ASTM F2322-12(2019)
(Test Method)Standard Test Methods for Physical Assault on Vertical Fixed Barriers for Detention and Correctional Facilities
Standard Test Methods for Physical Assault on Vertical Fixed Barriers for Detention and Correctional Facilities
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 A major concern for administrative officials is the security of barriers used in detention/correctional facilities. These test methods are designed to aid in identifying levels of physical security for walls which enclose or separate secure areas. This does not apply to the passage of contraband.
4.2 These test methods are not intended to provide a measure of resistance for a wall subjected to attack by corrosive agents, by high-powered rifles, explosives, sawing, or other such methods. These test methods are intended to evaluate the resistance of a wall to violent attacks by sustained manpower using battering devices, such as benches, bunks, or tables, and by handguns up to and including .44 magnum. Attacks from the outside and fire resistance ratings are not addressed in this standard.
4.3 The primary purpose or result of these test methods is to approximate the levels of abuse to which walls will potentially be subjected in the field. The desired result of its use is to help provide assurance of protection to the public, to facility administrative personnel, and to the inmates themselves.
4.4 It is recommended that detention/correctional facility administration provide adequate training, supervision, and preventative maintenance programs to enable walls to function as intended throughout the expected service life.
SCOPE
1.1 These test methods cover requirements for simulated service tests and testing equipment for determining the performance characteristics of walls designed to incarcerate inmates in detention and correctional institutions. The testing equipment provides for the setup and testing of two sample fixed barriers side-by-side, one with no openings and one equipped with a representative penetration in accordance with the American Correctional Association (ACA) standard for clear view area of 3 ft2 (0.279 m2), 12 in. (305 mm) wide by 36 in. (914 mm) high.
1.2 It is the intent of these test methods to help ensure that detention security walls perform at or above minimum acceptable levels to control passage of unauthorized or secure areas, to confine inmates, to delay and frustrate escape attempts, and to resist vandalism. It is recognized that in order to meet the intent of these test methods, opening assemblies within these walls must be compatible with the level of performance required by: Test Methods F1450, F1592, and F1643.
1.3 These test methods apply to walls enclosing or separating secure areas of detention/correctional facilities.
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The SI values given in parentheses are approximate and for information only.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: F2322 − 12 (Reapproved 2019)
Standard Test Methods for
Physical Assault on Vertical Fixed Barriers for Detention
and Correctional Facilities
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F2322; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
1.1 These test methods cover requirements for simulated 2.1 ASTM Standards:
service tests and testing equipment for determining the perfor- F1450 Test Methods for Hollow Metal Swinging Door
mance characteristics of walls designed to incarcerate inmates Assemblies for Detention and Correctional Facilities
in detention and correctional institutions. The testing equip- F1592 Test Methods for Detention Hollow Metal Vision
ment provides for the setup and testing of two sample fixed Systems
barriers side-by-side, one with no openings and one equipped F1643 Test Methods for Detention Sliding Door Locking
with a representative penetration in accordance with the Device Assembly
American Correctional Association (ACA) standard for clear F1915 Test Methods for Glazing for Detention Facilities
2 2
view area of 3 ft (0.279 m ), 12 in. (305 mm) wide by 36 in.
2.2 UL Standard:
(914 mm) high. UL-752 Bullet Resisting Equipment
2.3 ANSI Standard:
1.2 It is the intent of these test methods to help ensure that
ANSI/HMMA863 Guide Specifications for Detention Secu-
detention security walls perform at or above minimum accept-
rity Hollow Metal Doors and Frames
able levels to control passage of unauthorized or secure areas,
to confine inmates, to delay and frustrate escape attempts, and
3. Terminology
to resist vandalism. It is recognized that in order to meet the
3.1 Definitions:
intent of these test methods, opening assemblies within these
3.1.1 detention security—assurance of the restriction of
walls must be compatible with the level of performance
mobility of inmates to designated areas within a correctional or
required by: Test Methods F1450, F1592, and F1643.
detention facility.
1.3 These test methods apply to walls enclosing or separat-
3.1.2 forcible egress—an opening created in the test wall
ing secure areas of detention/correctional facilities.
which allows a 5 in. (127 mm) by 8 in. (203 mm) by 8 in. (203
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
mm)rigidrectangularboxtobepassedthroughitwithnomore
as the standard. The SI values given in parentheses are
than 10 lbf (44.5 N) of force.
approximate and for information only.
