ASTM C1087-23
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determining Compatibility of Liquid-Applied Sealants with Accessories Used in Structural Glazing Systems
Standard Test Method for Determining Compatibility of Liquid-Applied Sealants with Accessories Used in Structural Glazing Systems
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 In structural sealant glazing systems, the sealant functions as the structural adhesive and may also function as the primary weather seal. As the structural adhesive, the integrity of the adhesive bond is critical.
5.2 Changes in color and adhesion after exposure are two of the criteria that can be used to determine the compatibility of the system. Experience has shown that accessories that cause loss of adhesion or discoloration in this test method may also cause these occurrences in actual use.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers a laboratory screening procedure for determining the compatibility of liquid-applied structural sealant glazing sealants when in contact with accessories such as dry glazing gaskets, spacers, shims, and setting blocks after exposure to heat and ultraviolet light.
1.2 This test method includes the observation of three parameters as follows:
1.2.1 Changes in the color of the sealant,
1.2.2 Changes in the adhesion of the sealant to glass, and
1.2.3 Changes in the adhesion of the sealant to the accessory being tested.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Note 1: At this time, no comparable ISO standard exists.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: C1087 − 23
Standard Test Method for
Determining Compatibility of Liquid-Applied Sealants with
1
Accessories Used in Structural Glazing Systems
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C1087; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3. Terminology
1.1 This test method covers a laboratory screening proce- 3.1 Definitions—Definitions of the following terms used in
dure for determining the compatibility of liquid-applied struc- this test method are listed in Terminology C717: adhesive
tural sealant glazing sealants when in contact with accessories failure (adhesion loss), bead, bond breaker, cohesive failure,
such as dry glazing gaskets, spacers, shims, and setting blocks compatibility, gasket, glazing, sealant, setting blocks, shim,
after exposure to heat and ultraviolet light. spacer, structural sealant, standard conditions, and structural
sealant glazing.
1.2 This test method includes the observation of three
parameters as follows:
4. Summary of Test Method
1.2.1 Changes in the color of the sealant,
1.2.2 Changes in the adhesion of the sealant to glass, and
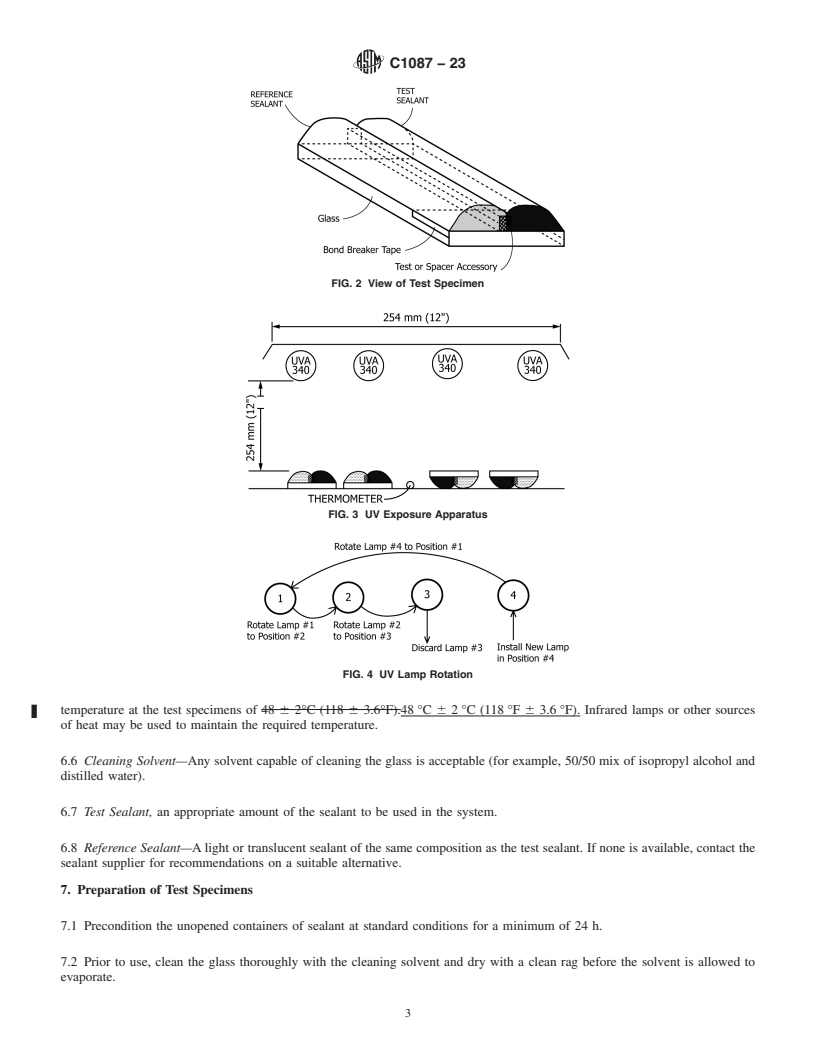
4.1 The test specimens are placed beneath ultraviolet lamps
1.2.3 Changes in the adhesion of the sealant to the accessory so that the radiation will hit the sealant directly on one
being tested.
specimen, and through the glass, on the other specimen (see
Fig. 1).
