ASTM D1135-86(2014)
(Test Method)Standard Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Blue Pigments
Standard Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Blue Pigments
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
3.1 These test methods are suitable for determining if impurities are present and establishing that the required pigments are present. These test methods may be used for manufacturing quality control.
SCOPE
1.1 These test methods cover procedures for the chemical analysis of blue pigments known commercially as iron blue, copper phthalocyanine blue, and ultramarine blue.
1.2 The analytical procedures appear in the following order:
Sections
IRON BLUE PIGMENTS
Identification
6
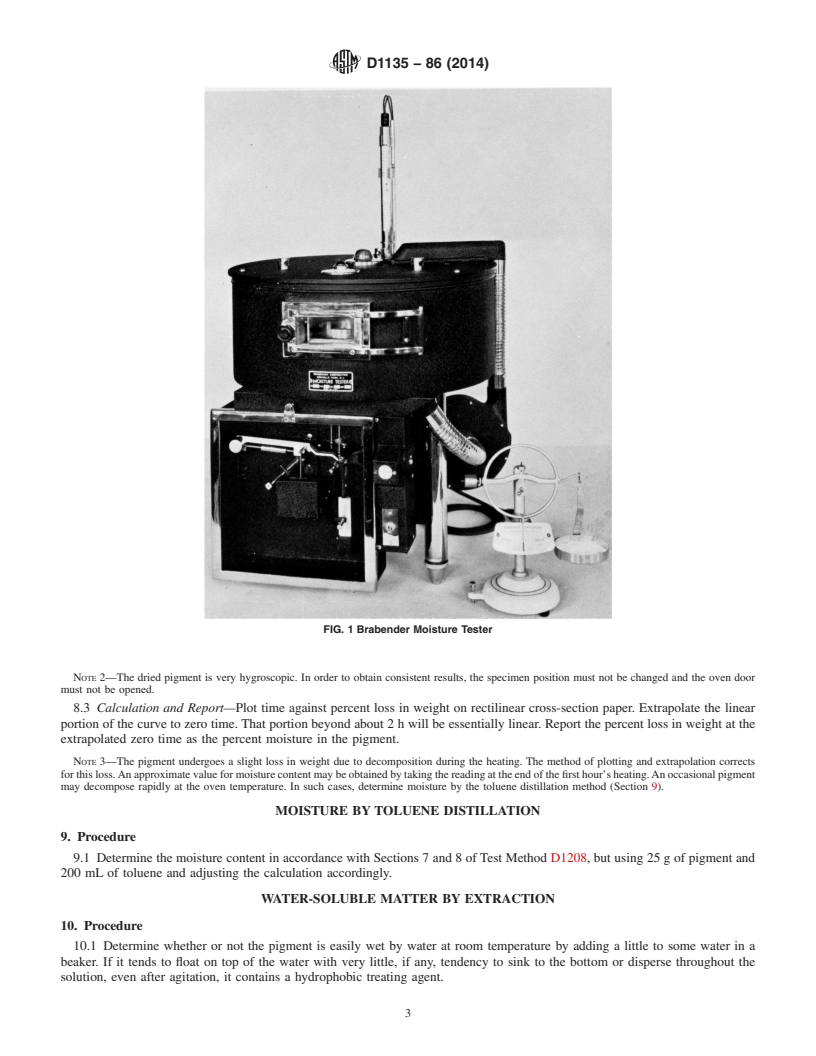
Moisture by the Brabender Moisture Tester
7 and 8
Moisture by Toluene Distillation
9
Water-Soluble Matter by Extraction
10
Water-Soluble Salts by Electrical Conductivity
11
Detection of Acid-Insoluble Extenders
12 and 13
Detection of Acid-Soluble Extenders
14 to 17
Detection of Organic Colors and Lakes
18
COPPER PHTHALOCYANINE BLUE PIGMENTS
Identification
19
Moisture and Other Volatile Matter
20
Detection of Basic Dye Derivatives
21
Detection of Other Organic Coloring Matter
22
Detection of Ultramarine Blue
23
Detection of Iron Blue
24
ULTRAMARINE BLUE
Identification
25
Moisture and Other Volatile Matter
26
Water-Soluble Matter
27
Detection of Basic Dye Derivatives
28
Detection of Other Organic Coloring Matter
29
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address the safety concerns associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D1135 − 86 (Reapproved 2014)
Standard Test Methods for
1
Chemical Analysis of Blue Pigments
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D1135; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
2
1.1 These test methods cover procedures for the chemical
2.1 ASTM Standards:
analysis of blue pigments known commercially as iron blue,
D280 Test Methods for Hygroscopic Moisture (and Other
copper phthalocyanine blue, and ultramarine blue.
Matter Volatile Under the Test Conditions) in Pigments
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
1.2 The analytical procedures appear in the following order:
D1208 Test Methods for Common Properties of Certain
Sections
Pigments
IRON BLUE PIGMENTS
D2448 Test Method for Water-Soluble Salts in Pigments by
Measuring the Specific Resistance of the Leachate of the
Identification 6
Moisture by the Brabender Moisture Tester 7 and 8
Pigment
Moisture by Toluene Distillation 9
E11 Specification for Woven Wire Test Sieve Cloth and Test
Water-Soluble Matter by Extraction 10
Sieves
Water-Soluble Salts by Electrical Conductivity 11
Detection of Acid-Insoluble Extenders 12 and 13
Detection of Acid-Soluble Extenders 14 to 17
3. Significance and Use
Detection of Organic Colors and Lakes 18
3.1 These test methods are suitable for determining if
COPPER PHTHALOCYANINE BLUE PIGMENTS
impurities are present and establishing that the required pig-
Identification 19
ments are present. These test methods may be used for
Moisture and Other Volatile Matter 20
manufacturing quality control.
