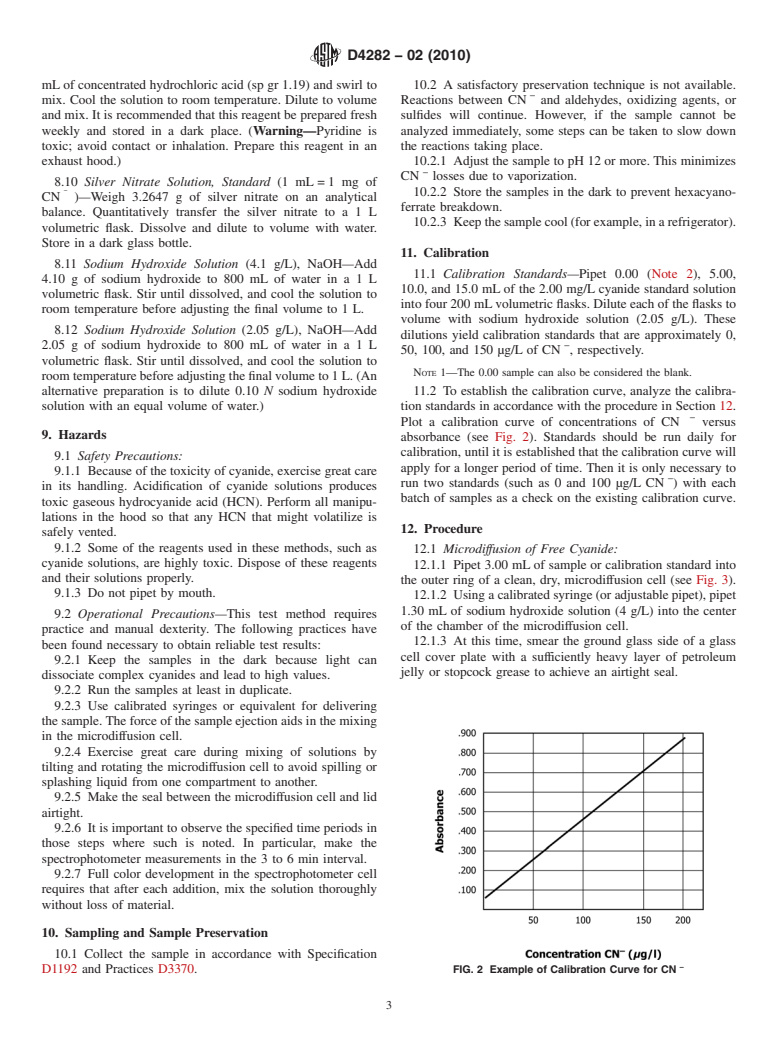
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard statements, see 8.6, 8.9, Section 9, and 12.2.1.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D4282 − 02(Reapproved 2010)
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Free Cyanide in Water and Wastewater by
Microdiffusion
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4282; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope D1193Specification for Reagent Water
D2777Practice for Determination of Precision and Bias of
1.1 This test method covers the determination of free
Applicable Test Methods of Committee D19 on Water
cyanides in waters and wastewaters. Free cyanide is here
D3370Practices for Sampling Water from Closed Conduits
defined as the cyanide which diffuses as cyanide (HCN), at
D3856Guide for Management Systems in Laboratories
room temperature, from a solution at pH 6.
Engaged in Analysis of Water
1.2 This test method does not include complexes that resist
D4210Practice for Intralaboratory Quality Control Proce-
dissociation, such as hexacyanoferrates and gold cyanide, nor
dures and a Discussion on Reporting Low-Level Data
does it include thiocyanate and cyanohydrin.
(Withdrawn 2002)
1.3 This test method may be applied to water and wastewa-
D5788Guide for Spiking Organics into Aqueous Samples
ter samples containing free cyanide from 10 to 150 µg/L.
D5789Practice for Writing Quality Control Specifications
Greater concentrations may be determined by appropriate
for Standard Test Methods for Organic Constituents
dilution. 4
(Withdrawn 2002)
1.4 This test method has been fully validated by collabora- D5847Practice for Writing Quality Control Specifications
tive testing as specified by Practice D2777.
for Standard Test Methods for Water Analysis
E275PracticeforDescribingandMeasuringPerformanceof
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
Ultraviolet and Visible Spectrophotometers
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica- 3. Terminology
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard
3.1 Foradefinitionoftermsusedinthistestmethodreferto
statements, see 8.6, 8.9, Section 9, and 12.2.1.