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
4.2 The control specimens for this test method are prepared
only. and tested identically to the test specimens except that the
accessory is eliminated.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
4.3 After the specimens are exposed, the test specimens are
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
compared to the control specimens.
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
4.4 In the testing of the specimens, any color change in the
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
sealant between the test specimen and the control is noted as
NOTE 1—At this time, no comparable ISO standard exists.
are any changes in the adhesion of the sealant to either the glass
or to the accessory. This test method requires the preparation of
1.5 This international standard was developed in accor-
eight test specimens (four controls and four test specimens for
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
each accessory being evaluated).
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
5. Significance and Use
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
5.1 In structural sealant glazing systems, the sealant func-
tions as the structural adhesive and may also function as the
2. Referenced Documents
primary weather seal. As the structural adhesive, the integrity
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
of the adhesive bond is critical.
C717 Terminology of Building Seals and Sealants
5.2 Changes in color and adhesion after exposure are two of
the criteria that can be used to determine the compatibility of
the system. Experience has shown that accessories that cause
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C24 on Building
loss of adhesion or discoloration in this test method may also
Seals and Sealants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C24.20 on
General Test Methods.
cause these occurrences in actual use.
Current edition approved May 1, 2023. Published May 2023. Originally
approved in 1987. Last previous edition approved in 2016 as C1087 – 16. DOI:
6. Apparatus and Materials
10.1520/C1087-23.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
6.1 Glass Panels, clear float glass, approximately 76.2 mm
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
1
by 50.8 mm by 6.4 mm (3 in. by 2 in. by ⁄4 in.). Eight panels
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. are required for each material being tested.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C1087 − 23
FIG. 4 UV Lamp Rotation
2 °C (118 °F 6 3.6
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: C1087 − 16 C1087 − 23
Standard Test Method for
Determining Compatibility of Liquid-Applied Sealants with
1
Accessories Used in Structural Glazing Systems
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C1087; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers a laboratory screening procedure for determining the compatibility of liquid-applied structural sealant
glazing sealants when in contact with accessories such as dry glazing gaskets, spacers, shims, and setting blocks after exposure
to heat and ultraviolet light.
1.2 This test method includes the observation of three parameters as follows:
1.2.1 Changes in the color of the sealant,
1.2.2 Changes in the adhesion of the sealant to glass, and
1.2.3 Changes in the adhesion of the sealant to the accessory being tested.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and healthsafety, health, and environmental practices and determine
the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
NOTE 1—At this time, no comparable ISO standard exists.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
C717 Terminology of Building Seals and Sealants
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions—Definitions of the following terms used in this test method are listed in Terminology C717: adhesive failure
(adhesion loss), bead, bond breaker, cohesive failure, compatibility, gasket, glazing, sealant, setting blocks, shim, spacer, structural
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C24 on Building Seals and Sealants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C24.20 on General
Test Methods.
Current edition approved June 1, 2016May 1, 2023. Published July 2016May 2023. Originally approved in 1987. Last previous edition approved in 20112016 as
C1087 – 00 (2011).C1087 – 16. DOI: 10.1520/C1087-16.10.1520/C1087-23.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C1087 − 23
sealant, standard conditions, and structural sealant glazing.
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 The test specimens are placed beneath ultraviolet lamps so that the radiation will hit the sealant directly on one specimen, and
through the glass, on the other specimen (see Fig. 1).
4.2 The control specimens for this test method are prepared and tested identically to the test specimens except that the accessory
is eliminated.
4.3 After the specimens are exposed, the test specimens are compared to the control specimens.
4.4 In the testing of the specimens, any color change in the sealant between the test specimen and the control is noted as are any
changes in the adhesion of the sealant to either the glass or to the accessory. This test method requires the preparation of eight test
specimens (four controls and four test specimens for each accessory being evaluated).
5. Significance and Use
5.1 In structural sealant glazing systems, the sealant functions as the structural adhesive and may also function as the primary
weather seal. As the structural adhesive, the integrity of the adhesive bond is critical.
5.2 Changes in color and adhesion after exposure are two of the criteria that can be used to determine the compatibility of the
system. Experience has shown that accessories that cause loss of adhesion or discoloration in this test method may also cause these
occurrences in actual use.
6. Apparatus and Materials
1
6.1 Glass Pane
...










Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.