ASTM D3162-12
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Carbon Monoxide in the Atmosphere (Continuous Measurement by Nondispersive Infrared Spectrometry)
Standard Test Method for Carbon Monoxide in the Atmosphere (Continuous Measurement by Nondispersive Infrared Spectrometry)
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
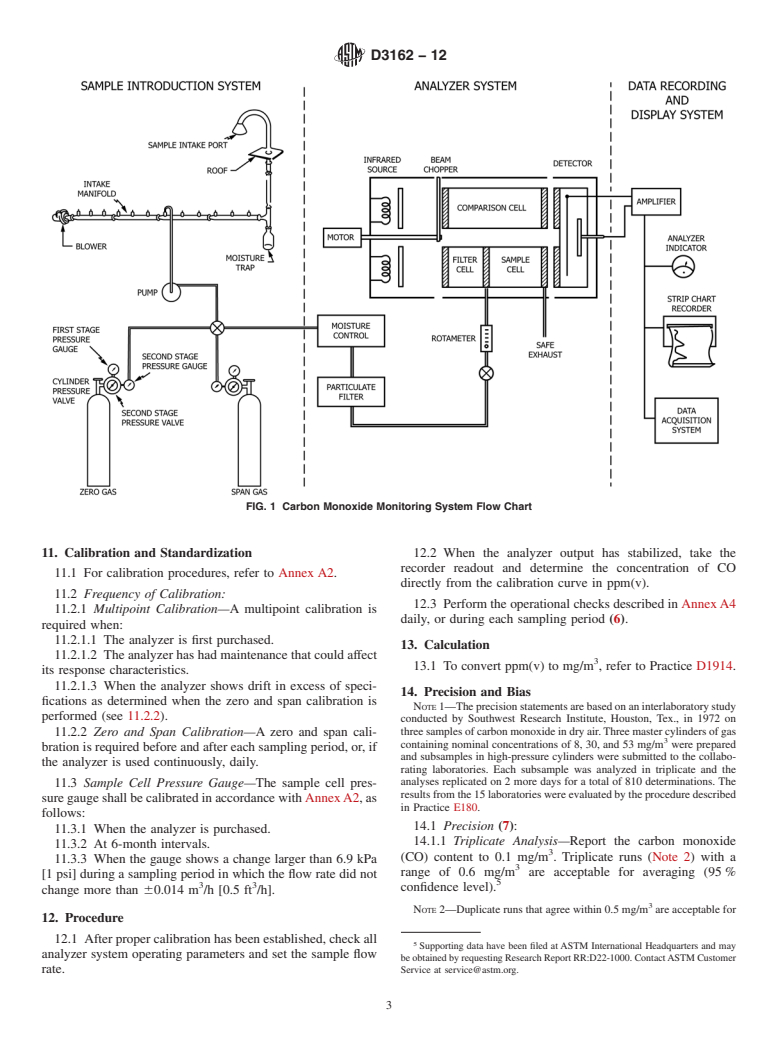
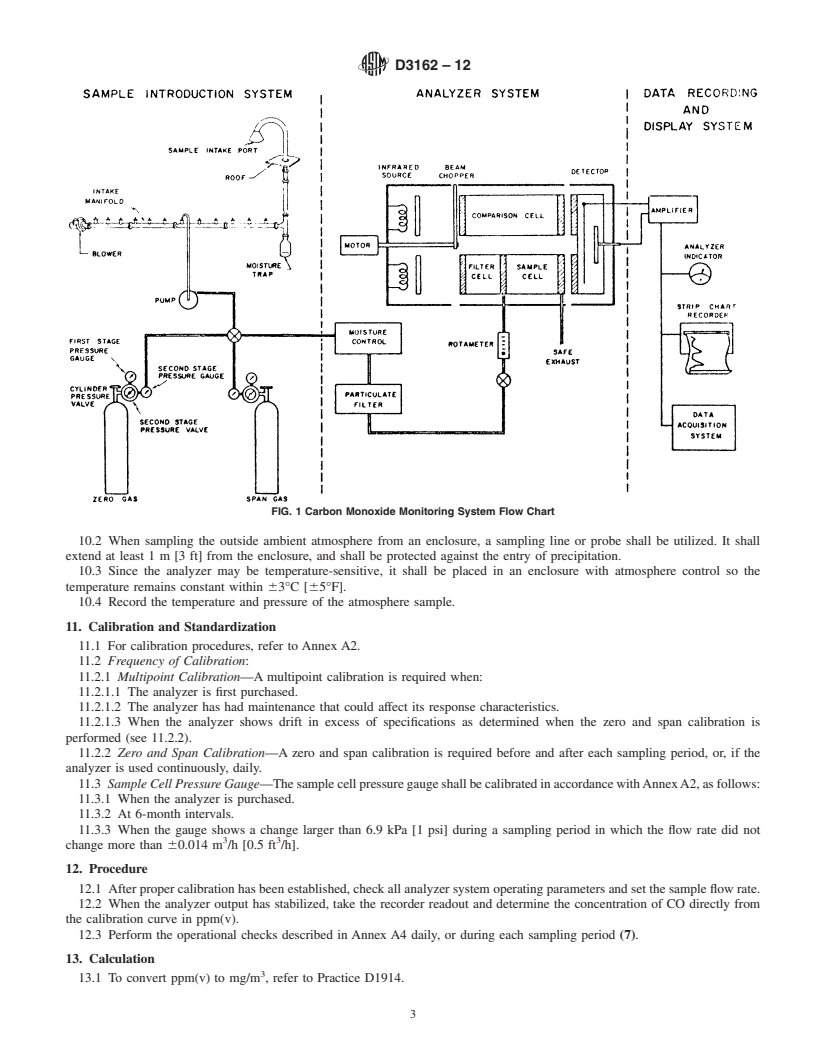
Determination of carbon monoxide is essential to evaluation of many air pollution complexes. This test method derives significance from providing such determination.
Carbon monoxide is formed in the process of incomplete combustion of hydrocarbon fuels, and is a constituent of the exhaust of gasoline engines. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has set primary and secondary air quality standards for CO that are designed to protect the public health and welfare (3, 4).
This test method is suitable for measurements appropriate for the purposes noted in 5.1 and 5.2.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method is applicable to the determination of the carbon monoxide (CO) concentration of the atmosphere between 0.6 mg/m3 (0.5 ppm(v)) and 115 mg/m3 (100 ppm(v)). The measuring principle is based on the absorption of infrared radiation by CO in the 4.7 μm region (1).
1.2 The test method has a limit of detection of about 0.6 mg/m3 (0.5 ppm(v)) carbon monoxide in air.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. See Section 9 for additional precautions.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D3162 − 12
Standard Test Method for
Carbon Monoxide in the Atmosphere (Continuous
1
Measurement by Nondispersive Infrared Spectrometry)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D3162; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope D3249 Practice for General Ambient Air Analyzer Proce-
dures
1.1 This test method is applicable to the determination of
