ASTM F876-08a
(Specification)Standard Specification for Crosslinked Polyethylene (PEX) Tubing
Standard Specification for Crosslinked Polyethylene (PEX) Tubing
ABSTRACT
This specification covers crosslinked polyethylene (PEX) tubing that is outside diameter controlled, made in standard thermoplastic tubing dimension ratios, and pressure rated for water at three temperatures. This specification covers one PEX tubing material in one standard dimension ratio and having pressure ratings for water of three temperatures. The pressure ratings decrease as the temperature is increased. PEX tubing shall be made from polyethylene compounds which have been crosslinked by peroxides, Azo compounds, or silane compounds in extrusion, or by electron beam after extrusion, or by other means such that the tubing meets the performance requirements. The following tests shall be performed: dimensions and tolerances; density; sustained pressure test; burst pressure; environmental stress cracking test; degree of crosslinking; stabilizer functionality; and oxidative stability in potable chlorinated water applications.
SCOPE
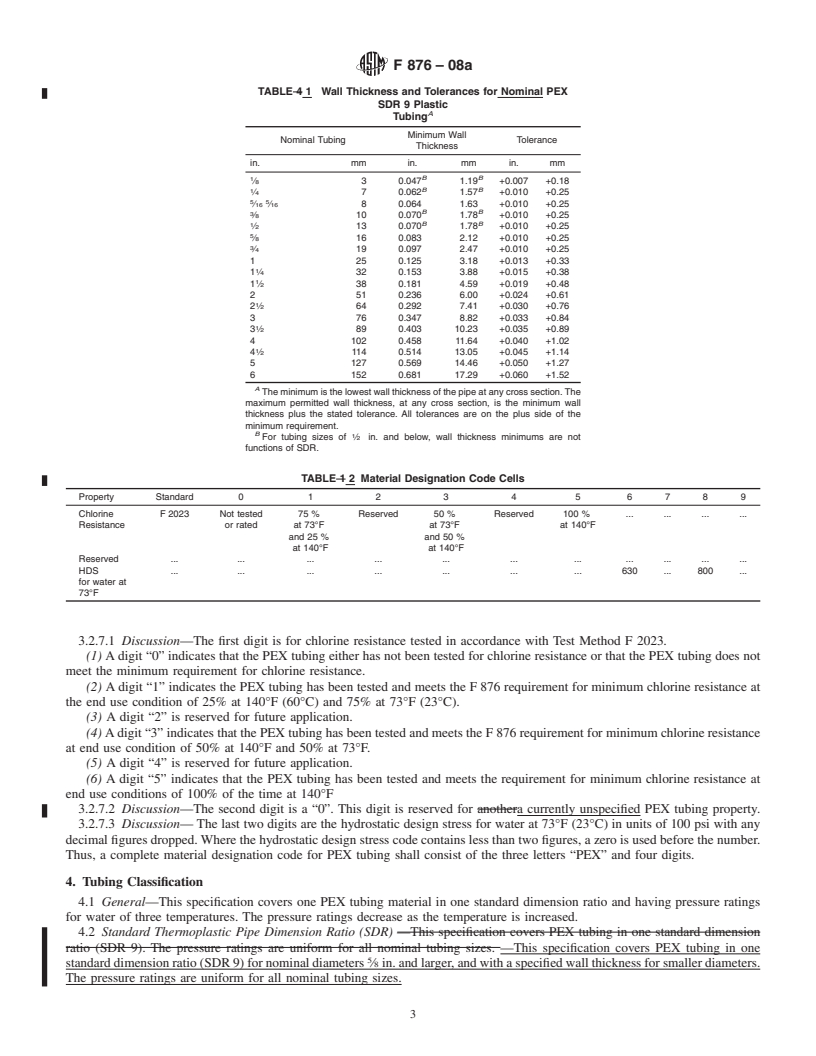
1.1 This specification covers crosslinked polyethylene (PEX) tubing that is outside diameter controlled, made in nominal SDR9 tubing dimension ratios except were noted, and pressure rated for water at three temperatures (see Appendix X1). Included are requirements and test methods for material, workmanship, dimensions, burst pressure, hydrostatic sustained pressure, excessive temperature pressure, excessive temperature-pressure, environmental stress cracking, stabilizer functionality, bent-tube hydrostatic pressure, oxidative stability in potable chlorinated water, and degree of crosslinking. Requirements for tubing markings are also given.
1.2 The text of this specification references notes, footnotes, and appendixes which provide explanatory material. These notes and footnotes (excluding those in tables and figures) shall not be considered as requirements of the specification.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.4 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the test methods portion, Section 7, of this specification: This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
An American National Standard
Designation: F 876 – 08a
Standard Specification for
1
Crosslinked Polyethylene (PEX) Tubing
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F 876; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* D 1598 Test Method for Time-to-Failure of Plastic Pipe
Under Constant Internal Pressure
1.1 This specification covers crosslinked polyethylene
D 1599 Test Method for Resistance to Short-Time Hydrau-
(PEX) tubing that is outside diameter controlled, made in
lic Pressure of Plastic Pipe, Tubing, and Fittings
nominal SDR9 tubing dimension ratios except were noted, and
D 1600 Terminology for Abbreviated Terms Relating to
pressure rated for water at three temperatures (see Appendix
Plastics
X1). Included are requirements and test methods for material,
3
D 1898 Practice for Sampling of Plastics
workmanship, dimensions, burst pressure, hydrostatic sus-
D 2122 Test Method for Determining Dimensions of Ther-
tained pressure, excessive temperature pressure, excessive
moplastic Pipe and Fittings
temperature-pressure, environmental stress cracking, stabilizer
D 2765 Test Methods for Determination of Gel Content and
functionality,bent-tubehydrostaticpressure,oxidativestability
Swell Ratio of Crosslinked Ethylene Plastics
in potable chlorinated water, and degree of crosslinking.