3.1.3 manufacturer—the party responsible for the
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
construction, fabrication, or supply of the test samples or
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
components used to construct the test samples.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.1.4 performance characteristic—the response of the wall
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
in any one of the tests described herein.
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accor- 3.1.5 test completion—conduct one test sequence for each
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard- wall.
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
3.1.6 testing laboratory—an independent third party mate-
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
rials testing laboratory.
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
These test methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F33 on Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Detention and Correctional Facilities and are the direct responsibility of Subcom- the ASTM website.
mittee F33.02 on Physical Barriers. Available from Underwriters Laboratories (UL), Corporate Progress, 333
Current edition approved April 1, 2019. Published April 2019. Originally Pfingsten Rd., Northbrook, IL 60062.
approved in 2003. Last previous edition approved in 2012 as F2322 – 12. DOI: Available fromAmerican National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
10.1520/F2322-12R19. 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
F2322 − 12 (2019)
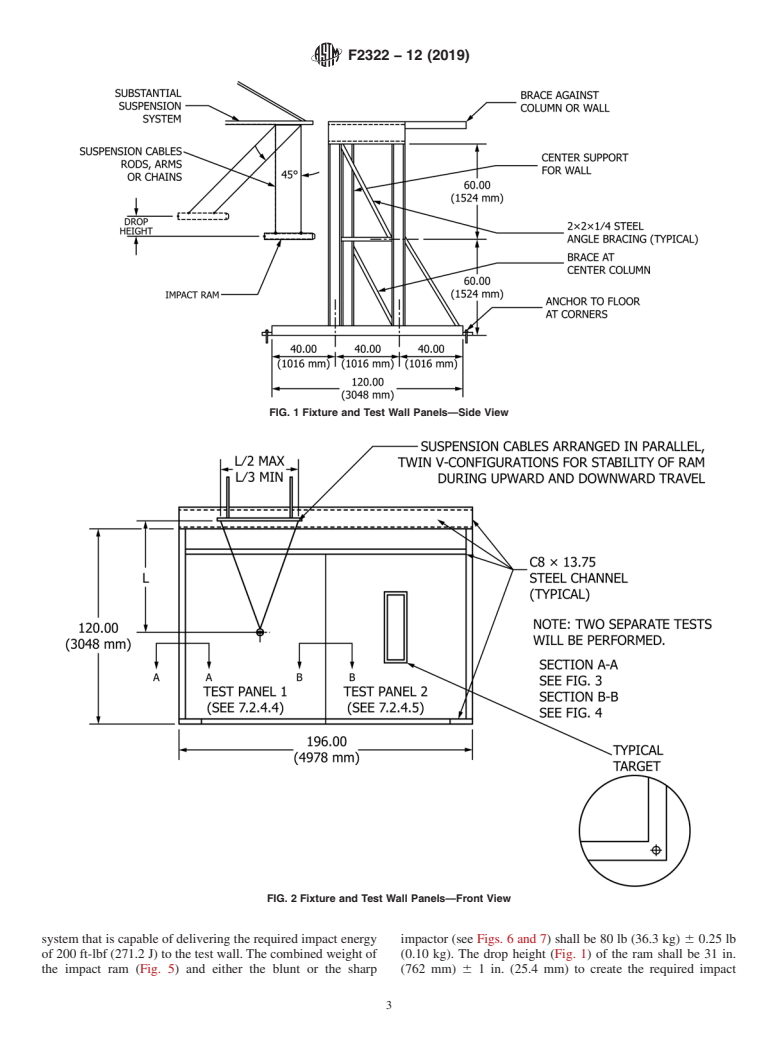
4. Significance and Use 6.2.1 The test wall support fixture shall simulate the rigidity
normally provided to a wall in a building by the ceiling, floor,
4.1 A major concern for administrative officials is the
and adjoining walls (Figs. 1-4). The inclusion of load bearing
security of barriers used in detention/correctional facilities.
conditions on the test wall is at the manufacturers’ option.
