ASTM A705/A705M-95(2000)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Age-Hardening Stainless Steel Forgings
Standard Specification for Age-Hardening Stainless Steel Forgings
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers age-hardening stainless steel forgings for general use.
1.2 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI (metric) units are to be regarded separately as standards; within the text and tables, the SI units are shown in [brackets]. The values stated in each system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each system must be used independent of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in nonconformance with the specification.
1.3 Unless the order specifies an "M" designation, the material shall be furnished to inch-pound units.
Note 1--Bar products are covered by Specification A564/A564M.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: A 705/A705M – 95 (Reapproved 2000)
Standard Specification for
Age-Hardening Stainless Steel Forgings
This standard is issued under the fixed designation A 705/A705M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3. Ordering Information
1.1 This specification covers age-hardening stainless steel 3.1 It is the responsibility of the purchaser to specify all
forgings for general use. requirements that are necessary for material ordered under this
1.2 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI specification. Such requirements may include but are not
(metric) units are to be regarded separately as standards; within limited to the following:
the text and tables, the SI units are shown in[brackets]. The 3.1.1 Quantity (weight or number of pieces),
values stated in each system are not exact equivalents; there- 3.1.2 Name of material (age-hardening stainless steel forg-
fore, each system must be used independent of the other. ings),
Combining values from the two systems may result in noncon- 3.1.3 Dimensions, including prints or sketches,
formance with the specification. 3.1.4 Type or UNS designation (Table 1),
1.3 Unless the order specifies an “M” designation, the 3.1.5 Heat treated condition (Section 5),
material shall be furnished to inch-pound units. 3.1.6 Transverse properties when required (7.4),
3.1.7 ASTM designation and date of issue, and
NOTE 1—Bar products are covered by Specification A 564/A 564M.
3.1.8 Special requirements (5.3, 5.4).
3.2 If possible the intended end use of the item should be
2. Referenced Documents
given on the purchase order, especially when the item is
2.1 ASTM Standards:
ordered for a specific end use or uses.
A 370 Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing
of Steel Products
NOTE 2—A typical ordering description is as follows: 5 age-hardening
stainless steel forgings, Type 630, solution-annealed, ASTM Specification
A 484/A484M Specification for General Requirements for
A 705 dated __ . End use: pump blocks for oil well equipment.
Stainless Steel Bars, Billets, and Forgings
A 564/A564M Specification for Hot-Rolled and Cold-
4. General Requirements
Finished Age-Hardening Stainless Steel Bars and Shapes
4.1 In addition to the requirements of this specification, all
A 751 Test Methods, Practices, and Terminology for
requirements of the current edition of Specification A 484/
Chemical Analysis of Steel Products
5 A 484M shall apply. Failure to comply with the general
E 527 Practice for Numbering Metals and Alloys (UNS)
requirements of Specification A 484/A 484M, constitutes non-
2.2 Other Documents:
conformance with this specification.
SAE J 1086 Recommended Practice for Numbering Metals
and Alloys (UNS)
5. Materials and Manufacture
5.1 Material for forgings shall consist of billets or bars,
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A-1 on Steel, either forged, rolled or cast, or a section cut from an ingot. The
Stainless Steel and Related Alloys, and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
cuts shall be made to the required length by a suitable process.
A01.17 on Flat Stainless Steel Products.
This material may be specified to Specification A 564/A 564M.
Current edition approved Jan. 15, 1995. Published March 1995. Originally
5.2 The material shall be forged by hammering, pressing,
published as A 705 – 74. Last previous edition A 705/A 705M – 94.
For ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code applications see related Specifi-
rolling, extruding, or upsetting to produce a wrought structure
cation SA-705/SA-705M in Section II of that Code.
throughout and shall be brought as nearly as possible to the
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.03.
4 finished shape and size by hot working.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.05.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.01.
Available from Society of Automotive Engineers, 400 Commonwealth Drive,
Warrendale, PA 15096.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
A 705/A705M – 95 (2000)
5.3 When specified on the order, sample forging may be 7.3 The impact strength shall be determined at 70 to 80°F
sectioned and etched to show flow lines and the condition in [20 to 25°C], by Charpy V-notch specimen Type A as described
regard to internal imperfections. When so specified, the ques- in Test Methods and Definitions A 370.
tion of acceptable and unacceptable metal flow shall be subject 7.4 Material tensile tested and, when specified, impact
to agreement between the manufacturer and the purchaser prior tested in the transverse direction (perpendicular to the forging
to order entry. flow lines) and meeting the requirements shown in Table 3
need not be tested in the longitudinal direction.
