ASTM D5575-18(2023)
(Classification)Standard Classification System for Copolymers of Vinylidene Fluoride (VDF) with Other Fluorinated Monomers
Standard Classification System for Copolymers of Vinylidene Fluoride (VDF) with Other Fluorinated Monomers
ABSTRACT
This classification system covers both developing property designations and specifications for thermoplastic compositions consisting of vinylidene fluoride (VDF) polymers modified with other fluoromonomers and property-enhancing additives. Four property codes are presented: code 1 - melt temperature, code 2 - melt-flow rate or melt viscosity, or both, code 3 - tensile strength and modulus, and code 5 - density. The melt temperatures, melt-flow rate, melt viscosity, tensile properties, specific gravity, volume resistivity, dielectric constant, dissipation factor, and limiting oxygen index shall be tested to meet the requirements prescribed.
SCOPE
1.1 This classification system covers both developing property designations and specifications for thermoplastic compositions consisting of vinylidene fluoride (VDF) polymers modified with other fluoromonomers and property-enhancing additives. The other fluoromonomers include one or more of the following: hexafluoropropylene (HFP), tetrafluoroethylene (TFE), and chlorotrifluoroethylene (CTFE). The additives are those that improve its flame resistance, processing, or physical properties. However, these additives are not normally considered to be reinforcing. This classification system covers thermoplastic compositions supplied in pellet or powder forms.
1.2 A designation or specification applies only to the virgin polymers prepared from vinylidene fluoride (>50 weight %) with one or more of the following comonomers: hexafluoropropylene, tetrafluoroethylene, and chlorotrifluoroethylene. Some polymers contain additives to enhance certain properties.
1.3 This system constitutes a line callout as a means of designating and specifying properties of VDF-based copolymers. At least four of the designated properties are used to define a polymer's specification. Specification criteria from international documents can be used if their criteria match designation properties currently used by this classification system.2 This classification system is not intended for the selection of materials.
1.4 The manufacturer of the virgin resin shall establish the designation of a resin based on the property value criteria in this classification system.
1.5 The minimum specification properties are established by this classification system. Additional specification properties, based on the designation properties cited, can be established by the resin supplier and customer.
1.6 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard.
1.7 The property tests are intended to provide information for specifications of modified VDF-copolymer compositions. It is not the purpose of this classification system to provide engineering data for design purposes.
Note 1: Although the values listed in Table 1, Table 2, Table 3, Table 4, and Table 5 are necessary to include the range of properties available in existing materials, they are not to be interpreted as implying that every possible combination of the properties exists or can be obtained. It is possible for a user or designer, using Tables 1-5, to call out property relationships that are physically impossible to occur in a copolymer made using current technology.
Position 5
Position 6
Position 7
Position 8
Code
Specific Gravity,
g/cm3
Code
Electrical a-c
Dielectric Constant
Loss
d-c Electric Volume
Code
Limiting Oxygen
Index
Code
Specimen Type
a
a
>10E3
a
a
D638 Type I
b
1.6 to
b
10E3 to 10E12
b
40 to
b
D638 Type II
c
1.7 to
c
>10E12
c
50 to
c
D638 Type III
d
1.8 to
d
d
60 to
d
D638 Type IV
e
1.9 to
e
e
70 to
e
ISO 527 Type 1A
f
2.0 to
f
f
80 to
f
ISO 527 Type 1B
g
2.1 to
g
g
>90
g
ISO 527 Typ...
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D5575 − 18 (Reapproved 2023)
Standard Classification System for
Copolymers of Vinylidene Fluoride (VDF) with Other
Fluorinated Monomers
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5575; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* 1.5 The minimum specification properties are established by
this classification system. Additional specification properties,
1.1 This classification system covers both developing prop-
based on the designation properties cited, can be established by
erty designations and specifications for thermoplastic compo-
the resin supplier and customer.
sitions consisting of vinylidene fluoride (VDF) polymers
1.6 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
modified with other fluoromonomers and property-enhancing
standard.
additives. The other fluoromonomers include one or more of
the following: hexafluoropropylene (HFP), tetrafluoroethylene
1.7 The property tests are intended to provide information
(TFE), and chlorotrifluoroethylene (CTFE). The additives are
for specifications of modified VDF-copolymer compositions. It
those that improve its flame resistance, processing, or physical
is not the purpose of this classification system to provide
properties. However, these additives are not normally consid-
engineering data for design purposes.
ered to be reinforcing. This classification system covers ther-
NOTE 1—Although the values listed in Table 1, Table 2, Table 3, Table
moplastic compositions supplied in pellet or powder forms.