D3631 Test Methods for Measuring Surface Atmospheric
the carbon monoxide (CO) concentration of the atmosphere
3 3 Pressure
between0.6mg/m (0.5ppm(v))and115mg/m (100ppm(v)).
E1 Specification for ASTM Liquid-in-Glass Thermometers
The measuring principle is based on the absorption of infrared
2 E180 Practice for Determining the Precision of ASTM
radiation by CO in the 4.7 µm region (1).
Methods for Analysis and Testing of Industrial and Spe-
4
1.2 The test method has a limit of detection of about 0.6
cialty Chemicals (Withdrawn 2009)
3
mg/m (0.5 ppm(v)) carbon monoxide in air.
3. Terminology
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the 3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 For definitions of terms used in this test method, refer
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica- to Terminology D1356 and Practice D3249.
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. See Section 9 for
additional precautions. 3.2.1 fall time—the time interval between initial response
and 90 % of final response after a step decrease in input
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
concentrations.
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
4. Summary of Test Method
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
4.1 An atmospheric sample is introduced into a sample
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
conditioning system and then into a nondispersive infrared
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
spectrometer (NDIR). The spectrometer measures the absorp-
2. Referenced Documents tionbyCOat4.7µmusingtwoparallelinfraredbeamsthrough
3 a sample and a reference cell and a selective detector. The
2.1 ASTM Standards:
detectorsignalisconductedtoanamplifiercontrolsection,and
D1356 Terminology Relating to Sampling and Analysis of
the analyzer output measured on a meter and recording system
Atmospheres
(2).
