ASTM F2389-04
(Specification)Standard Specification for Pressure-rated Polypropylene (PP) Piping Systems
Standard Specification for Pressure-rated Polypropylene (PP) Piping Systems
SCOPE
1.1 This specification establishes requirements for polypropylene (PP) piping system components made to metric sizes and IPS schedule 80 sizes, and pressure rated for water service and distribution supply (see Appendix X1). Included are criteria for materials, workmanship, dimensions and tolerances, product tests, and marking for polypropylene (PP) piping system components such as pipe, fittings, valves, and manifolds.
1.2 The components governed by this specification shall be permitted for use in water service lines, hot-and-cold water distribution, hydronic heating, and irrigation systems.
1.3 The pipe and fittings produced under this specification shall be permitted to be used to transport industrial process fluids, effluents, slurries, municipal sewage, etc. The user shall consult the manufacturer to determine whether the material being transported is compatible with the polypropylene piping system and will not affect the service life beyond limits acceptable to the user.
1.4 Units—The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory requirements prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: F 2389 – 04
Standard Specification for
Pressure-rated Polypropylene (PP) Piping Systems
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F 2389; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope D 1600 Terminology for Abbreviated Terms Related to
Plastics
1.1 This specification establishes requirements for polypro-
D 2122 Test Method for Determining Dimensions of Ther-
pylene (PP) piping system components made to metric sizes
moplastics Pipe and Fittings
and IPS schedule 80 sizes, and pressure rated for water service
D 2749 Symbols for Dimensions of Plastic Pipe Fittings
and distribution supply (see Appendix X1). Included are
D 3895 Test Method for Oxidative-Induction Time of Poly-
criteria for materials, workmanship, dimensions and toler-
olefins by Differential Scanning Calorimetry
ances, product tests, and marking for polypropylene (PP)
D 4101 Specification for Polypropylene Injection and Ex-
piping system components such as pipe, fittings, valves, and
trusion Materials
manifolds.
F 412 Terminology Relating to Plastic Piping Systems
1.2 The components governed by this specification shall be
2.2 International Organization for Standardization (ISO)
permitted for use in water service lines, hot-and-cold water
Standards:
distribution, hydronic heating, and irrigation systems.
ISO 3127 Thermoplastic Pipes—Determination of Resis-
1.3 The pipe and fittings produced under this specification
tance to External Blows—Round the Clock Method
shall be permitted to be used to transport industrial process
ISO 4065 Thermoplastics Pipes—Universal Wall Thickness
fluids, effluents, slurries, municipal sewage, etc. The user shall
Table
consult the manufacturer to determine whether the material
ISO 9080 Plastics Piping and Ducting Systems—
being transported is compatible with the polypropylene piping
Determination of the Long-Term Hydrostatic Strength of
system and will not affect the service life beyond limits
Thermoplastics Materials in Pipe Form by Extrapolation
acceptable to the user.
ISO 15874-2:2002 Plastics Piping Systems for Hot and
1.4 Units—The values stated in inch-pound units are to be
Cold Water Installations—Polypropylene (PP)—Part 2:
regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are
Pipes
mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for
ISO 15874-3:2002 Plastics Piping Systems for Hot and
information only and are not considered standard.
Cold Water Installations—Polypropylene (PP)—Part 3:
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
Fittings
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
ISO/TS 15874-7 Plastics Piping Systems for Hot and Cold
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
Water Installations—Polypropylene (PP)—Part 7: Guid-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
ance for the Assessment of Conformity
bility of regulatory requirements prior to use.
2.3 NSF International Standards:
2. Referenced Documents
NSF/ANSI 14 Plastics Piping System Components and
Related Materials
2.1 ASTM Standards:
NSF/ANSI 61 Drinking Water System Components—
D 792 Test Method for Density and Specific Gravity (Rela-
Health Effects
tive Density) of Plastics by Displacement
2.4 European Norm:
D 1505 Test Method for Density of Plastics by the Density-
prEN10226-1 PipeThreadsWherePressureTightJointsare
Gradient Technique
Made on the Threads—Part 1: Designation, Dimensions
D 1598 Test Method for Time-to-Failure of Plastic Pipe
and Tolerances
Under Constant Internal Pressure
2.5 American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME)
Standard:
This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee F17 on Plastic
Piping Systems and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F17.61 on Water.
