ASTM F809/F809M-95e1
(Specification)Standard Specification for Large Diameter Polybutylene Plastic Pipe (Withdrawn 2006)
Standard Specification for Large Diameter Polybutylene Plastic Pipe (Withdrawn 2006)
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers polybutylene (PB) pipe made in dimensions based on outside diameters from 3.5 to 42 in. in six standard dimension ratios, namely 11, 13.5, 17, 21, 26, and 32.5.
1.2 The outside diameter sizing system is known as the IPS system, whose measurements are in inch-pound units. Note 1-A complete metric companion to specification F809 has been developed-F809M; therefore no metric equivalents are presented in this specification.
1.3 The piping is intended for new construction and insertion renewal of old piping systems used for the transport of water, municipal sewage, industrial process liquids, effluents, slurries, etc. in both pressure and nonpressure systems. The components covered by this specification are intended for use in commercial and industrial process piping at temperatures up to 180°F. Note 2-The user must consult the manufacturer to assure himself that any degradation of the polybutylene pipe caused by the material being transported will not affect the service life beyond limits acceptable to the user.
1.4 All pipes produced under this specification are pressure-rated.
1.5 This specification includes criteria for classifying PB plastic pipe material and pipe, together with performance requirements and test methods for determining conformance to the requirements.
1.5.1 Quality control measures to be taken by manufacturers are outlined in the Appendix as a nonmandatory part of this specification.
1.6 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the test method portion, Section 7, of this specification: This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Standards Content (Sample)
e1
Designation: F 809/F809M – 95 An American National Standard
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR TESTING AND MATERIALS
100 Barr Harbor Dr., West Conshohocken, PA 19428
Reprinted from the Annual Book of ASTM Standards. Copyright ASTM
Standard Specification for
Large Diameter Polybutylene Plastic Pipe
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F 809/F809M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
e NOTE—F 809 and F 809M were combined editorially with no change in technical requirements in September 1996.
1. Scope if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user
of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health
1.1 This specification covers polybutylene (PB) pipe made
practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limita-
in dimensions based on outside diameters from 3.5 to 42 in. [90
tions prior to use.
to 1000 mm] in six standard dimension ratios, namely 11, 13.5,
17, 21, 26, and 32.5.
2. Referenced Documents
1.2 The outside diameter sizing system is known as the IPS
2.1 ASTM Standards:
[ISO] system, whose measurements are in inch-pound [SI]
D 618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics and Electrical
units. 2
Insulating Materials for Testing
1.3 The piping is intended for new construction and inser-
D 1598 Test Method for Time-to-Failure of Plastic Pipe
tion renewal of old piping systems used for the transport of
Under Constant Internal Pressure
water, municipal sewage, industrial process liquids, effluents,
D 1599 Test Method for Short-Time Hydraulic Failure Pres-
slurries, etc. in both pressure and nonpressure systems. The
sure of Plastic Pipe, Tubing, and Fittings
components covered by this specification are intended for use
D 1603 Test Method for Carbon Black in Olefin Plastics
in commercial and industrial process piping at temperatures up
D 2122 Test Method for Determining Dimensions of Ther-
to 180°F [82°C].
moplastic Pipe and Fittings
D 2290 Test Method for Apparent Tensile Strength of Ring
NOTE 1—The user must consult the manufacturer to assure himself that
or Tubular Plastics and Reinforced Plastics by Split Disk
any degradation of the polybutylene pipe caused by the material being
transported will not affect the service life beyond limits acceptable to the Method
user.
D 2321 Practice for Underground Installation of Thermo-
plastic Pipe for Sewers and Other Gravity-Flow Applica-
1.4 All pipes produced under this specification are pressure-
tions
rated.
D 2412 Test Method for Determination of External Loading
1.5 This specification includes criteria for classifying PB
Characteristics of Plastic Pipe by Parallel-Plate Loading
plastic pipe material and pipe, together with performance
D 2581 Specification for Polybutylene (PB) Plastics Mold-
requirements and test methods for determining conformance to
ing and Extrusion Materials
the requirements.