4, and Table 5 are necessary to include the range of properties available in
existing materials, they are not to be interpreted as implying that every
1.2 A designation or specification applies only to the virgin
possible combination of the properties exists or can be obtained. It is
polymers prepared from vinylidene fluoride (>50 weight %)
possible for a user or designer, using Tables 1-5, to call out property
with one or more of the following comonomers:
relationships that are physically impossible to occur in a copolymer made
hexafluoropropylene, tetrafluoroethylene, and chlorotrifluoro-
using current technology.
NOTE 2—Many of these polymers exhibit polymorphism. The type and
ethylene. Some polymers contain additives to enhance certain
extent of crystalline structure will vary with the thermomechanical history
properties.
of the sample. Properties vary based on the technique used to prepare the
specimens.
1.3 This system constitutes a line callout as a means of
designating and specifying properties of VDF-based copoly-
1.8 Test methods used in this classification system can result
mers. At least four of the designated properties are used to
in the incidental production of hazardous materials. Modified
define a polymer’s specification. Specification criteria from
VDF polymer fluoroplastics melt between 90 and 182°C (194
international documents can be used if their criteria match
and 359°F) and are thermally stable up to about 350°C (662°F),
designation properties currently used by this classification
or somewhat higher, depending on the composition.
system. This classification system is not intended for the
(Warning—Evolution of corrosive, colorless, and toxic hydro-
selection of materials.
gen fluoride can occur under certain conditions.)
1.9 This standard does not purport to address all of the
1.4 The manufacturer of the virgin resin shall establish the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
designation of a resin based on the property value criteria in
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
this classification system.
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
See Warning in 1.8 and Section 10 for specific hazards
This classification system is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D20 on
statements.
Plastics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.15 on Thermoplastic
Materials.
NOTE 3—Many, but not all of the codes and specifications found in this
Current edition approved March 15, 2023. Published March 2023. Originally
classification system are also in ISO 12086-1 and ISO 12086-2.
approved in 1994. Last previous edition approved in 2018 as D5575 - 18. DOI:
1.10 This international standard was developed in accor-
10.1520/D5575-18R23.
This standard is needed to cover commercial products outside the scope of
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
Specification D3222.
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Fluoropolymer property specification data from international standards can
include properties intentionally excluded from this classification system (for
example, composition). The only property criteria from other documents that can be Lovinger, A. J., “Poly(vinylidene fluoride),” Developments in Crystalline
used are those having similar properties allowed under the designation system. Polymers, Vol 1, Chapter 5, D.C. Bassett, Ed., Applied Science, London, 1982.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
D5575 − 18 (2023)
TABLE 1 Codes for the Information on Fluoropolymers Used in rable method is listed after each citation in parentheses.
