ASTM F1056-18
(Specification)Standard Specification for Socket Fusion Tools for Use in Socket Fusion Joining Polyethylene Pipe or Tubing and Fittings
Standard Specification for Socket Fusion Tools for Use in Socket Fusion Joining Polyethylene Pipe or Tubing and Fittings
ABSTRACT
This specification covers socket fusion tools for use in making socket fusion joints between polyethylene pipe or tubing and fittings as specified by certain specifications. It covers newly manufactured heater faces and used heater faces which have been recoated. Heater faces may be manufactured from aluminum, steel, or other suitable heat conducting material. The manufacture of these socket fusion tools shall be in accordance with good commercial practice so as to produce socket fusion tools meeting the requirements specified. Heater faces shall have surfaces free of cracks, voids, foreign inclusions, or injurious defects.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers socket fusion tools for use in making socket fusion joints between polyethylene pipe or tubing and fittings as specified by Specifications D3035, D2513, and D2683. This specification covers newly manufactured heater faces and used heater faces which have been recoated. Requirements for materials, workmanship, and dimensions are included. Where applicable on this specification, “pipe” shall mean “pipe” and “tubing.”
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.3 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:F1056 −18 An American National Standard
Standard Specification for
Socket Fusion Tools for Use in Socket Fusion Joining
