ASTM C1403-14
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Rate of Water Absorption of Masonry Mortars
Standard Test Method for Rate of Water Absorption of Masonry Mortars
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 This test method provides a laboratory procedure for determining the relative water absorption properties over time of mortars used for masonry construction. Because the specimens are made under laboratory conditions and do not take into account the effect of the masonry substrate or field mixing procedures, this method is not intended for field use. Data generated from this test method may be useful for determining the relative effectiveness of water repellent admixtures or the effect of other admixtures or mortar components on the water repellency of a mortar. However, use caution in interpreting the results. While the resistance of masonry to water penetration may be related to the water absorption of the mortar, it also depends on other factors, such as the workmanship, extent of bond, and the properties of the masonry units and mortar.
Note 1: This test method is specified in Specification C1384 for demonstrating compliance of mortar admixtures classified as Water Repellent. In this compliance testing, the admixed mortar is compared to a reference mortar made with the same mortar materials except that it does not include the admixture. For quality control testing of water repellent preblended dry mortar mixes, the reference mortar is not typically available since the water repellent additive is added during the manufacturing process prior to bagging the final product. In these cases, the procedure in Annex A1 can be used to determine the relative resistance of the mortar to absorption by capillary uptake.
SCOPE
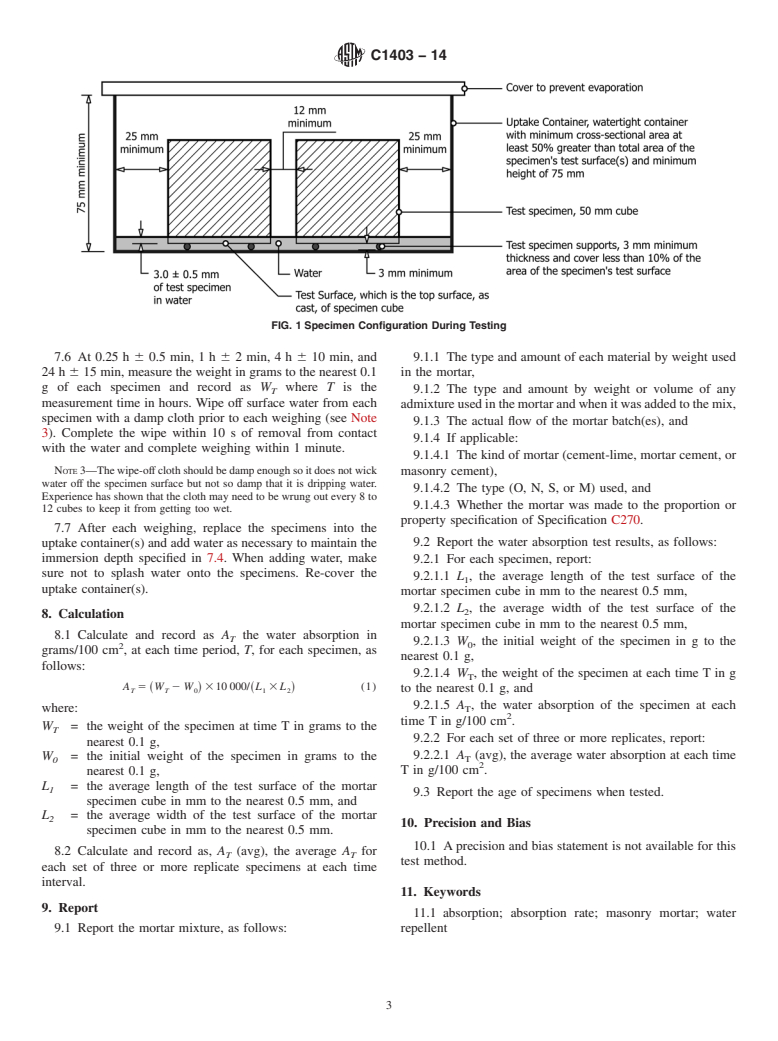
1.1 This test method covers a standardized laboratory procedure for determining the relative water absorption by capillary uptake (wicking) characteristics of masonry mortars. This test method is not applicable for determining the effectiveness of water repellent coatings.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.2.1 Inch-pound units are given in parentheses for temperature specification and are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: C1403 − 14
StandardTest Method for
Rate of Water Absorption of Masonry Mortars
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C1403; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* 3. Terminology
1.1 This test method covers a standardized laboratory pro-
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of terms used in this test
cedure for determining the relative water absorption by capil-
method, refer to Terminology C1180.
lary uptake (wicking) characteristics of masonry mortars. This
test method is not applicable for determining the effectiveness
4. Significance and Use
of water repellent coatings.