D 2837 Test Method for Obtaining Hydrostatic Design
1.5.1 Quality control measures to be taken by manufacturers
Basis for Thermoplastic Pipe Materials
are outlined in the appendix as a nonmandatory part of this
F 412 Terminology Relating to Plastic Piping Systems
specification.
2.2 ANSI Standard:
1.6 The values stated in either inch-pound or SI units are to
ANSI B 36.10 Standard Dimensions of Steel Pipe (IPS)
be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, SI units are
2.3 ISO Standard:
shown in brackets. The values stated in each system are not
ISO 3607 Polyethylene (PE) Pipes—Tolerances on Outside
exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used inde-
Diameters and Wall Thicknesses
pendently of the other. Combining values from the two systems
2.4 Federal Standard:
may result in nonconformance with the specification.
Fed. Std. No. 123 Marking for Shipment (Civil Agencies)
1.7 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the
2.5 Military Standard:
test method portion, Section 7, of this specification: This
standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns,
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.01.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.04.
1 4
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F-17 on Plastic Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.02.
Piping Systems and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F17.26 on Olefin Available from American National Standards Institute, 11 West 42nd Street,
Based Pipe. 13th Floor, New York, NY 10036.
Current edition approved Sept. 10, 1995. Published November 1995. Originally Available from Standardization Documents Order Desk, Bldg. 4 Section D, 700
published as F 809 – 83. Last previous edition F 809 – 89. Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA 19111-5094, Attn: NPODS.
F 809/F809M
MIL-STD-129 Marking for Shipment and Storage meeting the requirements of this specification are categorized
2.6 NSF Standards: by means of two criteria: (1) short-term strength tests (burst),
Standard No. 14 for Plastic Piping Components and Related and (2) sustained pressure tests. Because the maximum
Materials physical properties of the pipe are not developed until 10 days
Standard No. 61 for Drinking Water Systems after extrusion, short-term (burst) and sustained pressure
Components—Health Effects testing must be delayed for this period (see Annex A1.2).
NOTE 2—Piping used at elevated temperatures should be produced
3. Terminology
from the appropriate PB grade intended for this use.
3.1 Definitions:
5.2 Basic Materials—This specification covers PB pipe
3.1.1 Terms used in this specification are as defined in
made from Type II, Grade 1 (PB) plastic as defined in
Terminology F 412. The abbreviation for polybutylene is PB.
Specification D 2581.
3.2 Descriptions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
5.3 Compound—The PB plastic extrusion compound shall
3.2.1 relation between dimension ratio, hydrostatic design
meet the requirements of Type II, Grade 1, Class B with
stress, and hydrostatic pressure—the following expression is
antioxidants or Class C as described in Specification D 2581.
used in this specification to relate the dimension ratio,
5.4 Rework Material—Clean, rework material generated
hydrostatic stress, and pressure:
from the manufacturer’s own pipe production, may be used by
P=
the same manufacturer, as long as the pipe produced meets all
2S 2S
1 the requirements of this specification.
SDR 2 1
~D /t2 1!
O
6. Product Requirements
where:
6.1 Workmanship—The pipe shall be homogeneous
S = hydrostatic design stress, psi, [MPa]
throughout and essentially uniform in color, opacity, density,
P = internal pressure, psi, [MPa]
and other properties. The inside and outside surfaces shall be
D = average outside diameter, in. [mm],
O
semi-matte or glossy in appearance and free of sticky or tacky
t = minimum wall thickness, in. [mm], and
material. The pipe walls shall be free of cracks, holes, blisters,
D /t = dimension ratio = SDR.
O
voids, foreign inclusion, or other defects that are visible to the
naked eye and that may affect the wall integrity.
3.2.2 relation between hydrostatic design basis and
6.2 Dimensions and Tolerances:
hydrostatic design stress—the hydrostatic pressure rating of
6.2.1 Outside Diameters—The outside diameter shall be in
pipes described in this specification is based on the use of a
accordance with Table 1 when measured in accordance with
(service) design factor in accordance with the instruction given
7.4.1.
in Test Method D 2837 (see Annex A1).
