ASTM E496-96
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Measuring Neutron Fluence Rate and Average Energy From Neutron Generators by Radioactivation Techniques
Standard Test Method for Measuring Neutron Fluence Rate and Average Energy From Neutron Generators by Radioactivation Techniques
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers a general procedure for the measurement of the fast-neutron fluence rate produced by neutron generators utilizing the H(d,n) He reaction. Neutrons so produced are usually referred to as 14-MeV neutrons, but range in energy depending on a number of factors.
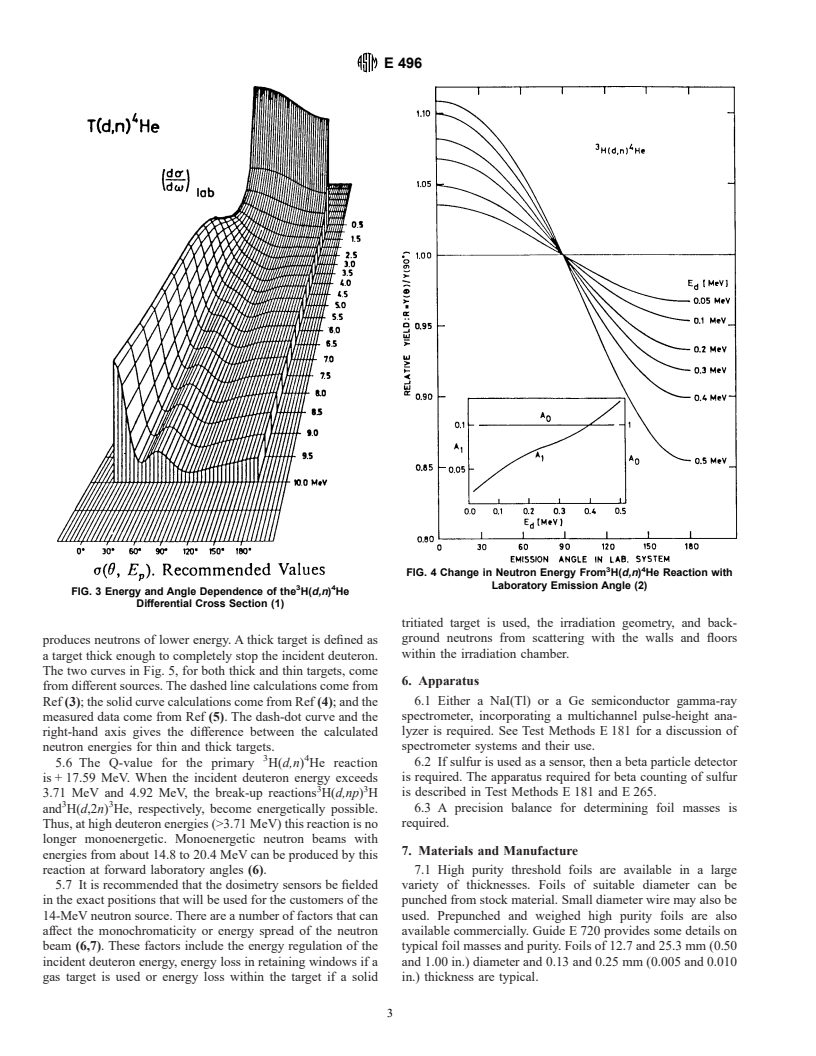
1.2 This test method uses the following threshold activation reactions: in aluminum, 27 Al(n,[alpha]) Na and 27 Al(n,p) Mg; in nickel, Ni(n,p) Co and Ni(n,2n) Ni; and in copper, Cu(n,2n) Cu and Cu(n,2n) Cu. The neutron fluence rate is determined from induced foil activities (as measured by gamma spectrometry) and reaction cross-section data.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
Designation: E 496 – 96
Standard Test Method for
Measuring Neutron Fluence and Average Energy
3
4
from H(d,n) He Neutron Generators by Radioactivation
1
Techniques
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E 496; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope ICRU Report 13—Neutron Fluence, Neutron Spectra and
3
Kerma
1.1 This test method covers a general procedure for the
ICRU Report 26—Neutron Dosimetry for Biology and
measurement of the fast-neutron fluence rate produced by
3
3 4
Medicine
neutron generators utilizing the H(d,n) He reaction. Neutrons
2.3 ISO Standard:
so produced are usually referred to as 14-MeV neutrons, but
4
Guide to the Expression of Uncertainty in Measurement
range in energy depending on a number of factors. This test
2.4 NIST Document:
method does not adequately cover fusion sources where the
Technical Note 1297—Guidelines for Evaluating and Ex-
velocity of the plasma may be an important consideration.