4.1 This test method provides a laboratory procedure for
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
determining the relative water absorption properties over time
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
of mortars used for masonry construction. Because the speci-
standard.
mensaremadeunderlaboratoryconditionsanddonottakeinto
1.2.1 Inch-poundunitsaregiveninparenthesesfortempera-
account the effect of the masonry substrate or field mixing
ture specification and are for information only.
procedures, this method is not intended for field use. Data
generated from this test method may be useful for determining
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
the relative effectiveness of water repellent admixtures or the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
effect of other admixtures or mortar components on the water
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
repellencyofamortar.However,usecautionininterpretingthe
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
results. While the resistance of masonry to water penetration
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
may be related to the water absorption of the mortar, it also
depends on other factors, such as the workmanship, extent of
2. Referenced Documents
bond, and the properties of the masonry units and mortar.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
NOTE 1—This test method is specified in Specification C1384 for
C109/C109M Test Method for Compressive Strength of
demonstrating compliance of mortar admixtures classified as Water
Hydraulic Cement Mortars (Using 2-in. or [50-mm] Cube
Repellent. In this compliance testing, the admixed mortar is compared to
Specimens)
areferencemortarmadewiththesamemortarmaterialsexceptthatitdoes
C270 Specification for Mortar for Unit Masonry
not include the admixture. For quality control testing of water repellent
preblended dry mortar mixes, the reference mortar is not typically
C305 Practice for Mechanical Mixing of Hydraulic Cement
available since the water repellent additive is added during the manufac-
Pastes and Mortars of Plastic Consistency
turing process prior to bagging the final product. In these cases, the
C511 Specification for Mixing Rooms, Moist Cabinets,
procedure in AnnexA1 can be used to determine the relative resistance of
Moist Rooms, and Water Storage Tanks Used in the
the mortar to absorption by capillary uptake.
Testing of Hydraulic Cements and Concretes
C778 Specification for Sand
5. Apparatus
C1180 Terminology of Mortar and Grout for Unit Masonry
5.1 Balance—A balance readable and accurate to 0.1 g.
C1384 Specification for Admixtures for Masonry Mortars
C1437 Test Method for Flow of Hydraulic Cement Mortar
5.2 Uptake Container—A watertight container with a mini-
mum cross sectional area that is at least 50 % greater than the
total area of the specimens’ test surface(s) and a minimum
depth of 75 mm. Provide a cover for the container to minimize
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee C12 on Mortars
and Grouts for Unit Masonry and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
evaporation.
C12.02 on Research and Methods of Test.
5.2.1 Usespecimensupportsthatallowaminimumof3mm
Current edition approved Dec. 15, 2014. Published January 2015. Originally
clearance from the bottom of the container and that cover a
approved in 1999. Last previous edition approved in 2013 as C1403 – 13. DOI:
10.1520/C1403-14.
maximum of 10 % of the area of the specimen’s test surface.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Usesupportsmadeofamaterialthatdoesnotfloatinwaterand
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
that does not rust, expand, or contract as a result of water
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. exposure.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
C1403 − 14
5.2.2 The container shall be flat so that when a specimen is preparedin6.1andthemoldsshallbeasspecifiedin5.3.Make
set on the supports the water level as specified in 7.4 shall not a minimum of three replicate specimens from each mortar
vary by more than 1 mm from one end of the specimen to the batch.
opposite end.