These test methods are designed to aid in identifying levels of
6.2.2 The fixture is designed to accommodate two test
physical security for walls which enclose or separate secure
samples; however, it is permissible to construct a test fixture
areas. This does not apply to the passage of contraband.
that accommodates one sample only, if the manufacturer so
4.2 These test methods are not intended to provide a
chooses.
measure of resistance for a wall subjected to attack by
6.2.3 Description of the Test Wall—The test wall shall be
corrosive agents, by high-powered rifles, explosives, sawing,
constructedandmountedinaverticalwalltestfixtureandshall
or other such methods. These test methods are intended to
be supported as described in 6.2.1 throughout the testing
evaluate the resistance of a wall to violent attacks by sustained
procedure. The wall specification shall be included as part of
manpower using battering devices, such as benches, bunks, or
the test report.
tables, and by handguns up to and including .44 magnum.
6.3 Wall Construction or Mounting for Impact Testing:
Attacks from the outside and fire resistance ratings are not
6.3.1 Construct or install the test walls as shown in Figs.
addressed in this standard.
1-4. Position the impact test ram on the outside of the fixture in
4.3 The primary purpose or result of these test methods is to
preparationtoadministertheseriesofimpactsdescribedin7.2.
approximate the levels of abuse to which walls will potentially
be subjected in the field. The desired result of its use is to help
7. Procedures
provide assurance of protection to the public, to facility
7.1 Bullet Penetration:
administrative personnel, and to the inmates themselves.
7.1.1 Scope—This test is designed to evaluate the capability
4.4 It is recommended that detention/correctional facility
of a test wall to resist the ballistic attack of a .44 magnum
administration provide adequate training, supervision, and
(Level 3) handgun.
preventative maintenance programs to enable walls to function
7.1.2 Significance and Use—This test is intended to simu-
as intended throughout the expected service life.
late a field situation whereby one or more firearms are being
used to attack a fixed barrier. The handgun is considered the
5. Sampling
most reasonably attainable firearm and the calibre, .44
magnum, is considered to be the most powerful that will
5.1 Samplewallshallbeconstructedinaccordancewith6.1.
potentially be reasonably attainable during a mass disturbance
5.2 Test reports shall include complete details of the test
or riot within a detention or correctional facility.
samples, details, photographs, or a combination thereof, of the
7.1.3 When specified by the contract documents of a
testing apparatus and installation or construction instructions
detention/correctional facility project, the wall samples for
(see Section 9).
bullet penetration shall be tested in accordance with Standard
5.3 Intheevent of failure in one or more of the performance
UL-752.Arepresentativesamplebaseduponthewallconstruc-
tests, the manufacturer shall provide another complete test
tion under investigation shall be tested. Minimum size shall be
sampleorshallcontinuetestinginanotherlocationonthewall,
3 ft, 0 in. (914 mm) by 3 ft, 0 in. (914 mm).
subject to the direction of the testing laboratory.
7.1.4 The level of performance shall meet the rating .44
magnum, Level 3.
6. Specimen Preparation
7.1.5 The pass/fail criteria shall be in accordance with
Standard UL-752.
6.1 Construction:
6.1.1 The construction of the test wall shall be representa-
7.2 Wall System Impact Test:
tive of the wall as it will be placed in service.
7.2.1 Scope—This test method is designed to evaluate the
6.1.2 Required results indicated in Table 1 are based upon a
capability of a complete test wall to resist repetitive impact
sample size of 8 ft (2438 mm) high by 8 ft (2438 mm) wide 6
forces at the designated critical areas.
4 in. (102 mm).
7.2.2 Significance and Use:
7.2.2.1 This test method is intended to closely simulate a
6.2 Impact Test Fixture:
sustained battering ram style attack and provide an evaluation
ofthecapabilityoftheassemblytoprevent,delay,andfrustrate
escape or access, or both, to unauthorized areas. The test shall
TABLE 1 Security Grades and Impact Load Requirements
be permitted to be used to aid in identifying a level of physical
Representative Barrier
Grade Number of security for various configurations of walls.
Duration Time
A
No. Impacts
7.2.2.2 An impact test of this design performed on a
(see X4.1)
completetestwallevaluatestheimpactfatiguestrengthandthe
1 600 60 min.
2 400 40 min.
qualityofconstructionandfabricationtechniquesaswellasthe
3 200 20 min.
strengths of materials used.
4 100 10 min.
