ASTM C1453-19
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for the Determination of Uranium by Ignition and the Oxygen to Uranium (O/U) Atomic Ratio of Nuclear Grade Uranium Dioxide Powders and Pellets
Standard Test Method for the Determination of Uranium by Ignition and the Oxygen to Uranium (O/U) Atomic Ratio of Nuclear Grade Uranium Dioxide Powders and Pellets
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 The test method is designed to show whether or not a material meets the specifications as given in Specifications C753 or C776.
5.2 The powder’s stoichiometry is useful for predicting the oxide's sintering behavior in the pellet production process.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of uranium and the oxygen to uranium atomic ratio in nuclear grade uranium dioxide powder and pellets.
1.2 This test method does not include provisions for preventing criticality accidents or requirements for health and safety. Observance of this test method does not relieve the user of the obligation to be aware of and conform to all international, national, or federal, state and local regulations pertaining to possessing, shipping, processing, or using source or special nuclear material.
1.3 This test method also is applicable to UO3 and U3O8 powder.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: C1453 − 19
Standard Test Method for
the Determination of Uranium by Ignition and the Oxygen to
Uranium (O/U) Atomic Ratio of Nuclear Grade Uranium
1
Dioxide Powders and Pellets
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C1453; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope C753Specification for Nuclear-Grade, Sinterable Uranium
Dioxide Powder
1.1 This test method covers the determination of uranium
C776SpecificationforSinteredUraniumDioxidePelletsfor
and the oxygen to uranium atomic ratio in nuclear grade
Light Water Reactors
uranium dioxide powder and pellets.
C859Terminology Relating to Nuclear Materials
1.2 This test method does not include provisions for pre-
C1267Test Method for Uranium by Iron (II) Reduction in
venting criticality accidents or requirements for health and
PhosphoricAcid Followed by Chromium (VI)Titration in
safety.Observanceofthistestmethoddoesnotrelievetheuser
the Presence of Vanadium
of the obligation to be aware of and conform to all
C1287Test Method for Determination of Impurities in
international, national, or federal, state and local regulations
Nuclear Grade Uranium Compounds by Inductively
pertaining to possessing, shipping, processing, or using source
Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry
or special nuclear material.
3. Terminology
1.3 This test method also is applicable to UO and U O
3 3 8
powder.
3.1 For definitions of terms used in this test method but not
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the defined herein, refer to Terminology C859.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
4. Summary of Test Method
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
4.1 A weighed portion of UO is converted to U O by
2 3 8
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
repeated ignition at 900°C in air, to a constant weight.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accor-
Corrections are made for nonvolatile and volatile impurities
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
including moisture, based on independent determinations de-
3,4
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
scribed in Test Methods C696 and C1287.
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
5. Significance and Use
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
5.1 The test method is designed to show whether or not a
material meets the specifications as given in Specifications
2. Referenced Documents
C753 or C776.
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
5.2 The powder’s stoichiometry is useful for predicting the
C696Test Methods for Chemical, Mass Spectrometric, and
oxide’s sintering behavior in the pellet production process.
SpectrochemicalAnalysis of Nuclear-Grade Uranium Di-
oxide Powders and Pellets
6. Interferences
6.1 The moisture content must be determined and a correc-
1
tion must be made for the moisture content otherwise a high
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM committee C26 on Nuclear
Fuel Cycle and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C26.05 on Methods of
bias will occur for the O/U ratio.
Test.
Current edition approved July 1, 2019. Published August 2019. Originally
approved in 2000. Last previous edition approved in 2011 as C1453–00 (2011).
3
DOI: 10.1520/C1453-19. Jones, R.J., Ed., “Selected Measurement Methods for Plutonium and Uranium
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or in the Nuclear Fuel Cycle,” USAEC Document TID-7029, 1963, AERDB, pp.
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM 91–93.
