ASTM F34-98
(Practice)Standard Practice for Construction of Test Cell for Liquid Extraction of Flexible Barrier Materials
Standard Practice for Construction of Test Cell for Liquid Extraction of Flexible Barrier Materials
SCOPE
1.1 This practice covers the construction of test cells which may be used for the extraction of components from flexible barrier materials by suitable extracting liquids, including foods and food simulating solvents.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety problems, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
Designation: F 34 – 98
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR TESTING AND MATERIALS
100 Barr Harbor Dr., West Conshohocken, PA 19428
Reprinted from the Annual Book of ASTM Standards. Copyright ASTM
Standard Practice for
Construction of Test Cell for Liquid Extraction of Flexible
1
Barrier Materials
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F 34; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of original
adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A superscript
epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope all reagents shall conform to the specifications of the Commit-
tee on Analytical Reagents of the American Chemical Society,
1.1 This practice covers the construction of test cells which
5
where such specifications are available. Other grades may be
may be used for the extraction of components from flexible
used, provided it is first ascertained that the reagent is of
barrier materials by suitable extracting liquids, including foods
sufficiently high purity to permit its use without lessening the
and food simulating solvents.
accuracy of the determination.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
5.2 Purity of Water— Unless otherwise indicated, refer-
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
ences to water shall be understood to mean referee reagent
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
grade corresponding to Specification D 1193.
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
5.3 n-Heptane, boiling point specified as 208°F (97°C),
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
freshly distilled.
2. Referenced Documents
6. Procedure
2.1 ASTM Standards:
2
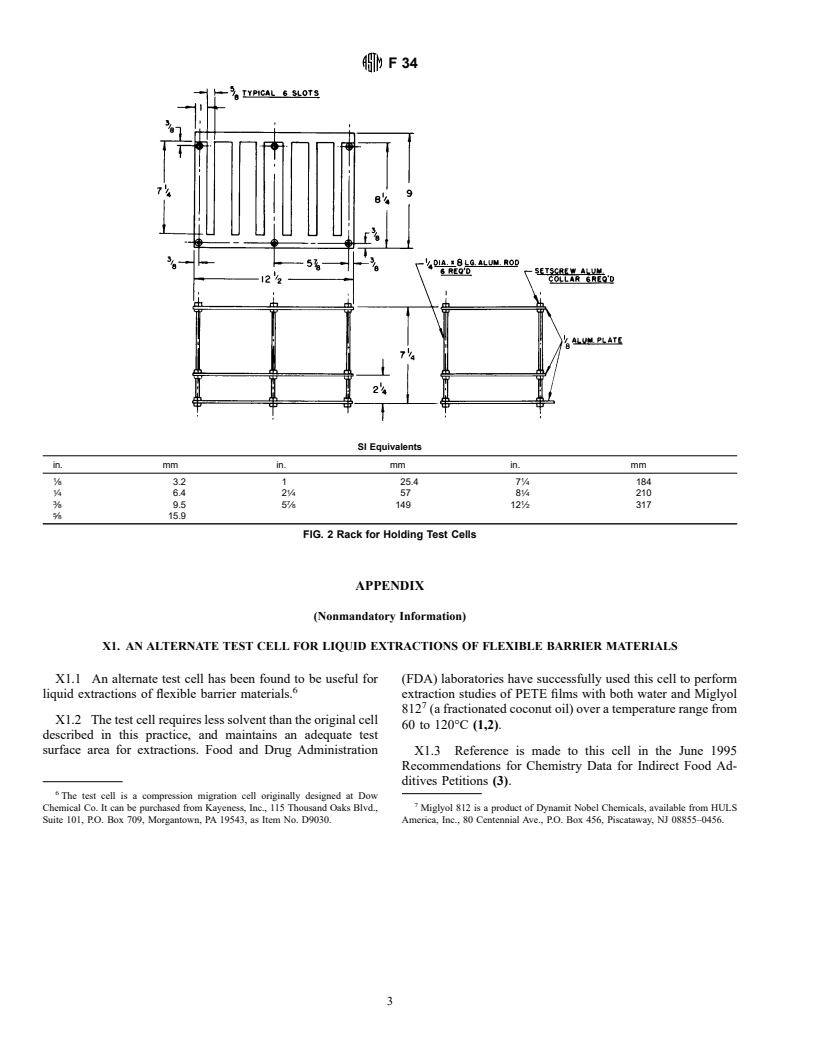
6.1 Construction of Test Cell (Fig. 1, Fig. 2)— Assemble as
D 1193 Specification for Reagent Water
follows:
2.2 AOAC International Methods of Analysis:
3 1
3
6.1.1 Two 8 by 11 ⁄8 by ⁄8-in. (203 by 289 by 3.2-mm) No.
Extractives from Flexible Barrier Materials
316 stainless steel plates, degreased.
2.3 Code of Federal Regulations:
1 1
4
6.1.2 One ⁄4 by 1 ⁄2-in. (6.4 by 38-mm) U-shaped virgin
Title 21, Sections 176.170 and 177 Subpart B
TFE-fluorocarbon gasket, grooved on both sides as shown.
1
3. Terminology
6.1.3 Twelve ⁄4 by 1-in. (6.4 by 25.4-mm) stainless steel
bolts with wing nuts.
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
1
6.1.4 One ⁄4 by 1 by 8-in. (6.4 by 25.4 by 203-mm)
3.1.1 flexible— for purpose of this practice, a term applying
TFE-fluorocarbon gasket plug tapered to provide a tight fit.
only to those flexible materials which can be inserted in the test
1 3
6.1.5 Six ⁄8 by ⁄8 by 3-in. (6.4 by 9.5 by 76-mm) plates.
cell without affecting their barrier properties.
6.2 Pre-Use Conditioning of Test Cell:
4. Significance and Use
6.2.1 Wash stainless steel plates and TFE-fluorocarbon gas-
kets in aqueous surfactant solution. Rinse with reagent water
4.1 Knowledge of extractives from flexible barrier materials
and dry at 122°F (50°C). Wash with n-heptane and redistilled
may serve many useful purposes. A test cell constructed as
acetone.
described in this practice may be used for obtaining such data.
6.2.2 For new TFE-fluorocarbon gaskets, immerse in
Another test cell has been found equivalent to the one
n-heptane overnight. Rinse gaskets with fresh n-heptane. Dry
described in this practice. See the appendix for the source of
gaskets at 122°F (50°C).
the alternate cell.
6.3 Use of Test Cell:
5. Reagents and Materials
6.3.1 Place one stainless steel plate of the cell on a flat
surface with bolts protruding up through the holes in the plate.
5.1 Purity of Reagents—Reagent grade chemicals shall be
Place a prepunched (Note 1) specimen (side to contact liquid
used in all tests. Unless otherwise indicated, it is intended that
up) on the plate with one edge of the specimen aligned with the
bottom of the plate, two edges aligned with the sides of the
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F-2 on Flexible
Barrier Materials and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F02.30 on Test
Methods.
5
Reagent Chemicals, American Chemical Society Specifications, American
Current edition approved Oct. 10, 1998. Published January 1999. Originally
published as F 34 – 63 T. Last previous edition F 34 – 92. Chemical Society, Washington, DC. For suggestions on the testing of reagents not
2
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 11.01. listed by the American Chemical Society, see Analar Standards for Laboratory
3
This method is available through the Association of Official Analytical Chemicals, BDH Ltd., Poole, Dorset, U.K., and the United States Pharmacopeia
Chemists, International, 481 North Frederick Ave., Gaithersburg, MD 20877–2504. and National Formulary, U.S. Pharmaceutical Convention, Inc. (USPC), Rockville,
4
Available from U. S. Government Printing Office, Washington, DC 20402. MD.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F34
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.