6.3 Immediately upon completion of casting, place the test
5.3 Specimen Molds—Metalnominal50-mmcubespecimen
specimens in a moist closet or moist room conforming to the
moldswithremovableplasticwatertightdisposableliners.The
requirements of Specification C511. Keep all test specimens in
plastic liners shall be rigid enough to retain their shape when
their molds and in the moist closet or moist room for 24 6 1
free standing and filled with mortar.
h with their upper surfaces exposed to the moist air but
protected from dripping water.
NOTE 2—For this test method, actual specimen dimensions are mea-
suredandusedtocalculateabsorptionperaunitarea;therefore,2-in.cube
6.4 At 24 6 1 h from the time of mixing remove the
specimen molds can be used interchangeably with 50-mm cube specimen
specimens from the molds. Mark the side of each specimen
molds.
indicating which surface is top, as cast. Cure the specimens in
5.4 Spoon—Ametal spoon approximately 230 mm in length
a moisture tight plastic bag at 24 6 8°C (75 6 15°F) until
and with a bowl approximately 100 mm in length.
placing in the oven in accordance with 6.5.
5.5 Straightedge—Asteelstraightedgenotlessthan150mm
6.5 Unless another age is specified, at the age of 28 days 6
long and approximately 1.5 to 3.0 mm thick.
12 h from the time of casting, remove the specimens from the
5.6 Tamper—A tamper made of a nonabsorptive,
plastic bag and dry in a ventilated oven at 110 6 5°C (230 6
nonabrasive, nonbrittle material such as a rubber compound
9°F) for not less than 24 h and until two successive weighings
having a ShoreAdurometer hardness of 80 6 10, or seasoned
at intervals of 2 h show an increment of loss not greater than
oakwoodrenderednonabsorptivebyimmersionfor15minutes
0.2 % of the last previously determined weight of the speci-
in paraffin at approximately 200°C (392°F), and having a cross
men.Removethespecimensfromtheovenandcoolinambient
section of 13 by 25 mm and a convenient length of 127 to 152
conditions (24 6 8°C (75 6 15°F)) and a relative humidity of
mm. The tamping face of the tamper shall be flat and at right
less than 80 % for a minimum of 2 h and until the specimens
angles to the length of the tamper.
reach ambient temperature. Begin testing within 24 h after
reaching ambient temperature.
5.7 Trowel, having a steel blade 100 to 150 mm in length,
with straight edges.
7. Procedure
5.8 Tapping Stick—A hardwood rod, having a diameter of
16 mm and a length of 150 mm. 7.1 Calculate the area of the test surface for each specimen
from the length and width of the test surface. The test surface
5.9 Timing Device—A suitable timing device capable of
is the top face of the cube, as cast. Using calipers, measure the
indicating elapsed time up to 24 h to the nearest 1 min.
length of the cube test surface to the nearest 0.5 mm at three
5.10 Calipers—Suitable calipers with parallel jaws for mea-
locationsalongitsheightandrecordas L theaveragelengthin
suring the dimensions of the hardened specimens to the nearest
millimetres to the nearest 0.5 mm. Using calipers, measure the
0.5 mm.
width of the cube test surface to the nearest 0.5 mm at three
locations along its height and record as L the average width in
6. Specimen Preparation 2
millimetres to the nearest 0.5 mm.
6.1 Prepare mortar according to Practice C305, adjusting
7.2 Record as W the initial weight in grams to the nearest
the water as necessary to obtain a flow of 110 6 5as
0.1 g of each individual specimen immediately prior to testing.
determined by Test Method C1437. Record the flow. If an
admixture is being added to the mortar, the dosage rate, time of
7.3 Place the uptake container on a flat level surface. Place
addition, and mixing sequence shall follow the manufacturer’s
all specimens in the uptake container(s) with their top faces, as
recommendation. If there is no manufacturer’s
cast, in contact with the specimen supports as illustrated in Fig.
recommendation, add a liquid admixture with the water and
1. Provide a minimum space of 12 mm between specimens and
addadryadmixturewiththecementitiouscomponents.Record
25 mm between specimens and the wall of the uptake con-
the type and amount of each material by weight used in the
tainer.
