ASTM D7024-04
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Steady State and Dynamic Thermal Performance of Textile Materials (Withdrawn 2013)
Standard Test Method for Steady State and Dynamic Thermal Performance of Textile Materials (Withdrawn 2013)
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This method provides for the determination of the steady state thermal resistance of a fabric or layers of fabrics and for the determination of the temperature regulating factor (TRF) as defined below. This test method is considered satisfactory for acceptance testing of commercial shipments because the round robin testing shows high precision and no bias for testing of textile fabrics and foams.
5.1.1 If there are differences of practical significance between reported test results for two laboratories (or more), comparative test should be performed to determine if there is a statistical bias between them, using competent statistical assistance. As a minimum, use the samples for such a comparative test that are as homogeneous as possible, drawn from the same lot of material as the samples that resulted in disparate results during initial testing and randomly assigned in equal numbers to each laboratory. The test results from the laboratories involved should be compared using a statistical test for unpaired data, a probability level chosen prior to the testing series. If bias is found, either its cause must be found and corrected, or future test results for that material must be adjusted in consideration of the known bias.
This test method is useful in quality and cost control during manufacture. It can be used to establish criteria for establishing thermal and comfort parameters for textiles particularly used in the clothing industry.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the overall thermal transmission coefficient due to conduction for dry specimens of textile fabrics, battings, and other materials and the determination of the temperature regulating factor (TRF) defined below.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
WITHDRAWN RATIONALE
This test method covers the determination of the overall thermal transmission coefficient due to conduction for dry specimens of textile fabrics, battings, and other materials and the determination of the temperature regulating factor (TRF) defined below.
Formerly under the jurisdiction of Committee D13 on Textiles, this test method was withdrawn in March 2013 in accordance with section 10.5.3.1 of the Regulations Governing ASTM Technical Committees, which requires that standards shall be updated by the end of the eighth year since the last approval date.
General Information
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D7024 − 04
StandardTest Method for
Steady State and Dynamic Thermal Performance of Textile
1,2
Materials
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7024; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope ing fabrics that store and release energy and thereby regulate
their surface temperature.
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the overall
thermal transmission coefficient due to conduction for dry
3.2 Fordefinitionsofothertextiletermsusedinthismethod
specimens of textile fabrics, battings, and other materials and
refer to Terminology D123.
the determination of the temperature regulating factor (TRF)
defined below.
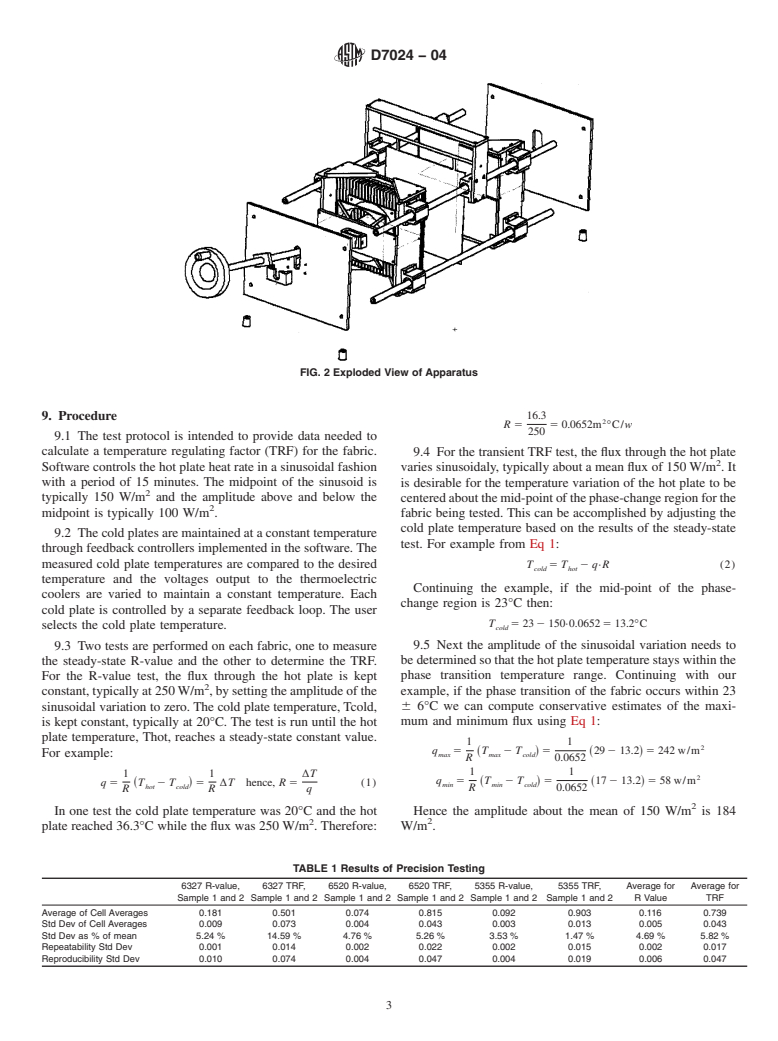
4. Summary of Test Method
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
4.1 In order to determine the steady state R-value and the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