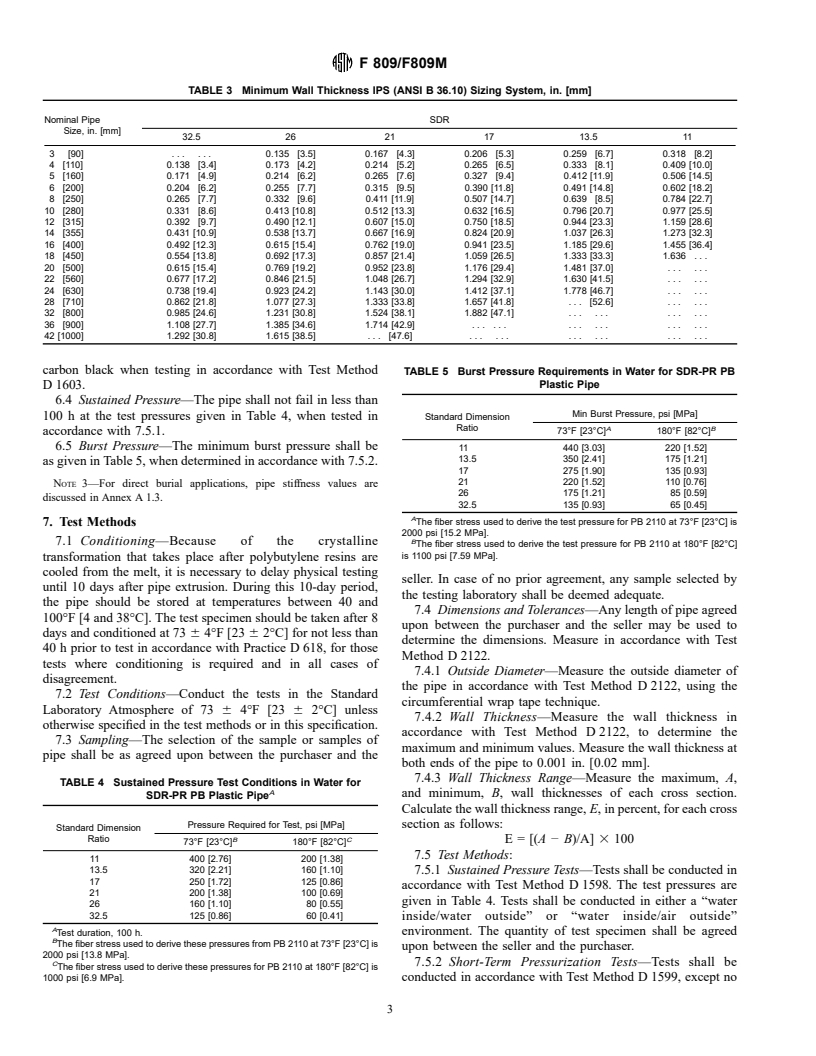
6.2.2 Wall Thicknesses—The minimum thicknesses shall be
3.2.3 standard thermoplastic pipe materials designation
in accordance with Table 3 when measured in accordance with
code—the pipe materials designation code shall consist of the
7.4.2.
abbreviation PB for the type of plastic, followed by the ASTM
6.2.3 Eccentricity—The wall thickness range shall not
type and grade in Arabic numerals and the hydrostatic design
exceed 12 % for any cross-section when measured in
stress at 73°F [23°C]. Where the hydrostatic design stress code
accordance with 7.4.3.
contains less than two fingers, a cipher shall be used before the
6.3 Carbon Black—The pipe shall contain at least 2 %
number. Thus a complete number code shall consist of two
letters and four figures for PB plastic pipe materials, for
example, PB2110.
TABLE 1 Outside Diameters and Tolerances IPS (inch/pound
units) Sizing System (ANSI B 36.10)
4. Pipe Classification
4.1 General—This specification covers PB pipe made from Actual Outside Diameters, in.
Nominal Pipe
A
PB plastic pipe material in six standard dimension ratios and Size, in.
