ASTM F1915-98
(Test Method)Standard Test Methods for Glazing for Detention Facilities
Standard Test Methods for Glazing for Detention Facilities
SCOPE
1.1 These test methods, including a fire test response method, cover the apparatus, procedures, and acceptance conditions for evaluating the normal operational performance and the performance characteristics under assault conditions of detention glazing used in window and door assemblies in detention and correctional facilities; thus, these test methods only give an indication of the performance characteristics of detention glazing in actual service. Such variables as installation and maintenance conditions are not considered except as otherwise included in this test method.
1.2 It is the intent of these test methods to help ensure that detention glazing performs at or above minimum acceptable levels to restrict inmate passage to unauthorized areas, to confine inmates, to delay and frustrate escape attempts and to resist vandalism.
1.3 Tools defined in these test methods are representative of similar tools or materials, which may become available to inmates within the secure perimeter of detention and correctional facilities, and which could be used to inflict similar product damage.
1.4 These test methods should not be used to establish or confirm the absolute prevention of forced entries or exits. These test methods define five factors (tool, temperature, techniques, time, and number of impacts) used to determine resistance to defined attacks.
1.5 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The SI values in stated parentheses are for information only.
1.6 In these test methods, the specimens are subjected to one or more specific sets of laboratory test conditions. If different test conditions are substituted or the end-use conditions are changed, it is not always possible by or from these test methods to predict changes in the physical attack, or fire-test-response characteristics measured, or both; therefore, the results are valid only for the physical attack, or fire-test-exposure conditions, or both, described in these test methods.
1.7 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: F 1915 – 98
Standard Test Methods for
1
Glazing for Detention Facilities
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F 1915; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
1.1 These test methods, including a fire test response
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
method, cover the apparatus, procedures, and acceptance
conditions for evaluating the normal operational performance
2. Referenced Documents
and the performance characteristics under assault conditions of
2.1 ASTM Standards:
detention glazing used in window and door assemblies in
F 1233 Test Method for Security Glazing Materials and
detention and correctional facilities; thus, these test methods
2
Systems
only give an indication of the performance characteristics of
F 1450 Test Methods for Hollow Metal Swinging Door
detention glazing in actual service. Such variables as installa-
2
Assemblies for Detention Facilities
tion and maintenance conditions are not considered except as
2.2 UL Standard:
otherwise included in this test method.
3
UL 752 Bullet Resisting Equipment
1.2 It is the intent of these test methods to help ensure that
2.3 NIJ Standard:
detention glazing performs at or above minimum acceptable
4
NIJ 0108.1 Ballistic Resistant Protective Materials
levels to restrict inmate passage to unauthorized areas, to
confine inmates, to delay and frustrate escape attempts and to
3. Terminology
resist vandalism.
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
1.3 Tools defined in these test methods are representative of
3.1.1 benchmark, n—an endpoint or intermediate point in
similar tools or materials, which may become available to
the test sequence as determined by the certification agency.
inmates within the secure perimeter of detention and correc-
3.1.2 detention security, n—assurance of the restriction of
tional facilities, and which could be used to inflict similar
mobility of inmates to designated areas within a correctional or
product damage.
detention facility.