temperature regulating for a sample fabric, the apparatus of
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
Fig. 1 is used. Fabric is sandwiched between a hot plate and
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
twocoldplates,oneoneithersideofthehotplate.Acontrolled
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
flux, either constant or varying, is maintained for the hot plate
while the cold plates are maintained at constant temperature.
2. Referenced Documents
To measure the steady state thermal resistance (R-value) of the
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
fabric,thecontrolledfluxisconstantandthetestproceedsuntil
D123Terminology Relating to Textiles
steady state is reached. To measure the temperature regulating
D1518Test Method for Thermal Resistance of Batting
factor (TRF), the flux is varied sinusoidally with time.
Systems Using a Hot Plate
D1776Practice for Conditioning and Testing Textiles
5. Significance and Use
D1777Test Method for Thickness of Textile Materials
5.1 This method provides for the determination of the
steady state thermal resistance of a fabric or layers of fabrics
3. Terminology
and for the determination of the temperature regulating factor
3.1 Definitions:
(TRF) as defined below. This test method is considered
3.1.1 temperature difference, ∆T—temperature difference
satisfactory for acceptance testing of commercial shipments
between two surfaces of a fabric, °C.
because the round robin testing shows high precision and no
3.1.2 temperature regulating factor, TRF—amplitude of the
bias for testing of textile fabrics and foams.
temperaturevariationofthehotplatedividedbytheproductof
5.1.1 If there are differences of practical significance be-
theamplitudeofthehotplatefluxvariationandthesteadystate
tween reported test results for two laboratories (or more),
R-value,alldeterminedaccordingtothetestprotocoldescribed
comparative test should be performed to determine if there is a
below. The temperature regulating factor is useful in compar-
statistical bias between them, using competent statistical assis-
tance.As a minimum, use the samples for such a comparative
test that are as homogeneous as possible, drawn from the same
1
ThistestmethodisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeD13onTextiles
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D13.51 on Conditioning and, lot of material as the samples that resulted in disparate results
Chemical and Thermal Properties.
during initial testing and randomly assigned in equal numbers
Current edition approved March 1, 2004. Published April 2004. DOI: 10.1520/
to each laboratory. The test results from the laboratories
D7024-04.
2 involved should be compared using a statistical test for
Thetestapparatusdescribedbelowiscoveredbyapatent.Interestedpartiesare
invited to submit information regarding the identification of an alternative(s) to this
unpaired data, a probability level chosen prior to the testing
patenteditemtotheASTMInternationalHeadquarters.Yourcommentswillreceive
series. If bias is found, either its cause must be found and
careful consideration at a meeting of the responsible technical committee, which
corrected, or future test results for that material must be
you may attend.
3
adjusted in consideration of the known bias.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
5.2 This test method is useful in quality and cost control
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. during manufacture. It can be used to establish criteria for
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959.
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.