Data Block 1
D150 Test Methods for AC Loss Characteristics and Permit-
Code Meaning tivity (Dielectric Constant) of Solid Electrical Insulation
A modified
D257 Test Methods for DC Resistance or Conductance of
B block copolymer
Insulating Materials
H homopolymer
K copolymer D618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
L graft polymer
D638 Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics
R random copolymer
D792 Test Methods for Density and Specific Gravity (Rela-
Z other
tive Density) of Plastics by Displacement
D883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
TABLE 2 Code-Letters Used in Data Block 2 (Intended D1238 Test Method for Melt Flow Rates of Thermoplastics
Application or Method of Processing, Essential Properties,
by Extrusion Plastometer
Additives, or Other Information
D1600 Terminology for Abbreviated Terms Relating to Plas-
Code Position 1 Code Positions 2 to 8
tics
A adhesives C colored
D2863 Test Method for Measuring the Minimum Oxygen
B blow molding D powder
Concentration to Support Candle-Like Combustion of
B1 extrusion blow molding D2 free-flowing
B2 injection blow molding D3 not free-flowing
Plastics (Oxygen Index)
C calendaring E expandable
D3222 Specification for Unmodified Poly(Vinylidene Fluo-
E extrusion F special burning characteristics
G general use F1 nonflammable ride) (PVDF) Molding Extrusion and Coating Materials
H coating F2 flame retarded
D3418 Test Method for Transition Temperatures and Enthal-
H1 powder coating F4 reduced smoke emission
pies of Fusion and Crystallization of Polymers by Differ-
H2 dip coating G granules
K cable and wire coating G1 pellets ential Scanning Calorimetry
L monofilament extrusion L light and weather stabilized
D3835 Test Method for Determination of Properties of
M molding (injection/transfer) M nucleated
Polymeric Materials by Means of a Capillary Rheometer
Q compression molding N natural (no color added)
R rotational molding N1 suitable for food contact
D3892 Practice for Packaging/Packing of Plastics
V thermoforming N2 high purity
D4591 Test Method for Determining Temperatures and
X no indication P impact modified
Heats of Transitions of Fluoropolymers by Differential
Y textile yarns, spinning R mold release agent
Z other S lubricated Scanning Calorimetry
T transparent
D4703 Practice for Compression Molding Thermoplastic
T1 translucent
Materials into Test Specimens, Plaques, or Sheets
T2 opaque
W1 improved chemical resistance
D5740 Guide for Writing Material Standards in the Classi-
Y increased electrical conductivity
fication Format
Z antistatic
IEEE/ASTM S1–10 Standard for Use of the International
System of Units (SI)
TABLE 3 Designatory and Specification Properties for Data Block