mortar. In addition, record the type and amount by weight or
7.4 Add room temperature (24 6 8°C (75 6 15°F) water to
volume of any admixture used and when it was added to the
the uptake container(s) so that the specimens are partially
mix. If applicable, record the kind of mortar (cement-lime,
immersed in 3.0 6 0.5 mm of water. When adding water make
mortar cement, or masonry cement), the type (O, N, S, or M),
sure not to splash water onto the specimens. Cover the uptake
and whether the mortar is ma
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: C1403 − 13 C1403 − 14
Standard Test Method for
Rate of Water Absorption of Masonry Mortars
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C1403; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 This test method covers a standardized laboratory procedure for determining the relative water absorption by capillary
uptake (wicking) characteristics of masonry mortars. This test method is not applicable for determining the effectiveness of water
repellent coatings.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.2.1 Inch-pound units are given in parentheses for temperature specification and are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
C109/C109M Test Method for Compressive Strength of Hydraulic Cement Mortars (Using 2-in. or [50-mm] Cube Specimens)
C270 Specification for Mortar for Unit Masonry
C305 Practice for Mechanical Mixing of Hydraulic Cement Pastes and Mortars of Plastic Consistency
C511 Specification for Mixing Rooms, Moist Cabinets, Moist Rooms, and Water Storage Tanks Used in the Testing of Hydraulic
Cements and Concretes
C778 Specification for Sand
C1180 Terminology of Mortar and Grout for Unit Masonry
C1384 Specification for Admixtures for Masonry Mortars
C1437 Test Method for Flow of Hydraulic Cement Mortar
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of terms used in this test method, refer to Terminology C1180.
4. Significance and Use
4.1 This test method provides a laboratory procedure for determining the relative water absorption properties over time of
mortars used for masonry construction. Because the specimens are made under laboratory conditions and do not take into account
the effect of the masonry substrate or field mixing procedures, this method is not intended for field use. Data generated from this
test method may be useful for determining the relative effectiveness of water repellent admixtures or the effect of other admixtures
or mortar components on the water repellency of a mortar. However, use caution in interpreting the results. While the resistance
of masonry to water penetration may be related to the water absorption of the mortar, it also depends on other factors, such as the
workmanship, extent of bond, and the properties of the masonry units and mortar.
NOTE 1—This test method is specified in Specification C1384 for demonstrating compliance of mortar admixtures classified as Water Repellent. In this
compliance testing, the admixed mortar is compared to a reference mortar made with the same mortar materials except that it does not include the
admixture. For quality control testing of water repellent preblended dry mortar mixes, the reference mortar is not typically available since the water
repellent additive is added during the manufacturing process prior to bagging the final product. In these cases, the procedure in Annex A1 can be used
to determine the relative resistance of the mortar to absorption by capillary uptake.
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C12 on Mortars and Grouts for Unit Masonryand and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C12.02
on on Research and Methods of Test.
Current edition approved July 15, 2013Dec. 15, 2014. Published August 2013January 2015. Originally approved in 1999. Last previous edition approved in 20122013 as
C1403 – 12.C1403 – 13. DOI: 10.1520/C1403-13.10.1520/C1403-14.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
C1403 − 14
5. Apparatus
5.1 Balance—A balance readable and accurate to 0.1 g.
5.2 Uptake Container—A watertight container with a minimum cross sectional area that is at least 50 % greater than the total
area of the specimens’ test surface(s) and a minimum depth of 75 mm. Provide a cover for the container to minimize evaporation.
5.2.1 Use specimen supports that allow a minimum of 3 mm clearance from the bottom of the container and that cover a
maximum of 10 % of the area of the specimen’s test surface. Use supports made of a material that does not float in water and that
does not rust, expand, or contract as a result of water exposure.
5.2.2 The container shall be flat so that when a specimen is set on the supports the water level as specified in 7.4 shall not vary
by more than 1 mm from one end of the specimen to the opposite end.
5.3 Specimen Molds—Metal nominal 50-mm cube specimen molds with removable plastic water tight disposable liners. The
plastic liners shall be rigid enough to retain their shape when free standing and filled with mortar.