Terminology D1129.
2. Referenced Documents
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
2.1 ASTM Standards: 3.2.1 free cyanide—refers to those simple cyanides or
D1129Terminology Relating to Water
looselyheldcomplexesofcyanidethatdiffuseatpH6,atroom
D1192Guide for Equipment for Sampling Water and Steam
temperature.
in Closed Conduits (Withdrawn 2003)
4. Summary of Test Method
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D19 on Water
4.1 The reactions are carried out in a microdiffusion cell.
andisthedirectresponsibilityofSubcommitteeD19.06onMethodsforAnalysisfor
Organic Substances in Water.
4.2 The sample is treated with cadmium ion to precipitate
Current edition approved June 15, 2010. Published December 2010. Originally
the hexacyanoferrates.
approved in 1983. Last previous edition approved in 2002 as D4282–02. DOI:
10.1520/D4282-02R10.
4.3 The sample is buffered at pH 6 and allowed to stand for
The paper by J. M. Kruse and L. E. Thibault “Determination of Free Cyanide
4h.
in Ferro- and Ferricyanides,”Analytical Chemistry, 45(13): 2260–2261; 1973 Nov.,
recommendsadiffusionatpH7.TheANSImodification(ANSIPH4.41-1978)uses
4.4 The HCN diffuses into sodium hydroxide solution.
pH 6. Using the conditions of the ANSI method, diffusion is completed within 4
hoursatpH6.LongerdiffusiontimewasrequiredatpH7onthesamplesanalyzed.
3 4.5 An aliquot of the sodium hydroxide solution is treated
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
with chloramine-T, and the cyanogen chloride formed is
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
reacted with barbituric acid in pyridine. The absorbance of the
the ASTM website.
4 color formed is measured using a spectrophotometer at a
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
www.astm.org. wavelength of 580 nm.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
D4282 − 02 (2010)
5. Significance and Use 8.4 Chloramine-T Reagent (10 g/L)—Dissolve 1.00 g of
chloramine-Tin 50 mLof water in a 100 mLvolumetric flask.
5.1 This test method is useful in distinguishing between the
Dilute to volume with water. Make this reagent fresh daily.
potentially available free cyanide (total cyanide) and the free
−
cyanide actually present. 8.5 Cyanide Solution, Standard (1.00 mL=2 µg CN )
—Pipet 2.00 mL of cyanide stock solution (approximately 1.0
5.2 This test method provides a convenient technique for
−
g/LCN )intoa1Lvolumetricflaskanddilutetovolumewith
making on-site free cyanide determinations.
sodium hydroxide solution (2.05 g/L).
6. Interferences
8.6 Cyanide Solution Stock—Dissolve 2.51 g of potassium
cyanide, KCN, in 500 mL of sodium hydroxide solution (2.05
6.1 Decomposition of Hexacyanoferrates During Diffusion:
g/L) ina1L volumetric flask. Dilute to volume with sodium
6.1.1 This decomposition is virtually eliminated by allow-
hydroxide solution (2.05 g/L). This solution contains approxi-
ing the sample to diffuse in the dark, and by precipitating the
−
mately 1.0 g/L cyanide (CN ). (Warning—KCN is highly
hexacyanoferrates with cadmium ion.
toxic, avoid contact or inhalation. Prepare and standardize this
6.2 Instability of Free Cyanide in Effluents—The reactivity
solution weekly.)
of free cyanide with such chemicals as aldehydes or oxidizing
8.6.1 Standardizing Cyanide Stock Solution:
agents, is not really a method interference. However, because
8.6.1.1 Using a silver electrode and a reference electrode,
of this instability, it is important for the diffusion to begin as
titrate 20.0 mL of the cyanide stock solution (in a beaker also
soon after sampling as possible. It is beyond the scope of this
containing 50 mL of sodium hydroxide solution (2.05 g/L))
testmethodtolistallthepossiblecyanidereactionsthatmaybe
with the silver nitrate standard solution.
encountered.
8.6.1.2 Record the mLof titration for use in the calculation
(see Fig. 1 for an example of a typical titration curve).
7. Apparatus
8.6.1.3 Calculate the concentration of the cyanide stock
7.1 Diffusion Cell, microdiffusion cell, Conway type, 68
solution using the following equation:
mm outside diameter.