Current edition approved June 1, 2004. Published July 2004. Available from the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 1, rue
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or de Varembé, Case postale 56 CH-1211 Geneva 20, Switzerland.
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Available from the Deutsches Institut für Normung, Burgrafenstrasse 6, 10787
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Berlin, Germany.
the ASTM website. Available from NSF International, 789 Dixboro Road, Ann Arbor, MI, 48105.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
F2389–04
B1.20.1 Pipe Threads, General Purpose, Inch psi (10.0 MPa) based on testing in accordance with ISO 9080
2.6 Plastic Pipe Institute (PPI) Technical Report: and classification of the lower confidence limit (s )at50
LCL
TR-4 PPI Listing of Hydrostatic Design Basis (HDB), years in accordance with ISO 12162.
Strength Design Basis (SDB), Pressure Design Basis 5.5 Categorized Required Strength (CRS )—The PP mate-
u,t
(PDB) and Minimum Required Strength (MRS) Ratings rial used in the pipe and fittings shall have a CRS value of
u,t
for Thermoplastic Piping Materials 280 psi (1.93 MPa) based on testing in accordance with ISO
9080 and classification of the lower confidence limit (s )at
LCL
3. Terminology
180°F (82°C) and 50 years.
5.6 Minimum Pressure Rating—The minimum pressure rat-
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 Definitions are in accordance with Terminology F 412 ing of the pipe shall be 160 psi (1.1 MPa) at 73°F (23°C) and
100 psi (0.69 MPa) at 180°F (82°C) for hot-and-cold distribu-
and abbreviations are in accordance withTerminology D 1600,
unless otherwise specified. tion and 160 psi (1.1 MPa) at 73°F (23°C) for cold water
service.
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.2.1 polypropylene random copolymer (PP-R), n—a pro- 5.7 Threads—Fittings shall be permitted to be threaded by
use of metal inserts molded into the fitting.
pylene plastic containing not more than 50 % of another
5.7.1 Metal threads shall be constructed of brass or stainless
olefinic monomer (or monomers), having no functional group
steel inserts molded into the fitting.
other than the olefinic group, copolymerized with the propy-
5.7.2 Threads shall not be molded or fabricated directly into
lene.
the polypropylene plastic.
3.2.1.1 Discussion—This term is also used for finished
5.8 The piping compound shall be permitted to include
compound which comprises the PP-R resin and additives such
colorants, antioxidants, reinforcing materials and additives
as colorants, UV inhibitors, and stabilizers. Polypropylene
necessary for the finished product. The modified material and
random copolymers containing more than one additional
finished product shall meet all requirements of this specifica-
monomer are often referred to as “terpolymers.”
tion.
3.2.2 plastic-to-metal transition fittings, n—a fitting de-
signed to provide a means of connection between the PPpiping
NOTE 1—The Plastics Pipe Institute (PPI) publishes listings of mini-
system and metal piping systems such as steel pipe and copper
mum required strength (MRS) and categorized required strength (CRS )
u,t
tubing. The fittings include a means of taking into account the
ratings for thermoplastic piping materials in Technical Report No. 4
differences in thermal expansion of the materials and maintain- (TR-4). ISO/TS 15874-7 provides guidance on evaluating the effect of
additives on long-term strength of the pipe and fittings material.
ing a pressure-tight seal over the intended use temperature
range.
6. Workmanship, Finish and Appearance
6.1 The pipe and fittings shall be free of visible cracks,
4. Classification
holes, foreign inclusions, blisters and other known injurious
4.1 General—This specification covers PP piping systems
defects.The pipe and fittings shall be uniform in color, opacity,
madefromPPmaterials(PP-R)invariousdimensionratiosand
density and other physical properties.
pressure ratings.
4.2 Thermoplastic Pipe Series and Schedule—This specifi-
7. Dimensions and Tolerances
cationcoversPPpipemadeinschedule80IPSsizesandmetric
7.1 Pipe Dimensions—Pipe dimensions shall meet the re-
sizes in accordance with ISO 4065.
quirements in 7.1.1 and 7.1.2.