7.2.3 Apparatus:
A
Number of impacts equally divided between blunt impactor (first sequence) and
7.2.3.1 The steel impact ram shall be equipped to be
sharp impactor, applied in cyclic sequences of 50 impacts each.
incorporated into a hinged or pivoted swinging pendulum
F2322 − 12 (2019)
FIG. 1 Fixture and Test Wall Panels—Side View
FIG. 2 Fixture and Test Wall Panels—Front View
system that is capable of delivering the required impact energy impactor (see Figs. 6 and 7) shall be 80 lb (36.3 kg) 6 0.25 lb
of 200 ft-lbf (271.2 J) to the test wall. The combined weight of (0.10 kg). The drop height (Fig. 1) of the ram shall be 31 in.
the impact ram (Fig. 5) and either the blunt or the sharp (762 mm) 6 1 in. (25.4 mm) to create the required impact
F2322 − 12 (2019)
FIG. 3 Section A-A from Fig. 2
FIG. 4 Section B-B from Fig. 2
energy at the bottom of the arc and at the point of contact with must be in good repair and well lubricated to minimize friction
the test wall. The angle of the suspension cables, rods, arm or
losses that could reduce the impact energy being delivered to
chains shall be no greater than 45° off vertical when the ram is
the test sample.
in the raised position.All pivot points in the suspension system
F2322 − 12 (2019)
NOTE 1—To prevent shifting during test procedures, any material added inside or outside the ram to satisfy the weight requirement shall be rigidly
attached.
FIG. 5 Steel Impact Ram
FIG. 6 Large Blunt Impactor
7.2.3.2 Large Blunt Impactor—The large blunt impactor techniques suitable to the wall construction and consistent with
shall be fabricated from C1010-C1020 carbon steel and shall ANSI/HMMA-863.Theclearopeningsizeshallbe:12in.(305
be attachable to the steel impact ram in accordance with Fig. 6. mm) wide by 36 in. (914 mm) high.
The striking surface of the impactor shall have a surface area 7.2.4.4 Apply the required number of impacts in accordance
2 2
of 4 6 0.04 in. (101.6 6 1.02 mm ) and shall have rounded with Table 1 to the test panel #1. If there are no predicted weak
edges similar to a 10 lb (4.54 kg) sledgehammer head. points in the solid panel, apply the impacts to a target area to
7.2.3.3 Sharp Impactor—The sharp impactor shall be fabri- be selected by the test agent at the time of the test. If there are
cated from C1010-C1020 carbon steel and shall be attachable predicted weak points such as seams, unsupported edges, or
to the steel impact ram in accordance with Fig. 7. The other types of wall joints, apply the impacts at one of those
sharpness of the impact point shall be similar to the end of a locations. Repeatability of impact location during each series
new Fireman’s axe at the beginning of the test sequence. shall be 62 in. (50 mm) horizontally and vertically from the
7.2.4 Procedure: designated impact target. Using the test apparatus in accor-
7.2.4.1 With the test fixture and test apparatus, deliver the dance with 7.2.3, begin the series of strikes against the selected
series of impacts listed in Table 1 to the test wall. target area of the test wall for the number of required impacts,
7.2.4.2 Construct or mount two 8 ft (2438 mm) high by 8 ft first with the blunt impactor followed by the sharp impactor on
(2438 mm) 6 4 in. (102 mm) wide test wall panels supported the pendulum in cyclic sequences of 50 impacts each. The
on all four sides in each half of the wall test fixture illustrated required impact energy for the blunt impactor is 200 ft-lbf
in Fig. 2. If the wall design requires control joints or seams, (271.2 J) per impact and the required impact energy for the
one will be included in the test wall for the purpose of testing. sharp impactor is 100 ft-lbf (135.6 J) per impact. During the
7.2.4.3 Construct one of the wall panels with no openings test, reposition the pendulum as necessary to produce the
and the other wall panel with a monolithic steel impact panel, maximum possible duress on the test wall, leading to wall
acting as a simulated window, installed using anchoring failure. The time for repositioning and change of impact heads
F2322 − 12 (2019)
FIG. 7 Sharp Impactor
is not to be included in the test duration time. Record the 8. Certification
number of strikes required to produce the first penetration of
8.1 The manufacturer shall provide test reports by an
the panel, and the number of strikes required to produce an
independent testing laboratory which certify that the test walls
opening large enough to achieve forcible egress.
were successfully tested in accordance with these test methods
7.2.4.5 App
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.