Detection of Basic Dye Derivatives 21
Detection of Other Organic Coloring Matter 22
Detection of Ultramarine Blue 23
4. Purity of Reagents and Water
Detection of Iron Blue 24
4.1 Purity of Reagents—Unless otherwise indicated, it is
ULTRAMARINE BLUE
intended that all reagents shall conform to the specifications of
Identification 25
theCommitteeonAnalyticalReagentsoftheAmericanChemi-
Moisture and Other Volatile Matter 26
3
cal Society, where such specifications are available. Other
Water-Soluble Matter 27
Detection of Basic Dye Derivatives 28 grades may be used, provided it is first ascertained that the
Detection of Other Organic Coloring Matter 29
reagent is of sufficiently high purity to permit its use without
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
lessening the accuracy of the determination.
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
4.2 Purity of Water—Unless otherwise indicated, references
standard.
towatershallbeunderstoodtomeanreagentwaterconforming
1.4 This standard does not purport to address the safety
to Type II of Specification D1193.
concerns associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the
user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health
practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limita-
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
tions prior to use.
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website.
1 3
These test methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D01 on Reagent Chemicals, American Chemical Society Specifications, American
Paint and Related Coatings, Materials, and Applications and are the direct Chemical Society, Washington, DC. For suggestions on the testing of reagents not
responsibility of Subcommittee D01.31 on Pigment Specifications. listed by the American Chemical Society, see Analar Standards for Laboratory
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2014. Published December 2014. Originally Chemicals, BDH Ltd., Poole, Dorset, U.K., and the United States Pharmacopeia
approved in 1950. Last previous edition approved in 2009 as D1135 – 86 (2009). and National Formulary, U.S. Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. (USPC), Rockville,
DOI: 10.1520/D1135-86R14. MD.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D1135 − 86 (2014)
5. Preparation of Sample
5.1 Mix the sample thoroughly and take a representative
portion for analysis. Reduce any lumps or coarse particles to a
fine powder by grinding.
5.2 Grind extracted pigments to pass a No. 80 (180-µm)
4
sieve. Discard any skins that do not pass through the sieve.
Mix the finely ground pigment thoroughly.
4
Detailed requirements for this sieve are given in Specification E11.
IRON BLUE
(Pruss
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D1135 − 86 (Reapproved 2009) D1135 − 86 (Reapproved 2014)
Standard Test Methods for
1
Chemical Analysis of Blue Pigments
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D1135; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope
1.1 These test methods cover procedures for the chemical analysis of blue pigments known commercially as iron blue, copper
phthalocyanine blue, and ultramarine blue.
1.2 The analytical procedures appear in the following order:
Sections
I ron Blue P igments
IRON BLUE PIGMENTS
Identification 6
Moisture by the Brabender Moisture Tester 7 and 8
Moisture by Toluene Distillation 9
Water-Soluble Matter by Extraction 10
Water-Soluble Salts by Electrical Conductivity 11
Detection of Acid-Insoluble Extenders 12 and 13
Detection of Acid-Soluble Extenders 14 to 17
Detection of Organic Colors and Lakes 18
C opper Phthalocyanine Blue Pigments
COPPER PHTHALOCYANINE BLUE PIGMENTS
Identification 19
Moisture and Other Volatile Matter 20
Detection of Basic Dye Derivatives 21
Detection of Other Organic Coloring Matter 22
Detection of Ultramarine Blue 23
Detection of Iron Blue 24
U ltramarine Blue
ULTRAMARINE BLUE
Identification 25
Moisture and Other Volatile Matter 26
Water-Soluble Matter 27
Detection of Basic Dye Derivatives 28
Detection of Other Organic Coloring Matter 29
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address the safety concerns associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of
this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior
to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D280 Test Methods for Hygroscopic Moisture (and Other Matter Volatile Under the Test Conditions) in Pigments
1
These test methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D01 on Paint and Related Coatings, Materials, and Applications and are the direct responsibility of
Subcommittee D01.31 on Pigment Specifications.
Current edition approved June 1, 2009Dec. 1, 2014. Published June 2009December 2014. Originally approved in 1950. Last previous edition approved in 20042009 as
D1135 – 86 (2004).(2009). DOI: 10.1520/D1135-86R09.10.1520/D1135-86R14.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’sstandard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D1135 − 86 (2014)
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
D1208 Test Methods for Common Properties of Certain Pigments
D2448 Test Method for Water-Soluble Salts in Pigments by Measuring the Specific Resistance of the Leachate of the Pigment
E11 Specification for Woven Wire Test Sieve Cloth and Test Sieves
3. Significance and Use
3.1 These test methods are suitable for determining if impurities are present and establishing that the required pigments are
present. These test methods may be used for manufacturing quality control.
4. Purity of Reagents and Water
4.1 Purity of Reagents—Unless otherwise indicated, it is intended that all reagents shall conform to the specifications of the
3
Committee on Analytical Reagents of the American Chemical Society, where such specifications are available. Other grades may
be used, provided it is first ascertained that the reagent is of sufficiently high purity to permit its use without lessening the accuracy
of the determination.
4.2 Purity of Water—Unless otherwise indicated, references to water shall be understood to mean reagent water conforming to
Type II of Specification D1193.
5. Preparation of Sample
5.1 Mix the sample thoroughly and take a representative portion for analysis. Reduce any lumps or coarse particles to a fine
powder by grinding.
4
5.2 Grind extracted pigments to pass a No. 80 (180-μm) sieve. Discard any skins that do not pass through the sieve. Mix the
finely ground pigment thoroughly.
3
Reagent Chemical
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.