5.4 When specified on the order, the manufacturer shall
submit for approval of the purchaser a sketch showing the 7.5 Samples cut from forging shall conform to the mechani-
cal properties of Table 3 when heat treated as specified in Table
shape of the rough forging before machining, or before heat
treating for mechanical properties. 2 and Table 3 and tested in accordance with Test Methods and
Definitions A 370.
5.5 The grain size shall be as fine as practicable and
precautions shall be taken to minimize grain growth.
8. Prolongations for Tests
5.6 Material of types other than XM-9 shall be furnished in
8.1 Subject to Section 7, the forgings shall be produced with
the solution-annealed condition, or in the equalized and over-
prolongations for testing, unless otherwise specified. The
tempered condition, as noted in Table 2, unless otherwise
producer may elect to submit an extra forging to represent each
specified by the purchaser.
test lot instead of prolongations, or the test specimens can be
5.6.1 Types 630, XM-16, and XM-25 may be furnished in
taken from the forgings themselves.
the solution-annealed or age-hardened condition.
9. Number of Tests
6. Chemical Composition
9.1 For all classes of forgings weighing from 5000 to 7000
6.1 The steel shall conform to the chemical composition
lb [2300 to 3200 kg] each, at least one tension test shall be
limits specified in Table 1.
made from each forging.
6.2 Methods and practices relating to chemical analysis
9.2 For all classes of forgings weighing more than 7000 lb
required by this specification shall be in accordance with Test
[3200 kg] each, one tension test shall be made from each end
Methods, Practices, and Terminology A 751.
of each forging. In the case of ring forgings, the tension test
specimen shall be removed from each of two locations on the
7. Mechanical Properties
periphery, approximately 180° apart, or insofar as practicable,
7.1 The material, as represented by mechanical test speci-
from opposite ends of the forging.
mens, shall conform to the mechanical property requirements 9.3 For forgings weighing less than 5000 lb [2300 kg] each,
specified in Table 2 and shall be capable of developing the
one tension test shall be made from each size classification for
properties in Table 3 when heat treated as specified in Table 3.
each heat in each heat treating charge. Where continuous heat
7.2 The yield strength shall be determined by the offset
treating furnaces are used, tests shall be made on 10 % of the
method as described in the current edition of Test Methods and forgings of each size classification from each heat subjected to
Definitions A 370. The limiting permanent offset shall be 0.2 % the same heat treatment practice.
of the gage length of the specimen.
A
TABLE 1 Chemical Requirements
Composition, %
UNS Type Carbon Manganese Phospho- Sul- Sili- Chromium Nickel Alumi- Molyb- Tita- Copper Other
B
Designation rus fur con num denum nium Elements
C
S17400 630 0.07 1.00 0.040 0.030 1.00 15.00–17.50 3.00–5.00 . . . 3.00–5.00
S17700 631 0.09 1.00 0.040 0.030 1.00 16.00–18.00 6.50–7.75 0.75–1.50 . . . .
S15700 632 0.09 1.00 0.040 0.030 1.00 14.00–16.00 6.50–7.75 0.75–1.50 2.00–3.00 . . .
D
S35500 634 0.10–0.15 0.50–1.25 0.040 0.030 0.50 15.00–16.00 4.00–5.00 . 2.50–3.25 . .
S17600 635 0.08 1.00 0.040 0.030 1.00 16.00–17.50 6.00–7.50 0.40 . 0.40–1.20 . .
C
S15500 XM-12 0.07 1.00 0.040 0.030 1.00 14.00–15.50 3.50–5.50 . . . 2.50–4.50
E
S13800 XM-13 0.05 0.20 0.010 0.008 0.10 12.25–13.25 7.50–8.50 0.90–1.35 2.00–2.50 . .
F
S45500 XM-16 0.03 0.50 0.015 0.015 0.50 11.00–12.50 7.50–9.50 . 0.50 0.90–1.40 1.50–2.50
F
S45503 . 0.010 0.50 0.010 0.010 0.20 11.00–12.50 7.50–9.50 . 0.50 1.00–1.35 1.50–2.50
G
S45000 XM-25 0.05 1.00 0.030 0.030 1.00 14.00–16.00 5.00–7.00 . 0.50–1.00 . 1.25–1.75
A
Limits are in percent maximum unless shown as a range or stated otherwise.
B
New designation established in accordance with Practice E 527 and SAEJ1086, Recommended Practice for Numbering Metals and alloys (UNS).
C
Columbium plus tantalum 0.15–0.45.
D
Nitrogen 0.07–0.13.
E
Nitrogen 0.01.
F
Columbium plus tantalum 0.10–0.50.