50 3 mLsilvernitrate 5mg/L CN instocksolution
~ !
7.2 Micropipets, 0.10 mL, 1.00 mL.
1.00mLofsilvernitratesolutionisequalto1 mgofCN .
7.3 Spectrophotometer, conforming to Practice E275.
8.7 Potassium Phosphate Buffer Solution (Acidified)—Add
8.0mLofconcentratedphosphoricacid(spgr1.69),H PO,to
7.4 Spectrophotometer Cell, 1 cm equipped with a stopper.
3 4
100 mL of potassium phosphate solution.
7.5 Pipet or Syringe, adjustable (to deliver 1.30 mL).
8.8 Potassium Phosphate Solution, 190 g/L—Add 400 mL
7.6 Calomel Reference Electrode , with saturated KNO
of water toa2L beaker. Add and dissolve 14.5 g of sodium
electrolyte, or the equivalent.
hydroxide, NaOH. Add and dissolve 190 g of potassium
7.7 pH Meter.
phosphate, monobasic, KH PO . Add water to 950 mL to aid
2 4
dissolution. Adjust the pH of the solution to pH 5.9 to 6.1,
7.8 Silver Electrode.
using100g/Lsodiumhydroxidesolution.Transferthesolution
8. Reagents
toa1L volumetric flask, and dilute to volume with water.
8.1 Purity of Reagents—Reagent grade chemicals shall be
8.9 Pyridine-Barbituric Acid Reagent—Add 15.0 g of bar-
used in all tests. Unless otherwise indicated, it is intended that
bituricacidtoa250mLvolumetricflask.Washdownthesides
reagents shall conform to the specifications of the Committee
of the flask with just enough water to moisten the barbituric
on Analytical Reagents of the American Chemical Society
acid. Add 75 mL of pyridine and swirl to mix. Slowly add 15
where such specifications are available. Other grades may be
used provided it is first ascertained that the reagent is of
sufficient purity to permit its use without lessening the accu-
racy of the determination.
8.2 Purity of Water—Unless otherwise indicated, reference
towatershallbeunderstoodtomeanreagentwaterconforming
to Type II of Specification D1193.
8.3 Cadmium Chloride Solution (10 g/L), CdCl —Dissolve
10.0 g of anhydrous cadmium chloride in 750 mL of water in
a 1 L volumetric flask. Dilute to volume with water.
One source of supply for these cells is Arthur H. Thomas, No. 3806-F-10.
Reagent Chemicals, American Chemical Society Specifications, American
Chemical Society, Washington, DC. For Suggestions on the testing of reagents not
listed by the American Chemical Society, see Annual Standards for Laboratory
Chemicals, BDH Ltd., Poole, Dorset, U.K., and the United States Pharmacopeia
NOTE 1—Twenty millilitres of 2.51 g/L KCN titrated with AgNO .
and National Formulary, U.S. Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. (USPC), Rockville,
MD. FIG. 1 Typical Titration Curve Standardizing KCN Solution
D4282 − 02 (2010)
mLof concentrated hydrochloric acid (sp gr 1.19) and swirl to 10.2 A satisfactory preservation technique is not available.
−
mix. Cool the solution to room temperature. Dilute to volume Reactions between CN and aldehydes, oxidizing agents, or
and mix. It is recommended that this reagent be prepared fresh sulfides will continue. However, if the sample cannot be
weekly and stored in a dark place. (Warning—Pyridine is analyzed immediately, some steps can be taken to slow down
toxic; avoid contact or inhalation. Prepare this reagent in an the reactions taking place.
exhaust hood.) 10.2.1 Adjust the sample to pH 12 or more.This minimizes
−
CN losses due to vaporization.
8.10 Silver Nitrate Solution, Standard (1 mL=1 mg of
−
10.2.2 Store the samples in the dark to prevent hexacyano-
CN )—Weigh 3.2647 g of silver nitrate on an analytical
ferrate breakdown.
balance. Quantitatively transfer the silver nitrate toa1L
10.2.3 Keepthesamplecool(forexample,inarefrigerator).
volumetric flask. Dissolve and dilute to volume with water.
Store in a dark glass bottle.