4
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Petit, G.D. and Keinberger, C.A., “Preparation of Stoichiometric U O ,”
3 8
the ASTM website. Analytical Chemistry, ANCHA, Vol 25, 1961, p. 579.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
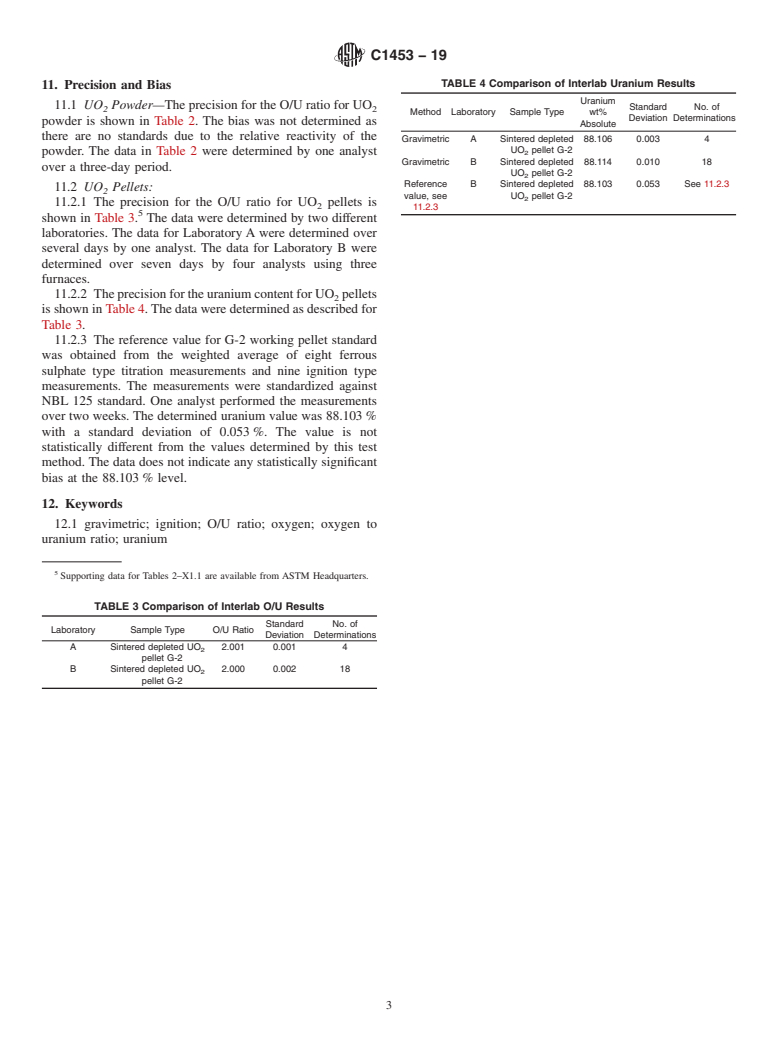
C1453 − 19
TABLE 2 UO Powder Results
6.2 A nonvolatile impurity correction must be made other-
2
wiseahighbiaswilloccurfortheuraniumvalue.Anextended Uranium wt Standard Standard No. of
Sample Type O/U Ratio
% Absolute Deviation Deviation Determinations
ignition time may be required if significant amounts of anions
Sample A 87.796 0.005 2.065 0.
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: C1453 − 00 (Reapproved 2011) C1453 − 19
Standard Test Method for
the Determination of Uranium by Ignition and the Oxygen to
Uranium (O/U) Atomic Ratio of Nuclear Grade Uranium
1
Dioxide Powders and Pellets
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C1453; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers the determination of uranium and the oxygen to uranium atomic ratio in nuclear grade uranium
dioxide powder and pellets.
1.2 This test method does not include provisions for preventing criticality accidents or requirements for health and safety.
Observance of this test method does not relieve the user of the obligation to be aware of and conform to all international, national,
or federal, state and local regulations pertaining to possessing, shipping, processing, or using source or special nuclear material.
1.3 This test method also is applicable to UO and U O powder.
3 3 8
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This test method also is applicable to UO and U O powder.
3 3 8
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
C696 Test Methods for Chemical, Mass Spectrometric, and Spectrochemical Analysis of Nuclear-Grade Uranium Dioxide
Powders and Pellets
C753 Specification for Nuclear-Grade, Sinterable Uranium Dioxide Powder
C776 Specification for Sintered Uranium Dioxide Pellets for Light Water Reactors
C859 Terminology Relating to Nuclear Materials
C1267 Test Method for Uranium by Iron (II) Reduction in Phosphoric Acid Followed by Chromium (VI) Titration in the
Presence of Vanadium
C1287 Test Method for Determination of Impurities in Nuclear Grade Uranium Compounds by Inductively Coupled Plasma
Mass Spectrometry
3. Terminology
3.1 For definitions of terms used in this test method but not defined herein, refer to Terminology C859.
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 A weighed portion of UO is converted to U O by repeated ignition at 900°C in air, to a constant weight. Corrections are
2 3 8
made for nonvolatile and volatile impurities including moisture, based on independent determinations described in Test Methods
3,4
C696 and C1287.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM committee C26 on Nuclear Fuel Cycle and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C26.05 on Methods of Test.
Current edition approved July 1, 2011July 1, 2019. Published July 2011August 2019. Originally approved in 2000. Last previous edition approved in 20062011 as
C1453 – 00 (2011).R06. DOI: 10.1520/C1453-00R11.10.1520/C1453-19.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Jones, R.J., Ed., “Selected Measurement Methods for Plutonium and Uranium in the Nuclear Fuel Cycle,” USAEC Document TID-7029, 1963, AERDB, pp. 91–93.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C1453 − 19
5. Significance and Use
5.1 The test method is designed to show whether or not a material meets the specifications as given in Specifications C753 or
C776.
5.2 The powder’s stoichiometry is useful for predicting the oxide’s sintering behavior in the pellet production process.
6. Interferences
6.1 The moisture content must be determined and a correction must be made for the moisture content otherwise a high bias will
occur for the O/U ratio.
6.2 A nonvolatile impurity correction must be made otherwise a high bias will occur for the uranium value. An extended ignition
time may be required if significant amount
...










Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.