G
Columbium 8 times carbon minimum.
A 705/A705M – 95 (2000)
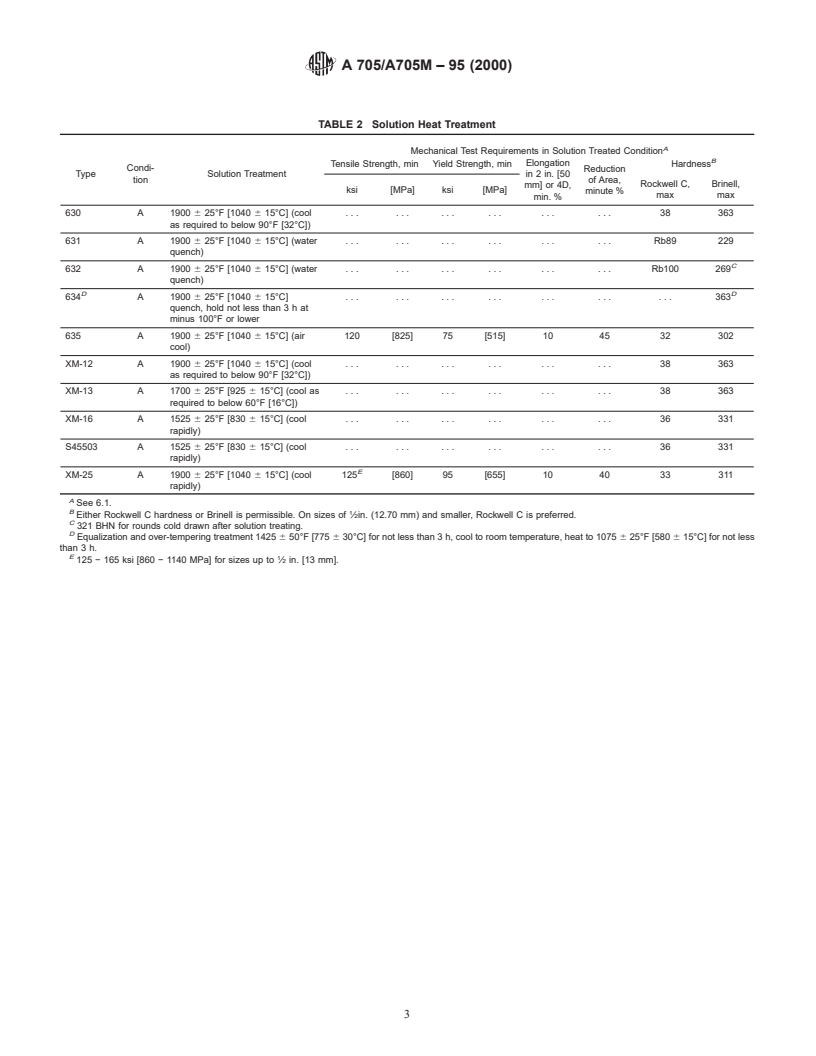
TABLE 2 Solution Heat Treatment
A
Mechanical Test Requirements in Solution Treated Condition
B
Elongation
Tensile Strength, min Yield Strength, min Hardness
Condi- Reduction
Type Solution Treatment in 2 in. [50
tion of Area,
Rockwell C, Brinell,
mm] or 4D,
ksi [MPa] ksi [MPa]
minute %
max max
min. %
630 A 1900 6 25°F [1040 6 15°C] (cool . . . . . . 38 363
as required to below 90°F [32°C])
631 A 1900 6 25°F [1040 6 15°C] (water . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Rb89 229
quench)
C
632 A 1900 6 25°F [1040 6 15°C] (water . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Rb100 269
quench)
D D
634 A 1900 6 25°F [1040 6 15°C] . . . . . . . 363
quench, hold not less than3hat
minus 100°F or lower
635 A 1900 6 25°F [1040 6 15°C] (air 120 [825] 75 [515] 10 45 32 302
cool)
XM-12 A 1900 6 25°F [1040 6 15°C] (cool . . . . . . 38 363
as required to below 90°F [32°C])
XM-13 A 1700 6 25°F [925 6 15°C] (cool as . . . . . . 38 363
required to below 60°F [16°C])
XM-16 A 1525 6 25°F [830 6 15°C] (cool . . . . . . 36 331
rapidly)
S45503 A 1525 6 25°F [830 6 15°C] (cool . . . . . . 36 331
rapidly)
E
XM-25 A 1900 6 25°F [1040 6 15°C] (cool 125 [860] 95 [655] 10 40 33 311
rapidly)
A
See 6.1.
B
Either Rockwell C hardness or Br
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.