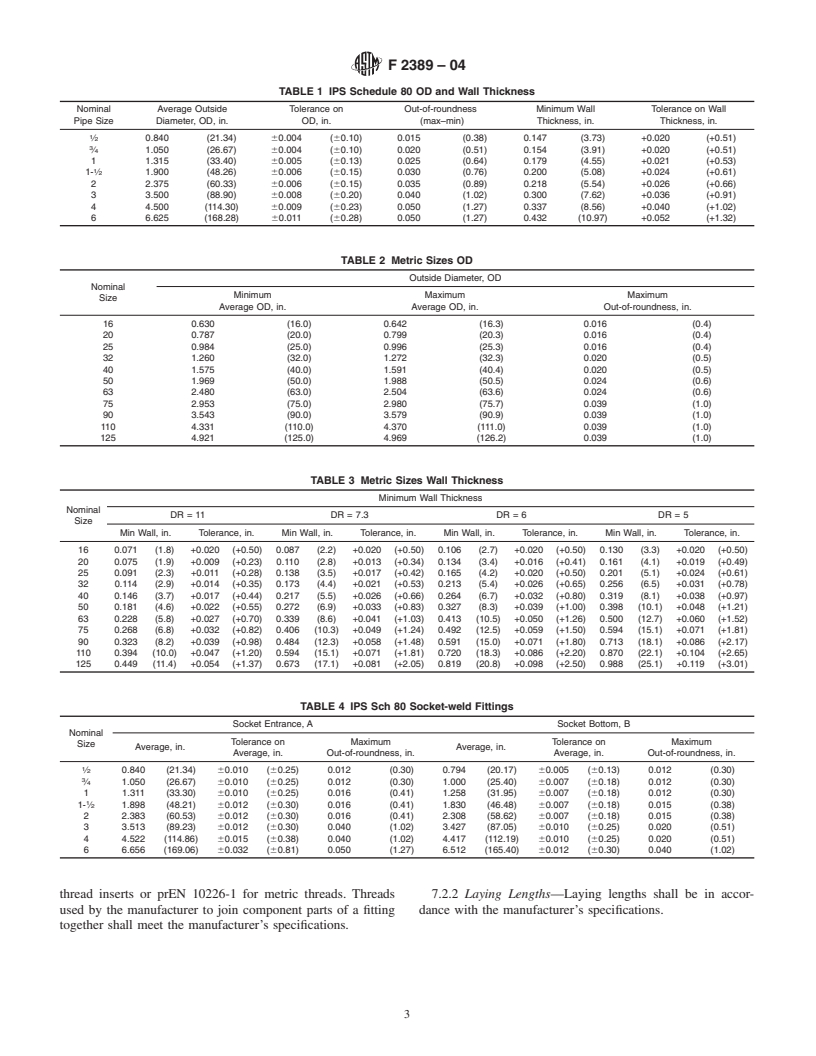
7.1.1 Outside Diameters—The outside diameters and toler-
5. Materials and Manufacture
ances shall be as shown in Table 1 (IPS Sch. 80), or Tables 2
5.1 The pipe and fittings shall be polypropylene material of
and 3 (metric series), when measured in accordance with Test
type PP-R. Clean rework material, of the same PP-R resin
Method D 2122. For diameters not shown in these tables, the
generated from the manufacturer’s own pipe or fitting produc-
tolerance shall be the same percentage of outside diameter as
tion, shall be permitted to be used provided the pipe or fittings
those for the closest listed diameter.
produced meet all requirements of this specification.
7.1.2 Wall Thicknesses—The wall thicknesses and toler-
5.2 For pipe compound, the melt flow rate (MFR) shall not
ances shall be as shown in Table 1, or Tables 2 and 3, when
exceed 10.8 grain/10 min (0.7 g/10 min), when tested in
measured in accordance with Test Method D 2122. For wall
accordancewithD 1238usingconditionsof4.76lbm(2.16kg)
thicknesses (DR’s) not shown in these tables, the minimum
at 446°F (230°C).
wall thickness shall be as calculated using the DR and outside
5.3 The density of the unreinforced, natural color PP mate-
3 3 diameter, and the tolerance on the wall thickness shall be the
rial shall not exceed 56.9 lbm/ft (912 kg/m ), when tested in
same percentage of the calculated minimum wall thickness as
accordance with Test Method D 1505 or Test Method D 792.
for the closest listed minimum wall thickness.