11. Calibration
8.11 Sodium Hydroxide Solution (4.1 g/L), NaOH—Add
11.1 Calibration Standards—Pipet 0.00 (Note 2), 5.00,
4.10 g of sodium hydroxide to 800 mL of water ina1L
10.0, and 15.0 mL of the 2.00 mg/L cyanide standard solution
volumetric flask. Stir until dissolved, and cool the solution to
intofour200mLvolumetricflasks.Diluteeachoftheflasksto
room temperature before adjusting the final volume to 1 L.
volume with sodium hydroxide solution (2.05 g/L). These
8.12 Sodium Hydroxide Solution (2.05 g/L), NaOH—Add
dilutions yield calibration standards that are approximately 0,
−
2.05 g of sodium hydroxide to 800 mL of water ina1L
50, 100, and 150 µg/L of CN , respectively.
volumetric flask. Stir until dissolved, and cool the solution to
NOTE 1—The 0.00 sample can also be considered the blank.
roomtemperaturebeforeadjustingthefinalvolumeto1L.(An
alternative preparation is to dilute 0.10 N sodium hydroxide 11.2 To establish the calibration curve, analyze the calibra-
solution with an equal volume of water.) tion standards in accordance with the procedure in Section 12.
−
Plot a calibration curve of concentrations of CN versus
9. Hazards
absorbance (see Fig. 2). Standards should be run daily for
calibration, until it is established that the calibration curve will
9.1 Safety Precautions:
apply for a longer period of time. Then it is only necessary to
9.1.1 Because of the toxicity of cyanide, exercise great care
−
run two standards (such as 0 and 100 µg/L CN ) with each
in its handling. Acidification of cyanide solutions produces
batch of samples as a check on the existing calibration curve.
toxic gaseous hydrocyanide acid (HCN). Perform all manipu-
lations in the hood so that any HCN that might volatilize is
12. Procedure
safely vented.
9.1.2 Some of the reagents used in these methods, such as
12.1 Microdiffusion of Free Cyanide:
cyanide solutions, are highly toxic. Dispose of these reagents
12.1.1 Pipet 3.00 mLof sample or calibration standard into
and their solutions properly.
the outer ring of a clean, dry, microdiffusion cell (see Fig. 3).
9.1.3 Do not pipet by mouth.
12.1.2 Usingacalibratedsyringe(oradjustablepipet),pipet
1.30 mL of sodium hydroxide solution (4 g/L) into the center
9.2 Operational Precautions—This test method requires
of the chamber of the microdiffusion cell.
practice and manual dexterity. The following practices have
12.1.3 At this time, smear the ground glass side of a glass
been found necessary to obtain reliable test results:
cell cover plate with a sufficiently heavy layer of petroleum
9.2.1 Keep the samples in the dark because light can
jelly or stopcock grease to achieve an airtight seal.
dissociate complex cyanides and lead to high values.
9.2.2 Run the samples at least in duplicate.
9.2.3 Use calibrated syringes or equivalent for delivering
thesample.Theforceofthesampleejectionaidsinthemixing
in the microdiffusion cell.
9.2.4 Exercise great care during mixing of solutions by
tilting and rotating the microdiffusion cell to avoid spilling or
splashing liquid from one compartment to another.
9.2.5 Make the seal between the microdiffusion cell and lid
airtight.
9.2.6 It is important to observe the specified time periods in
those steps where such is noted. In particular, make the
spectrophotometer measurements in the 3 to 6 min interval.
9.2.7 Full color development in the spectrophotometer cell
requires that after each addition, mix the solution thoroughly
without loss of material.
10. Sampling and Sample Preservation
10.1 Collect the sample in accordance with Specification
−
D1192 and Practices D3370. FIG. 2 Example of Calibration Curve for CN
D4282 − 02 (2010)
Typical Cell
(a)
Filling Inner Compartment Filling Outer Compartment
(b) (c)
FIG. 3 Microdiffusion Cell
12.1.4 Usingamicropipet,pipet0.5mLof10g/Lcadmium microdiffusion cell, inject at an angle in order to force the
chloridesolution(10g/L)intothesampleintheoutsideringof
solutionaroundthechamber,andquicklysealwiththegreased
themicrodiffusioncell.Tiltandrotatethecellfor15stoensure
glass plate.
mixing.
12.1.6 Tilt and rotate the cell for 15 s to ensure proper
12.1.5 Immediately inject 1.0 mL of potassium phosphate
mixing.
solution (190 g/L) into the sample in the outside ring of the
D4282 − 02 (2010)
12.1.7 Keep the covered c
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.