5
pressing the Uncertainty of NIST Measurement Results
1.2 This test method uses threshold activation reactions to
determine the average energy of the neutrons and the neutron
3. Terminology
fluence at that energy. At least three activities, chosen from an
3.1 Definitions—Refer to Terminology E 170.
appropriate set of dosimetry reactions, are required to charac-
terize the average energy and fluence. The required activities
4. Summary of Test Method
are typically measured by gamma ray spectroscopy.
4.1 This test method describes the determination of the
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
average neutron energy and fluence by use of three activities
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
from a select list of dosimetry reactions. Three dosimetry
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
reactions are chosen based on a number of factors including the
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
intensity of the neutron field, the reaction half-lives, the slope
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
of the dosimetry reaction cross section near 14-MeV, and the
minimum time between sensor irradiation and the gamma
2. Referenced Documents
counting. The activities from these selected reactions are
2.1 ASTM Standards:
measured. Two of the activities are used, in conjunction with
E 170 Terminology Relating to Radiation Measurements
2 the nuclear data for the dosimetry reactions, to determine the
and Dosimetry
average neutron energy. The third activity is used, along with
E 181 Test Methods for Detector Calibration and Analysis
2 the neutron energy and nuclear data for the selected reaction, to
of Radionuclides
determine the neutron fluence. The uncertainty of the neutron
E 261 Practice for Determining Neutron Fluence Rates,
2 energy and the neutron fluence is determined from the activity
Fluence, and Spectra by Radioactivation Techniques
measurement uncertainty and from the nuclear data.
E 265 Test Method for Measuring Reaction Rates and
2
Fast-Neutron Fluences by Radioactivation of Sulfur-32
5. Significance and Use
E 720 Guide for Selection and Use of Neutron-Activation
5.1 Refer to Practice E 261 for a general discussion of the
Foils for Determining Neutron Spectra Employed in
2 measurement of fast-neutron fluence rates with threshold
Radiation-Hardness Testing of Electronics
detectors.
2.2 International Commission on Radiation Units and
5.2 Refer to Test Method E 265 for a general discussion of
Measurements (ICRU) Reports:
the measurement of fast-neutron fluence rates by radioactiva-
tion of sulfur-32.
1 3
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E-10 on Nuclear Available from the International Commission on Radiation Units, 7910
Technology and Applicationsand is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee Woodmont Ave., Washington, DC 20014.
4
E10.07on Radiation Dosimetry for Radiation Effects on Materials and Devices. Available from American National Standards Institute, 11 W. 42nd St., 13th
Current edition approved Dec. 10, 1996. Published February 1997. Originally Floor, New York, NY 10036.
5
published as E 496 – 73. Last previous edition E 496 – 87 (1994). Available from National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg,
2
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 12.02. MD 20899.
Copyright © ASTM, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E 496
3 4
3 4
FIG. 1 Variation of 0 Degree H(d,n) He Differential Cross Section FIG. 2 Variation of 0 Degree H(d,n) He Differential Cross Section
with Incident Deuteron Energy (1) with Incident Deuteron Energy (1)
with energy, and clearly indicate that maximum neutron yield
5.3 Reactions used
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.