5.4 Minimum Required Strength (MRS)—The PP material
7.1.3 Threaded Pipe—Pipe covered by this specification
used in the pipe and fittings shall have an MRS value of 1450
shall not be threaded.
7.2 Fittings Dimensions—Fittings dimensions shall meet
the requirements in 7.2.1 through 7.2.4.
European Committee for Standardization, 36, rue de Stassart, B-1050 Brussels.
7.2.1 Threads—Taper threads for joining fittings shall com-
Available from the Plastics Pipe Institute, 1825 Connecticut Ave. N.W., Suite
630, Washington, DC 20009. ply with the requirements of ASME B1.20.1 for NPT metal
F2389–04
TABLE 1 IPS Schedule 80 OD and Wall Thickness
Nominal Average Outside Tolerance on Out-of-roundness Minimum Wall Tolerance on Wall
Pipe Size Diameter, OD, in. OD, in. (max–min) Thickness, in. Thickness, in.
⁄2 0.840 (21.34) 60.004 (60.10) 0.015 (0.38) 0.147 (3.73) +0.020 (+0.51)
⁄4 1.050 (26.67) 60.004 (60.10) 0.020 (0.51) 0.154 (3.91) +0.020 (+0.51)
1 1.315 (33.40) 60.005 (60.13) 0.025 (0.64) 0.179 (4.55) +0.021 (+0.53)
1- ⁄2 1.900 (48.26) 60.006 (60.15) 0.030 (0.76) 0.200 (5.08) +0.024 (+0.61)
2 2.375 (60.33) 60.006 (60.15) 0.035 (0.89) 0.218 (5.54) +0.026 (+0.66)
3 3.500 (88.90) 60.008 (60.20) 0.040 (1.02) 0.300 (7.62) +0.036 (+0.91)
4 4.500 (114.30) 60.009 (60.23) 0.050 (1.27) 0.337 (8.56) +0.040 (+1.02)
6 6.625 (168.28) 60.011 (60.28) 0.050 (1.27) 0.432 (10.97) +0.052 (+1.32)
TABLE 2 Metric Sizes OD
Outside Diameter, OD
Nominal
Minimum Maximum Maximum
Size
Average OD, in. Average OD, in. Out-of-roundness, in.
16 0.630 (16.0) 0.642 (16.3) 0.016 (0.4)
20 0.787 (20.0) 0.799 (20.3) 0.016 (0.4)
25 0.984 (25.0) 0.996 (25.3) 0.016 (0.4)
32 1.260 (32.0) 1.272 (32.3) 0.020 (0.5)
40 1.575 (40.0) 1.591 (40.4) 0.020 (0.5)
50 1.969 (50.0) 1.988 (50.5) 0.024 (0.6)
63 2.480 (63.0) 2.504 (63.6) 0.024 (0.6)
75 2.953 (75.0) 2.980 (75.7) 0.039 (1.0)
90 3.543 (90.0) 3.579 (90.9) 0.039 (1.0)
110 4.331 (110.0) 4.370 (111.0) 0.039 (1.0)
125 4.921 (125.0) 4.969 (126.2) 0.039 (1.0)
TABLE 3 Metric Sizes Wall Thickness
Minimum Wall Thickness
Nominal
DR=11 DR=7.3 DR=6 DR=5
Size
Min Wall, in. Tolerance, in. Min Wall, in. Tolerance, in. Min Wall, in. Tolerance, in. Min Wall, in. Tolerance, in.