2.2 IEC and ISO Standards:
IEC 60093 Recommended Methods of Test for Volume and
A
Position Number Property
Surface Resistivities of Electrical Insulating Materials
B
1 melt temperature
B IEC 60250 Recommended Methods for the Determination of
2 melt flow rate/melt viscosity
B
3 tensile strength and modulus
the Permittivity and Dielectric Dissipation Factor of
4 tensile elongation
Electrical Insulating Materials at Power, Audio and Radio
B
5 density
Frequencies Including Metre Wavelengths
6 electrical
7 flammability by oxygen index (OI)
ISO 291 Plastics—Standard Atmospheres for Conditioning
8 specimen preparation method and type
and Testing (Practice D618)
A
Property test information for Positions 1 to 7 are given in Section 8.
ISO 293 Plastics—Compression Molding Test Specimens of
B
Positions 1, 2, 3, and 5 are mandated as the minimum specification properties.
Thermoplastic Materials (Practice 4703)
ISO 472 Plastics—Vocabulary (Terminology D883)
ISO 527/1,2,3 Plastics—Determination of Tensile Properties
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
(Test Method D638)
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
ISO 1043/1 Plastics—Symbols—Part 1: Symbols for Basic
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Polymers and Their Special Characteristics (Terminology
D883)
2. Referenced Documents
ISO 1043/2 Plastics—Symbols—Part 2: Fillers and Rein-
2.1 ASTM Standards:
forcing Materials (Terminology D883)
NOTE 4—For ASTM and ISO documents, the equivalent or a compa-
ISO 1133 Plastics—Determination of the Melt Mass-Flow
Rate (MFR) and the Melt Volume-Flow Rate (MVR) of
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from American National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
the ASTM website. 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
D5575 − 18 (2023)
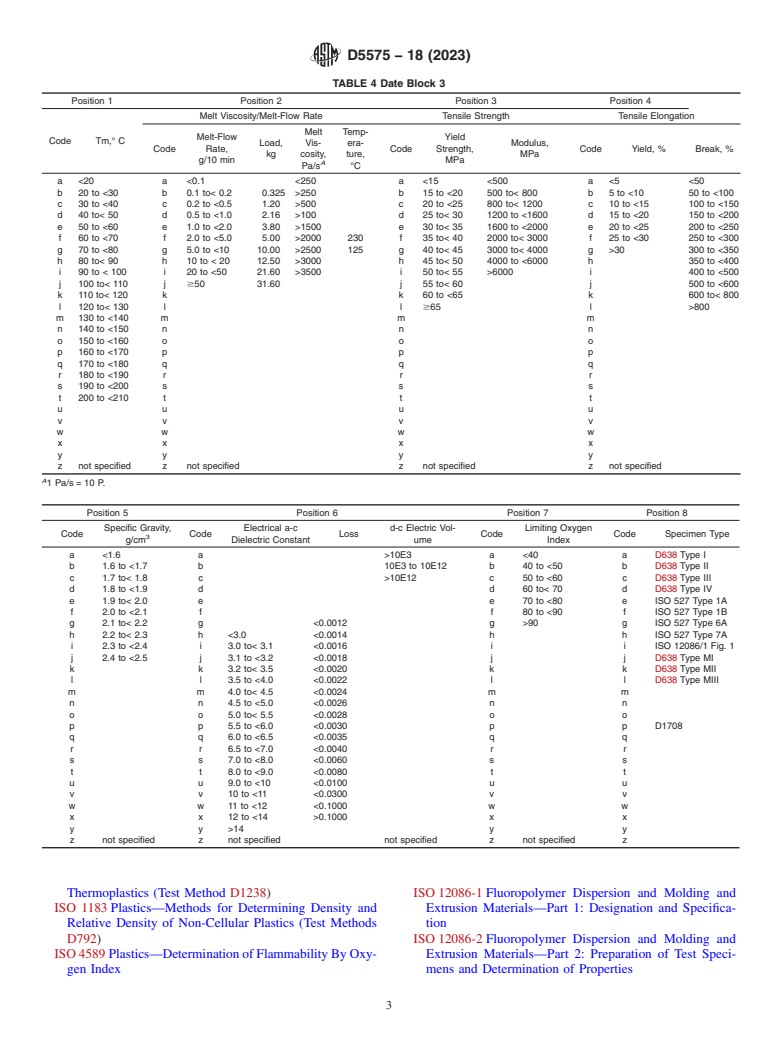
TABLE 4 Date Block 3
Position 1 Position 2 Position 3 Position 4
Melt Viscosity/Melt-Flow Rate Tensile Strength Tensile Elongation
Melt Temp-
Melt-Flow Yield
Code Tm,° C
Load, Vis- era- Modulus,
Code Rate, Code Strength, Code Yield, % Break, %
kg cosity, ture, MPa
g/10 min MPa
A
Pa/s °C
a <20 a <0.1 <250 a <15 <500 a <5 <50
b 20 to <30 b 0.1 to< 0.2 0.325 >250 b 15 to <20 500 to< 800 b 5 to <10 50 to <100
c 30 to <40 c 0.2 to <0.5 1.20 >500 c 20 to <25 800 to< 1200 c 10 to <15 100 to <150
d 40 to< 50 d 0.5 to <1.0 2.16 >100 d 25 to< 30 1200 to <1600 d 15 to <20 150 to <200
e 50 to <60 e 1.0 to <2.0 3.80 >1500 e 30 to< 35 1600 to <2000 e 20 to <25 200 to <250
f 60 to <70 f 2.0 to <5.0 5.00 >2000 230 f 35 to< 40 2000 to< 3000 f 25 to <30 250 to <300
g 70 to <80 g 5.0 to <10 10.00 >2500 125 g 40 to< 45 3000 to< 4000 g >30 300 to <350