Nominal Tolerance
water pressure ratings.
3 3.500 60.016
4.2 Standard Thermoplastic Pipe Dimension Ratios 4 4.500 60.020
5 5.563 60.025
(SDR)—This specification covers PB pipe in six standard
6 6.625 60.030
dimension ratios, namely: 11, 13.5, 17, 21, 26, and 32.5. These
8 8.625 60.039
10 10.750 60.048
are referred to as SDR11, SDR13.5, SDR17, SDR21, SDR26,
12 12.750 60.057
and SDR32.5, respectively. The pressure rating is uniform for
14 14.000 60.063
all nominal pipe sizes for a given PB pipe material and SDR
16 16.000 60.072
(see Table X1.1, Appendix). 18 18.000 60.081
20 20.000 60.090
22 22.000 60.099
5. Materials
24 24.000 60.108
5.1 General—Polybutylene plastics used to make pipe
28 28.000 60.126
32 32.000 60.144
36 36.000 60.162
7 42 42.000 60.189
Available from the National Sanitation Foundation, P.O. Box 1468, Ann Arbor,
A
MI 48106. As specified in ISO 3607.
F 809/F809M
TABLE 3 Minimum Wall Thickness IPS (ANSI B 36.10) Sizing System, in. [mm]
Nominal Pipe SDR
Size, in. [mm]
32.5 26 21 17 13.5 11
3 [90] . . . . . . 0.135 [3.5] 0.167 [4.3] 0.206 [5.3] 0.259 [6.7] 0.318 [8.2]
4 [110] 0.138 [3.4] 0.173 [4.2] 0.214 [5.2] 0.265 [6.5] 0.333 [8.1] 0.409 [10.0]
5 [160] 0.171 [4.9] 0.214 [6.2] 0.265 [7.6] 0.327 [9.4] 0.412 [11.9] 0.506 [14.5]
6 [200] 0.204 [6.2] 0.255 [7.7] 0.315 [9.5] 0.390 [11.8] 0.491 [14.8] 0.602 [18.2]
8 [250] 0.265 [7.7] 0.332 [9.6] 0.411 [11.9] 0.507 [14.7] 0.639 [8.5] 0.784 [22.7]
10 [280] 0.331 [8.6] 0.413 [10.8] 0.512 [13.3] 0.632 [16.5] 0.796 [20.7] 0.977 [25.5]
12 [315] 0.392 [9.7] 0.490 [12.1] 0.607 [15.0] 0.750 [18.5] 0.944 [23.3] 1.159 [28.6]
14 [355] 0.431 [10.9] 0.538 [13.7] 0.667 [16.9] 0.824 [20.9] 1.037 [26.3] 1.273 [32.3]
16 [400] 0.492 [12.3] 0.615 [15.4] 0.762 [19.0] 0.941 [23.5] 1.185 [29.6] 1.455 [36.4]
18 [450] 0.554 [13.8] 0.692 [17.3] 0.857 [21.4] 1.059 [26.5] 1.333 [33.3] 1.636 . . .
20 [500] 0.615 [15.4] 0.769 [19.2] 0.952 [23.8] 1.176 [29.4] 1.481 [37.0] . . . . . .
22 [560] 0.677 [17.2] 0.846 [21.5] 1.048 [26.7] 1.294 [32.9] 1.630 [41.5] . . . . . .
24 [630] 0.738 [19.4] 0.923 [24.2] 1.143 [30.0] 1.412 [37.1] 1.778 [46.7] . . . . . .
28 [710] 0.862 [21.8] 1.077 [27.3] 1.333 [33.8] 1.657 [41.8] . . . [52.6] . . . . . .
32 [800] 0.985 [24.6] 1.231 [30.8] 1.524 [38.1] 1.882 [47.1] . . . . . . . . . . . .