NOTE 2—For this test method, actual specimen dimensions are measured and used to calculate absorption per a unit area; therefore, 2-in. cube specimen
molds can be used interchangeably with 50-mm cube specimen molds.
5.4 Spoon—A metal spoon approximately 230 mm in length and with a bowl approximately 100 mm in length.
5.5 Straightedge—A steel straightedge not less than 150 mm long and approximately 1.5 to 3.0 mm thick.
5.6 Tamper—A tamper made of a nonabsorptive, nonabrasive, nonbrittle material such as a rubber compound having a Shore
A durometer hardness of 80 6 10, or seasoned oak wood rendered nonabsorptive by immersion for 15 minutes in paraffin at
approximately 200°C (392°F), and having a cross section of 13 by 25 mm and a convenient length of 127 to 152 mm. The tamping
face of the tamper shall be flat and at right angles to the length of the tamper.
5.7 Trowel, having a steel blade 100 to 150 mm in length, with straight edges.
5.8 Tapping Stick—A hardwood rod, having a diameter of 16 mm and a length of 150 mm.
5.9 Timing Device—A suitable timing device capable of indicating elapsed time up to 24 h to the nearest 1 min.
5.10 Calipers—Suitable calipers with parallel jaws for measuring the dimensions of the hardened specimens to the nearest 0.5
mm.
6. Specimen Preparation
6.1 Prepare mortar according to Practice C305, adjusting the water as necessary to obtain a flow of 110 6 5 as determined by
Test Method C1437. Record the flow. If an admixture is being added to the mortar, the dosage rate, time of addition, and mixing
sequence shall follow the manufacturer’s recommendation. If there is no manufacturer’s recommendation, add a liquid admixture
with the water and add a dry admixture with the cementitious components. Record the type and amount of each material by weight
used in the mortar. In addition, record the type and amount by weight or volume of any admixture used and when it was added
to the mix. If applicable, record the kind of mortar (cement-lime, mortar cement, or masonry cement), the type (O, N, S, or M),
and whether the mortar is made to the proportion or property specification of Specification C270.
6.1.1 To test the behavior of mortar components independent of the qualities of the masonry sand use a blend of equal parts by
weight of graded standard sand and standard 20 - 30 sand conforming to Specification C778.
6.2 Prepare 50-mm cube specimens according to Test Method C109/C109M except the mortar shall be the mortar prepared in
6.1 and the molds shall be as specified in 5.3. Make a minimum of three replicate specimens from each mortar batch.
6.3 Immediately upon completion of casting, place the test specimens in a moist closet or moist room conforming to the
requirements of Specification C511. Keep all test specimens in their molds and in the moist closet or moist room for 24 6 1 h with
their upper surfaces exposed to the moist air but protected from dripping water.
6.4 At 24 6 1 h from the time of mixing remove the specimens from the molds. Mark the side of each specimen indicating
which surface is top, as cast. Cure the specimens in a moisture tight plastic bag at 24 6 8°C (75 6 15°F) until placing in the oven
in accordance with 6.5.
6.5 Unless another age is specified, at the age of 28 days 6 12 h from the time of casting, remove the specimens from the plastic
bag and dry in a ventilated oven at 110 6 5°C (230 6 9°F) for not less than 24 h and until two successive weighings at intervals
of 2 h show an increment of loss not greater than 0.2 % of the last previously determined weight of the specimen. Remove the
specimens from the oven and cool in ambient conditions (24 6 8°C (75 6 15°F)) and a relative humidity of less than 80 % for
a minimum of 2 h and until the specimens reach ambient temperature. Begin testing within 24 h after reaching ambient
temperature.
7. Procedure
7.1 Calculate the area of the test surface for each specimen from the length and width of the test surface. The test surface is
the top face of the cube, as cast. Using calipers, measure the length of the cube test surface to the nearest 0.5 mm at three locations
C1403 − 14
along its height and record as L the average length in millimetres to the nearest 0.5 mm. Using calipers, measure the width of
the cube test surface to the nearest 0.5 mm at three locations along its height and record as L the average width in millimetres
to the nearest 0.5 mm.
7.2 Record as W the initial weight in grams to the nearest 0.1 g of each indiv
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.