D1357 Practice for Planning the Sampling of the Ambient
4.1.1 Some instruments use gas filter correlation to compare
Atmosphere
the IR absorption spectrum between the measured gas and
D1914 PracticeforConversionUnitsandFactorsRelatingto
othergasespresentinthegasbeingsampled,inasinglesample
Sampling and Analysis of Atmospheres
cell. These instruments utilize a concentrated sample of CO as
a filter for the IR transmitted through the sample cell to
1 produce a beam that cannot be further attenuated by the CO in
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D22 on Air
Quality and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D22.03 on Ambient the sample, and thus produces the reference beam. The
Atmospheres and Source Emissions.
broadbandradiationthatpassesthroughthesamplecellandthe
Current edition approved April 1, 2012. Published May 2012. Originally
CO filter is filtered again by a narrow-band-pass filter that
approved in 1973. Last previous edition approved in 2005 as D3162 – 94 (2005).
allows only the CO-sensitive portion of the band to pass to the
DOI: 10.1520/D3162-12.
2
The boldface numbers in parentheses refer to the list of references at the end of
detector. The removal of wavelengths sensitive to other gases
the standard.
reduces interferences.
3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
4
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
the ASTM website. www.astm.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D3162 − 12
4.2 The concentration of CO in the sample is determined 7.2 Sample Conditioning System, consisting of pump, flow
from a calibration curve prepared using standard calibration control valve, pressure relief valv
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:D3162–94(Reapproved2005) Designation:D3162–12
Standard Test Method for
Carbon Monoxide in the Atmosphere (Continuous
1
Measurement by Nondispersive Infrared Spectrometry)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D3162; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method is applicable to the determination of the carbon monoxide (CO) concentration of the atmosphere between
3 3
0.6 mg/m (0.5 ppm(v)) and 115 mg/m (100 ppm(v)). The measuring principle is based on the absorption of infrared radiation by
2
CO in the 4.7 µm region (1).
3
1.2 The test method has a limit of detection of about 0.6 mg/m (0.5 ppm(v)) carbon monoxide in air.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use. See Section 9 for additional precautions.
2. Referenced Documents
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D1356 Terminology Relating to Sampling and Analysis of Atmospheres
D1357 Practice for Planning the Sampling of the Ambient Atmosphere
D1914 Practice for Conversion Units and Factors Relating to Sampling and Analysis of Atmospheres
D3249 Practice for General Ambient Air Analyzer Procedures
D3631 Test Methods for Measuring Surface Atmospheric Pressure E1
E1 Specification for ASTM Liquid-in-Glass Thermometers
E180 Practice for Determining the Precision ofASTM Methods forAnalysis and Testing of Industrial and Specialty Chemicals
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 For definitions of terms used in this test method, refer to Terminology D1356 and Practice D3249.
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.2.1 fall time—the time interval between initial response and 90 % of final response after a step decrease in input
concentrations.
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 An atmospheric sample is introduced into a sample conditioning system and then into a nondispersive infrared spectrometer
(NDIR). The spectrometer measures the absorption by CO at 4.7 µm using two parallel infrared beams through a sample and a
reference cell and a selective detector. The detector signal is conducted to an amplifier control section, and the analyzer output
measured on a meter and recording system (2).
4.1.1 Some instruments use gas filter correlation to compare the IR absorption spectrum between the measured gas and other
gases present in the gas being sampled, in a single sample cell. These instruments utilize a concentrated sample of CO as a filter
for the IR transmitted through the sample cell to produce a beam that cannot be further attenuated by the CO in the sample, and
thus produces the reference beam. The broadband radiation that passes through the sample cell and the CO filter is filtered again
by a narrow-band-pass filter that allows only the CO-sensitive portion of the band to pass to the detector. The removal of
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D22 on Air Quality and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D22.03 on Ambient Atmospheres
and Source Emissions.
Current edition approved Oct.April 1, 2005.2012. Published January 2006.May 2012. Originally approved in 1973. Last previous edition approved in 20002005 as
´1
D3162 - 94 (2000) .(2005). DOI: 10.1520/D3162-94R05.
2
The boldface numbers in parentheses refer to the list of references at the end of the standard.
3
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D3162–12
wavelengths sensitive to other gases reduces interferences.
4.2 The concentration of CO in the sample is determined from a calibration curve prepared using standard calibration gases.
5. Significance and Use
5.1 Determination of carbon monoxide is essential to evaluation of many air pollution complexes. This test me
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.