1.4 These test methods should not be used to establish or
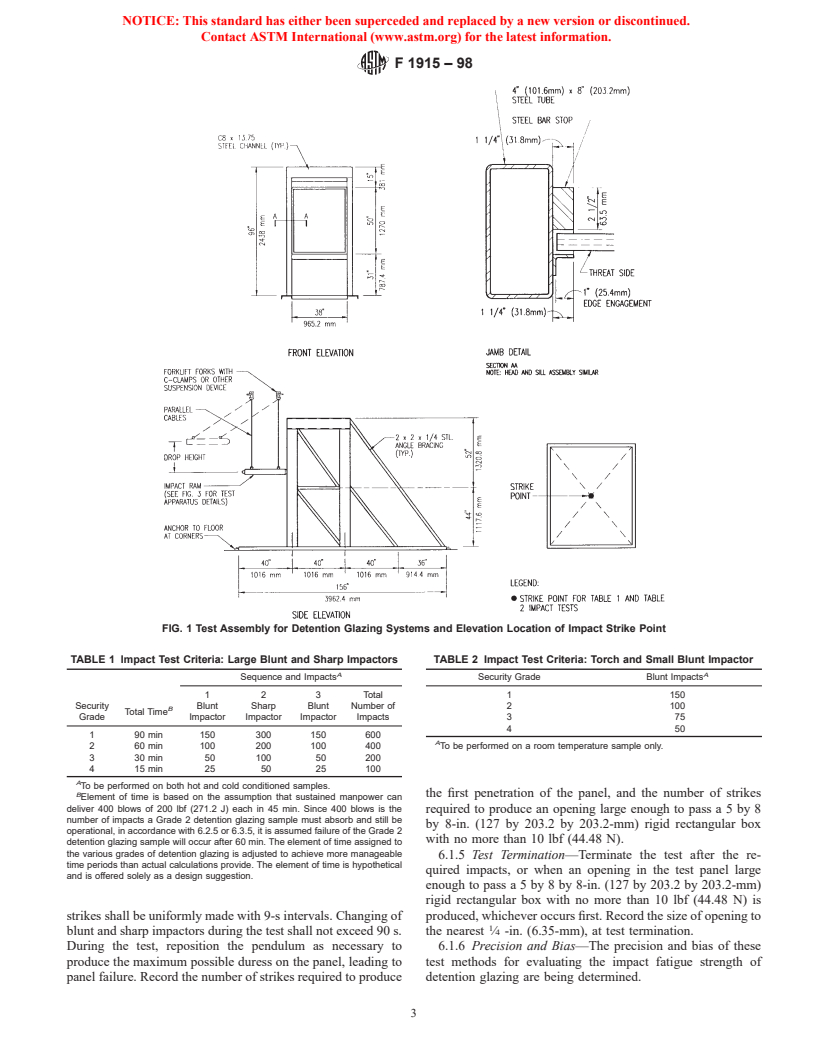
3.1.3 forcible egress, n—the ability to passa5by8by 8-in.
confirm the absolute prevention of forced entries or exits.
(127 by 203.2 by 203.2-mm) rigid box through an opening in
These test methods define five factors (tool, temperature,
the test sample created by destructive testing procedures with
techniques, time, and number of impacts) used to determine
no more than 10 lb (44.48 N) of force.
resistance to defined attacks.
3.1.4 frame, n—an assembly of members surrounding and
1.5 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
supporting a window or windows.
as the standard. The SI values in stated parentheses are for
3.1.5 glazing, n—any infill material, usually transparent or
information only.
translucent glass, polycarbonate, or combination thereof, used
1.6 In these test methods, the specimens are subjected to one
in a security detention frame.
or more specific sets of laboratory test conditions. If different
3.1.6 glazing stop, n—a formed metal section used to secure
test conditions are substituted or the end-use conditions are
glazing or panel in a frame.
changed, it is not always possible by or from these test methods
3.1.7 head or header, n—the horizontal member that forms
to predict changes in the physical attack, or fire-test-response
the top of a frame.
characteristics measured, or both; therefore, the results are
3.1.8 hollow metal, n—a term used in reference to such
valid only for the physical attack, or fire-test-exposure condi-
items as doors, frames, partitions, enclosures, and other items
tions, or both, described in these test methods.
that are fabricated from metal sheet, usually carbon steel.
1.7 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
2
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 15.07.
1 3
These test methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F-33 on Available from Underwriters Laboratories, 333 Pfingsten Rd., Northbrook, IL
Detention and Correctional Facilities and are the direct responsibility of Subcom- 60062-2096.
4
mittee F33.02 on Physical Barriers. Available from National Institute of Justice, 810 Seventh St., NW, Washington,
Current edition approved Sept. 10, 1998. Published February 1999. DC 20531.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.