ASTM D1316-20
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Fineness of Grind of Printing Inks By the NPIRI Grindometer
Standard Test Method for Fineness of Grind of Printing Inks By the NPIRI Grindometer
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 Oversize particles in a printing ink may damage a printing plate, plug a cell, clog a nozzle and adversely affect the appearance of printed ink films. Fineness of grind measurements are useful for deciding when to stop the dispersion process and for determining if the test material meets specifications as agreed upon between the supplier and the customer.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method describes the procedure for determining the fineness of grind of printing inks using a NPIRI Grindometer. It evaluates the size of the largest particles in a finished dispersion but not average particle size or concentration of sizes.
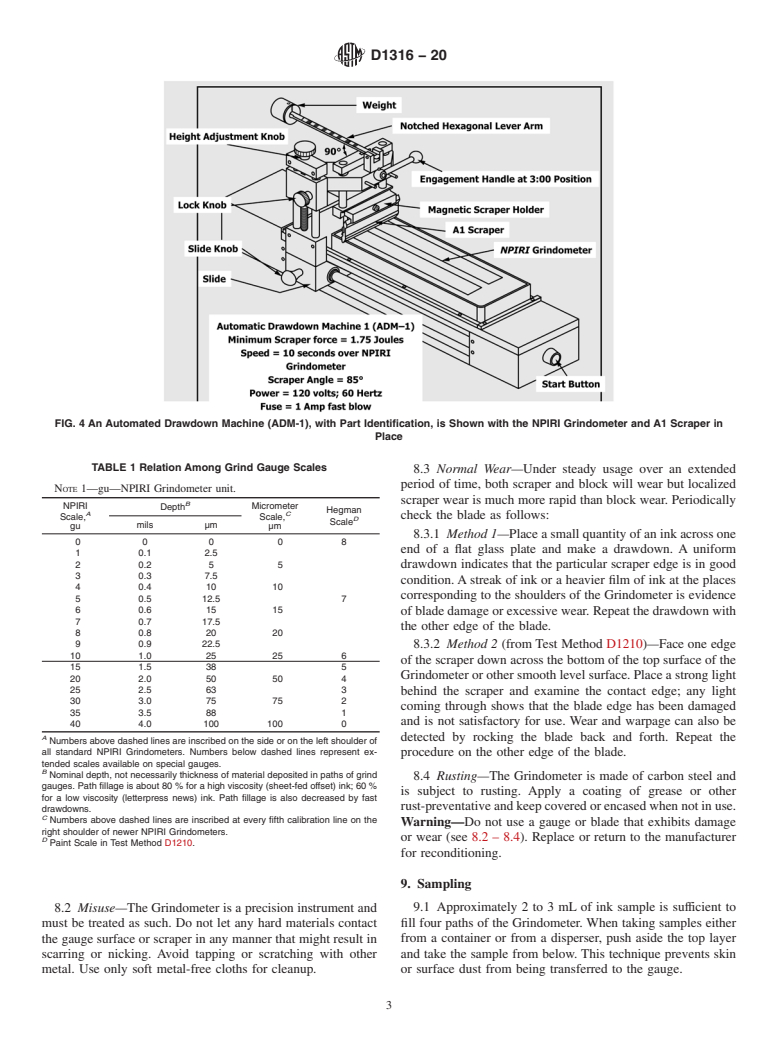
1.2 This test method covers both manual and automatic drawdowns using an A1 scraper.
1.3 This test method is applicable to any dispersion that is fine enough to fall within the 0 to 25 μm range of the specified grind gauge. With a minor variation in procedure, it is applicable to both paste (nonvolatile) and liquid (volatile) inks.
Note 1: The 0 to 25 μm gauge specified in this test method is similar in principle to the 0 to 100 μm Hegman gauge described in Test Method D1210 and the various gauges described in ISO 1524:2000. Sieve analysis for concentration of particles above 45 μm is covered in Test Method D2067.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation:D1316 −20
Standard Test Method for
Fineness of Grind of Printing Inks By the NPIRI
1
Grindometer
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D1316; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope D1210 Test Method for Fineness of Dispersion of Pigment-
Vehicle Systems by Hegman-Type Gage
1.1 This test method describes the procedure for determin-
D2067 Test Method for Coarse Particles in Printing Ink
ing the fineness of grind of printing inks using a NPIRI
Dispersions
Grindometer. It evaluates the size of the largest particles in a
D6846 Practice for Preparing Prints of Paste Printing Inks
finished dispersion but not average particle size or concentra-
with a Printing Gage
tion of sizes.
E177 Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in
1.2 This test method covers both manual and automatic
ASTM Test Methods
drawdowns using an A1 scraper.
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
1.3 This test method is applicable to any dispersion that is
3
fine enough to fall within the 0 to 25 µm range of the specified 2.2 ISO Standards:
ISO 1524:2000 Paints, varnishes and printing inks — Deter-
grind gauge. With a minor variation in procedure, it is
applicable to both paste (nonvolatile) and liquid (volatile) inks. mination of fineness of grind
NOTE 1—The 0 to 25 µm gauge specified in this test method is similar
3. Terminology
in principle to the 0 to 100 µm Hegman gauge described in Test Method
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
D1210andthevariousgaugesdescribedinISO1524:2000.Sieveanalysis
for concentration of particles above 45 µm is covered in Test Method
3.1.1 fineness of grind, n—a measure of the size and
D2067.
prevalence of oversize particles in a printing ink dispersion.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.1.2 NPIRI grind unit (gu), n—the distance equal to 2.5 µm
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
or 0.1 mils on a grind gauge.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.1.3 scratch, n—a depression at least 10 mm in length in
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
the surface of a grind gauge drawdown.
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
3.1.3.1 Discussion—A scratch develops when a particle (or
1.5 This international standard was developed in accor-
agglomerate) is trapped between the blade and the bottom of
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
the path and is drawn along by the blade.
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
3.1.4 speckle, n—protuberance of particles above the sur-
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
face of a grind gauge drawdown.
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
3.1.4.1 Discussion—Speckles occur at gauge depths greater
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
than those at which scratches occur and are caused by oversize
2. Referenced Documents
particles that are not hard enough or of the proper size to
2 produce scratches.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
4. Summary of Test Method
1 4.1 This test method utilizes a NPIRI Grindometer having
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D01 on Paint
and Related Coatings, Materials, andApplications and is the direct responsibility of
twoprecisionmachinedgrooveseach25.4mm(1in.)wideand
Subcommittee D01.56 on Printing Inks.
witha0to25µm(0to1 mil) taper.The test specimen is drawn
Current edition approved June 1, 2020. Published June 2020. Originally
down the paths slowly if a nonvolatile (paste) ink, briskly if a
approved in 1954. Last previous edition approved in 2011 as D1316 – 06 (2011)
volatile(liquid)ink.Thedrawdownsareexaminedforthescale
which was withdrawn January 2020 and reinstated in June 2020. DOI: 10.1520/
D1316-20.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
3
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Available from International Organization for Standardization (ISO), ISO
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Central Secretariat, BIBC II, Chemin de Blandonnet 8, CP 401, 1214 Vernier,
the ASTM website. Geneva, Switzerland, http://www.iso.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
------------
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.