D 2837 Test Method for Obtaining Hydrostatic Design
Requirements for tubing markings are also given.
Basis forThermoplastic Pipe Materials or Pressure Design
1.2 Thetextofthisspecificationreferencesnotes,footnotes,
Basis for Thermoplastic Pipe Products
and appendixes which provide explanatory material. These
D 3895 Test Method for Oxidative-Induction Time of Poly-
notesandfootnotes(excludingthoseintablesandfigures)shall
olefins by Differential Scanning Calorimetry
not be considered as requirements of the specification.
F 412 Terminology Relating to Plastic Piping Systems
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
F 2023 Test Method for Evaluating the Oxidative Resis-
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
tance of Crosslinked Polyethylene (PEX) Tubing and
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
Systems to Hot Chlorinated Water
and are not considered standard.
2.2 ANSI Standard:
1.4 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the
4
B36.10 Standards Dimensions of Steel Pipe (IPS)
test methods portion, Section 7, of this specification: This
2.3 Federal Standard:
standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns,
5
FED-STD-123 Marking for Shipment (Civil Agencies)
if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user
2.4 Military Standard:
of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health
5
MIL-STD-129 Marking for Shipment and Storage
practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limita-
2.5 NSF Standard:
tions prior to use.
NSF/ANSI 14 for Plastic Piping Components and Related
6
2. Referenced Documents Materials
4
2
2.6 ISO Standards:
2.1 ASTM Standards:
ISO 1167 Thermoplastics pipes, fittings and assemblies for
D 618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
theconveyanceoffluids--Determinationoftheresistance
D 792 TestMethodsforDensityandSpecificGravity(Rela-
to internal pressure -- Part 1: General method
tive Density) of Plastics by Displacement
ISO 13760 Plastics pipes for the conveyance of fluids under
D 1505 Test Method for Density of Plastics by the Density-
pressure -- Miner’s rule -- Calculation method for cumu-
Gradient Technique
lative damage
1 3
This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee F17 on Plastic Withdrawn. The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced
Piping Systems and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F17.26 on Olefin on www.astm.org.
4
Based Pipe. Available fromAmerican National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
Current edition approved Sept. 1, 2008. Published September 2008. Originally 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
5
approved in 1984. Last previous edition approved 2008 as F 876 – 08. Available from Standardization Documents Order Desk, DODSSP, Bldg. 4,
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or Section D, 700 Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA 19111-5098, http://
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM www.dodssp.daps.mil.
6
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from NSF International, P.O. Box 130140, 789 N. Dixboro Rd.,Ann
the ASTM website. Arbor, MI 48113-0140, http://www.
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
An American National Standard
Designation:F 876–08 Designation: F 876 – 08a
Standard Specification for
1
Crosslinked Polyethylene (PEX) Tubing
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F 876; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 This specification covers crosslinked polyethylene (PEX) tubing that is outside diameter controlled, made in standard
thermoplasticnominal SDR9 tubing dimension ratios except were noted, and pressure rated for water at three temperatures (see
Appendix X1). Included are requirements and test methods for material, workmanship, dimensions, sustained pressure, burst
pressure, environmental stress cracking, stabilizer migration resistance, and degree of crosslinking. Methods of marking are also
given. ). Included are requirements and test methods for material, workmanship, dimensions, burst pressure, hydrostatic sustained
pressure, excessive temperature pressure, excessive temperature-pressure, environmental stress cracking, stabilizer functionality,
bent-tubehydrostaticpressure,oxidativestabilityinpotablechlorinatedwater,anddegreeofcrosslinking.Requirementsfortubing
markings are also given.
1.2 The text of this specification references notes, footnotes, and appendixes which provide explanatory material. These notes
and footnotes (excluding those in tables and figures) shall not be considered as requirements of the specification.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.4 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the test methods portion, Section 7, of this specification: This standard
does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this
standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D 618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
D 792 Test Methods for Density and Specific Gravity (Relative Density) of Plastics by Displacement
D 1505 Test Method for Density of Plastics by the Density-Gradient Technique
D 1598 Test Method for Time-to-Failure of Plastic Pipe Under Constant Internal Pressure
D 1599 Test Method for Resistance to Short-Time Hydraulic Pressure of Plastic Pipe, Tubing, and Fittings
D 1600 Terminology for Abbreviated Terms Relating to Plastics
3
D 1898 Practice for Sampling of Plastics
D 2122 Test Method for Determining Dimensions of Thermoplastic Pipe and Fittings
D 2765 Test Methods for Determination of Gel Content and Swell Ratio of Crosslinked Ethylene Plastics
D 2837 Test Method for Obtaining Hydrostatic Design Basis for Thermoplastic Pipe Materials or Pressure Design Basis for
Thermoplastic Pipe Products
D 3895 Test Method for Oxidative-Induction Time of Polyolefins by Differential Scanning Calorimetry
F 412 Terminology Relating to Plastic Piping Systems
F 2023 Test Method for Evaluating the Oxidative Resistance of Crosslinked Polyethylene (PEX) Tubing and Systems to Hot
Chlorinated Water
2.2 ANSI Standard:
4
B36.10 Standards Dimensions of Steel Pipe (IPS)
2.3 Federal Standard:
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee F17 on Plastic Piping Systems and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F17.26 on Olefin Based
Pipe.
Current edition approved Aug.Sept. 1, 2008. Published AugustSeptember 2008. Originally approved in 1984. Last previous edition approved 20072008 as F 876 – 078.
2
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Withdrawn.
3
Withdrawn. The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on www.astm.org.
4
Available from American National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St., 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.