h 80 to< 90 h 10 to < 20 12.50 >3000 h 45 to< 50 4000 to <6000 h 350 to <400
i 90 to < 100 i 20 to <50 21.60 >3500 i 50 to< 55 >6000 i 400 to <500
j 100 to< 110 j $50 31.60 j 55 to< 60 j 500 to <600
k 110 to< 120 k k 60 to <65 k 600 to< 800
l 120 to< 130 l l $65 l >800
m 130 to <140 m m m
n 140 to <150 n n n
o 150 to <160 o o o
p 160 to <170 p p p
q 170 to <180 q q q
r 180 to <190 r r r
s 190 to <200 s s s
t 200 to <210 t t t
u u u u
v v v v
w w w w
x x x x
y y y y
z not specified z not specified z not specified z not specified
A
1 Pa/s = 10 P.
Position 5 Position 6 Position 7 Position 8
Specific Gravity, Electrical a-c d-c Electric Vol- Limiting Oxygen
Code Code Loss Code Code Specimen Type
g/cm Dielectric Constant ume Index
a <1.6 a >10E3 a <40 a D638 Type I
b 1.6 to <1.7 b 10E3 to 10E12 b 40 to <50 b D638 Type II
c 1.7 to< 1.8 c >10E12 c 50 to <60 c D638 Type III
d 1.8 to <1.9 d d 60 to< 70 d D638 Type IV
e 1.9 to< 2.0 e e 70 to <80 e ISO 527 Type 1A
f 2.0 to <2.1 f f 80 to <90 f ISO 527 Type 1B
g 2.1 to< 2.2 g <0.0012 g >90 g ISO 527 Type 6A
h 2.2 to< 2.3 h <3.0 <0.0014 h h ISO 527 Type 7A
i 2.3 to <2.4 i 3.0 to< 3.1 <0.0016 i i ISO 12086/1 Fig. 1
j 2.4 to <2.5 j 3.1 to <3.2 <0.0018 j j D638 Type MI
k k 3.2 to< 3.5 <0.0020 k k D638 Type MII
l l 3.5 to <4.0 <0.0022 l l D638 Type MIII
m m 4.0 to< 4.5 <0.0024 m m
n n 4.5 to <5.0 <0.0026 n n
o o 5.0 to< 5.5 <0.0028 o o
p p 5.5 to <6.0 <0.0030 p p D1708
q q 6.0 to <6.5 <0.0035 q q
r r 6.5 to <7.0 <0.0040 r r
s s 7.0 to <8.0 <0.0060 s s
t t 8.0 to <9.0 <0.0080 t t
u u 9.0 to <10 <0.0100 u u
v v 10 to <11 <0.0300 v v
w w 11 to <12 <0.1000 w w
x x 12 to <14 >0.1000 x x
y y >14 y y
z not specified z not specified not specified z not specified z
Thermoplastics (Test Method D1238) ISO 12086-1 Fluoropolymer Dispersion and Molding and
ISO 1183 Plastics—Methods for Determining Density and Extrusion Materials—Part 1: Designation and Specifica-
Relative Density of Non-Cellular Plastics (Test Methods tion
D792) ISO 12086-2 Fluoropolymer Dispersion and Molding and
ISO 4589 Plastics—Determination of Flammability By Oxy- Extrusion Materials—Part 2: Preparation of Test Speci-
gen Index mens and Determination of Properties
D5575 − 18 (2023)
TABLE 5 Codes for Filler and Physical Form of Materials for Use
3.3.4 HFP—hexafluoropropylene (1,1,2,3,3,3-hexaflu-
in Data Block 4
oropropylene).
Code Material Code Form/Structure
3.3.5 MFR—melt-flow rate.
B boron B beads, spheres, balls
C carbon C chips, cuttings
3.3.6 MV—melt viscosity.
CG graphite D powder
3.3.7 PVDF—poly(vinylidene fluoride).
E clay F fiber
G glass G ground
3.3.8 TFE—tetrafluoroethylene (1,1,2,2-tetrafluoro-
K calcium carbonate H whisker
M mineral, metal K knitted fabric ethylene). D1600
Ma aluminum oxide L layer
3.3.9 VDF—vinylidene fluoride (1,1,-difluoroethylene).
Mb bronze M mat (thick)
MC calcium fluoride N nonwoven (fabric)
3.3.10 VDF/CTFE—vinylidene fluoride/
Md molybdenum disulfide P paper
chlorotrifluoroethylene copolymer.
Me stainless steel S roving
P mica T scale, flake
3.3.11 VDF/HFP—vinylidene fluoride/hexafluoropro-
Q silica V cord
penecopolymer.
R aramid W veneer
S synthetic, organic X not specified
3.3.12 VDF/TFE—vinylidene fluoride/tetrafluoroethylene
T talcum Y yarn
copolymer.
X not specified Z others
Z none
3.3.13 VDF/TFE/HFP—vinylidene fluoride/
tetrafluoroethylene/hexafluoropropene copolymer.
4. Classification and Designation
3. Terminology
4.1 The classification and
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.