16 0.071 (1.8) +0.020 (+0.50) 0.087 (2.2) +0.020 (+0.50) 0.106 (2.7) +0.020 (+0.50) 0.130 (3.3) +0.020 (+0.50)
20 0.075 (1.9) +0.009 (+0.23) 0.110 (2.8) +0.013 (+0.34) 0.134 (3.4) +0.016 (+0.41) 0.161 (4.1) +0.019 (+0.49)
25 0.091 (2.3) +0.011 (+0.28) 0.138 (3.5) +0.017 (+0.42) 0.165 (4.2) +0.020 (+0.50) 0.201 (5.1) +0.024 (+0.61)
32 0.114 (2.9) +0.014 (+0.35) 0.173 (4.4) +0.021 (+0.53) 0.213 (5.4) +0.026 (+0.65) 0.256 (6.5) +0.031 (+0.78)
40 0.146 (3.7) +0.017 (+0.44) 0.217 (5.5) +0.026 (+0.66) 0.264 (6.7) +0.032 (+0.80) 0.319 (8.1) +0.038 (+0.97)
50 0.181 (4.6) +0.022 (+0.55) 0.272 (6.9) +0.033 (+0.83) 0.327 (8.3) +0.039 (+1.00) 0.398 (10.1) +0.048 (+1.21)
63 0.228 (5.8) +0.027 (+0.70) 0.339 (8.6) +0.041 (+1.03) 0.413 (10.5) +0.050 (+1.26) 0.500 (12.7) +0.060 (+1.52)
75 0.268 (6.8) +0.032 (+0.82) 0.406 (10.3) +0.049 (+1.24) 0.492 (12.5) +0.059 (+1.50) 0.594 (15.1) +0.071 (+1.81)
90 0.323 (8.2) +0.039 (+0.98) 0.484 (12.3) +0.058 (+1.48) 0.591 (15.0) +0.071 (+1.80) 0.713 (18.1) +0.086 (+2.17)
110 0.394 (10.0) +0.047 (+1.20) 0.594 (15.1) +0.071 (+1.81) 0.720 (18.3) +0.086 (+2.20) 0.870 (22.1) +0.104 (+2.65)
125 0.449 (11.4) +0.054 (+1.37) 0.673 (17.1) +0.081 (+2.05) 0.819 (20.8) +0.098 (+2.50) 0.988 (25.1) +0.119 (+3.01)
TABLE 4 IPS Sch 80 Socket-weld Fittings
Socket Entrance, A Socket Bottom, B
Nominal
Tolerance on Maximum Tolerance on Maximum
Size
Average, in. Average, in.
Average, in. Out-of-roundness, in. Average, in. Out-of-roundness, in.
⁄2 0.840 (21.34) 60.010 (60.25) 0.012 (0.30) 0.794 (20.17) 60.005 (60.13) 0.012 (0.30)
⁄4 1.050 (26.67) 60.010 (60.25) 0.012 (0.30) 1.000 (25.40) 60.007 (60.18) 0.012 (0.30)
1 1.311 (33.30) 60.010 (60.25) 0.016 (0.41) 1.258 (31.95) 60.007 (60.18) 0.012 (0.30)
1- ⁄2 1.898 (48.21) 60.012 (60.30) 0.016 (0.41) 1.830 (46.48) 60.007 (60.18) 0.015 (0.38)
2 2.383 (60.53) 60.012 (60.30) 0.016 (0.41) 2.308 (58.62) 60.007 (60.18) 0.015 (0.38)
3 3.513 (89.23) 60.012 (60.30) 0.040 (1.02) 3.427 (87.05) 60.010 (60.25) 0.020 (0.51)
4 4.522 (114.86) 60.015 (60.38) 0.040 (1.02) 4.417 (112.19) 60.010 (60.25) 0.020 (0.51)
6 6.656 (169.06) 60.032 (60.81) 0.050 (1.27) 6.512 (165.40) 60.012 (60.30) 0.040 (1.02)
thread inserts or prEN 10226-1 for metric threads. Threads 7.2.2 Laying Lengths—Laying lengths shall be in accor-
used by the manufacturer to join component parts of a fitting dance with the manufacturer’s specifications.
together shall meet the manufacturer’s specifications.
F2389–04
TABLE 5 IPS Sch 80 Socket-weld Fittings
Socket depth, C Wall Thickness
Nominal
Size
Min, in. Max, in. Socket, E, Min, in. Body, F, Min, in
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.