36 [900] 1.108 [27.7] 1.385 [34.6] 1.714 [42.9] . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
42 [1000] 1.292 [30.8] 1.615 [38.5] . . . [47.6] . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
carbon black when testing in accordance with Test Method
TABLE 5 Burst Pressure Requirements in Water for SDR-PR PB
D 1603. Plastic Pipe
6.4 Sustained Pressure—The pipe shall not fail in less than
Min Burst Pressure, psi [MPa]
100 h at the test pressures given in Table 4, when tested in Standard Dimension
A B
Ratio
73°F [23°C] 180°F [82°C]
accordance with 7.5.1.
6.5 Burst Pressure—The minimum burst pressure shall be
11 440 [3.03] 220 [1.52]
13.5 350 [2.41] 175 [1.21]
as given in Table 5, when determined in accordance with 7.5.2.
17 275 [1.90] 135 [0.93]
21 220 [1.52] 110 [0.76]
NOTE 3—For direct burial applications, pipe stiffness values are
26 175 [1.21] 85 [0.59]
discussed in Annex A 1.3.
32.5 135 [0.93] 65 [0.45]
A
The fiber stress used to derive the test pressure for PB 2110 at 73°F [23°C] is
7. Test Methods
2000 psi [15.2 MPa].
B
7.1 Conditioning—Because of the crystalline
The fiber stress used to derive the test pressure for PB 2110 at 180°F [82°C]
is 1100 psi [7.59 MPa].
transformation that takes place after polybutylene resins are
cooled from the melt, it is necessary to delay physical testing
seller. In case of no prior agreement, any sample selected by
until 10 days after pipe extrusion. During this 10-day period,
the testing laboratory shall be deemed adequate.
the pipe should be stored at temperatures between 40 and
7.4 Dimensions and Tolerances—Any length of pipe agreed
100°F [4 and 38°C]. The test specimen should be taken after 8
upon between the purchaser and the seller may be used to
days and conditioned at 73 6 4°F [23 6 2°C] for not less than
determine the dimensions. Measure in accordance with Test
40 h prior to test in accordance with Practice D 618, for those
Method D 2122.
tests where conditioning is required and in all cases of
7.4.1 Outside Diameter—Measure the outside diameter of
disagreement.
the pipe in accordance with Test Method D 2122, using the
7.2 Test Conditions—Conduct the tests in the Standard
circumferential wrap tape technique.
Laboratory Atmosphere of 73 6 4°F [23 6 2°C] unless
7.4.2 Wall Thickness—Measure the wall thickness in
otherwise specified in the test methods or in this specification.
accordance with Test Method D 2122, to determine the
7.3 Sampling—The selection of the sample or samples of
maximum and minimum values. Measure the wall thickness at
pipe shall be as agreed upon between the purchaser and the
both ends of the pipe to 0.001 in. [0.02 mm].
7.4.3 Wall Thickness Range—Measure the maximum, A,
TABLE 4 Sustained Pressure Test Conditions in Water for
A
and minimum, B, wall thicknesses of each cross section.
SDR-PR PB Plastic Pipe
Calculate the wall thickness range, E, in percent, for each cross
Pressure Required for Test, psi [MPa]
section as follows:
Standard Dimension
Ratio B C
E=[(A− B)/A] 3 100
73°F [23°C] 180°F [82°C]
7.5 Test Methods:
11 400 [2.76] 200 [1.38]
13.5 320 [2.21] 160 [1.10]
7.5.1 Sustained Pressure Tests—Tests shall be conducted in
17 250 [1.72] 125 [0.86]
accordance with Test Method D 1598. The test pressures are
21 200 [1.38] 100 [0.69]
given in Table 4. Tests shall be conducted in either a “water
26 160 [1.10] 80 [0.55]
32.5 125 [0.86] 60 [0.41] inside/water outside” or “water inside/air outside”
A
Test duration, 100 h. environment. The quantity of test specimen shall be agreed
B
The fiber stress used to derive these pressures from PB 2110 at 73°F [23°C] is
upon between the seller and the purchaser.
2000 psi [13.8 MPa].
C 7.5.2 Short-Term Pressurization Tests—Tests shall be
The fiber stress used to derive these pressures for PB 2110 at 180°F [82°C] is
1000 psi [6.9 MPa]. conducted in accordance with Test Method D 1599, except no
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.