1
Polyethylene Pipe or Tubing and Fittings
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F1056; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* 3. Terminology
1.1 This specification covers socket fusion tools for use in 3.1 Definitions:
making socket fusion joints between polyethylene pipe or 3.1.1 General—Definitions are in accordance with Termi-
tubing and fittings as specified by Specifications D3035, nology F412 and abbreviations are in accordance with Termi-
D2513, and D2683. This specification covers newly manufac- nology D1600, unless otherwise specified.
tured heater faces and used heater faces which have been
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
recoated. Requirements for materials, workmanship, and di-
3.2.1 chamfer tool—a device that is used to chamfer the
mensions are included. Where applicable on this specification,
outside edge of the pipe. The chamfer allows the pipe end to
“pipe” shall mean “pipe” and “tubing.”
easily enter the pipe heater face and easily enter the heated
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded fitting. Chamfering is optional for all sizes but commonly done
1
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical for 1 ⁄4-in. IPS and larger sizes.
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
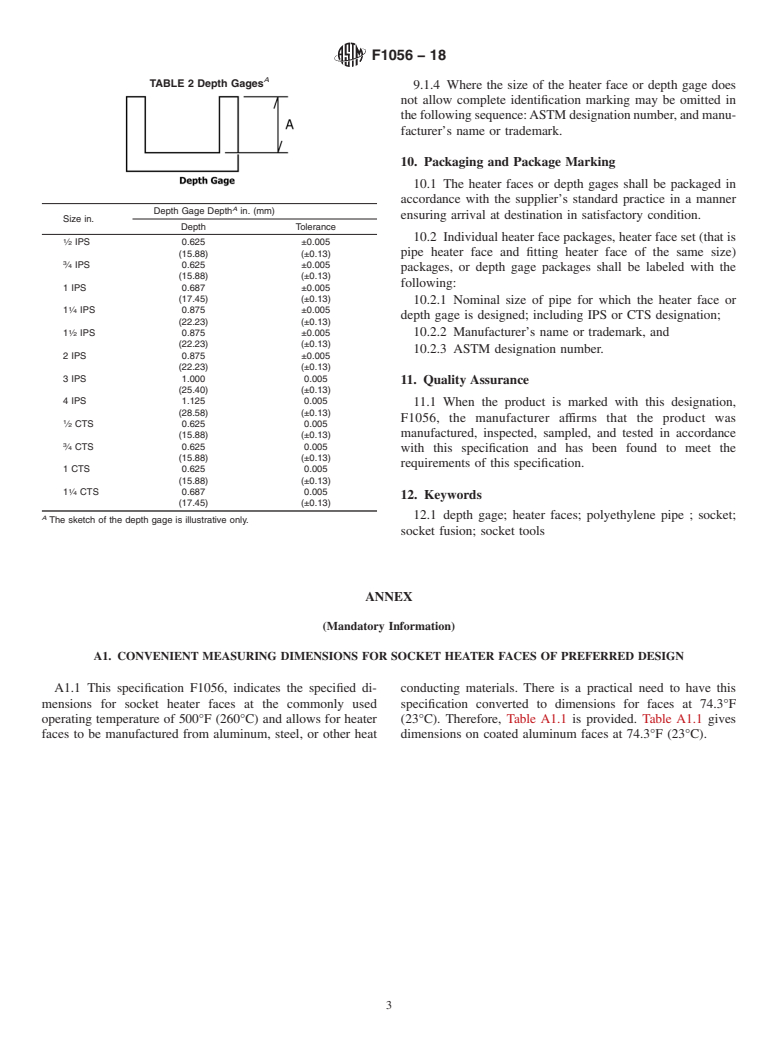
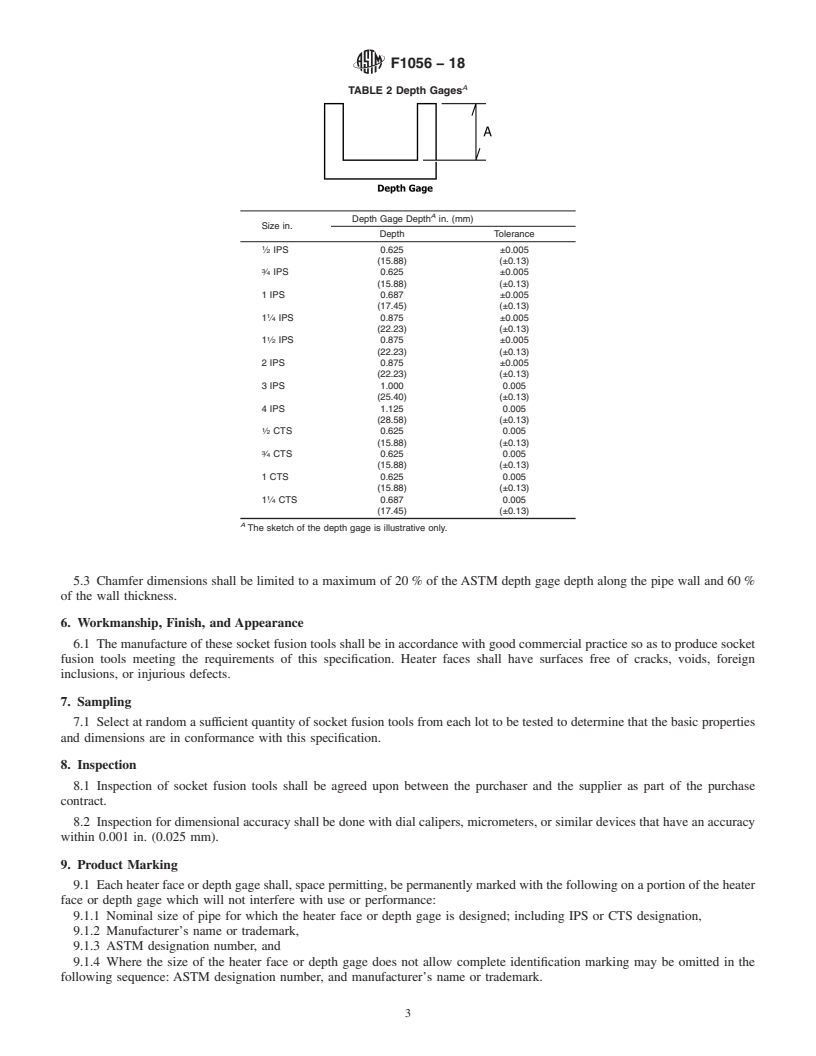
3.2.2 depth gage—a device that is used to locate the
and are not considered standard.
rounding clamp a prescribed distance from the end of the pipe.
1.3 This international standard was developed in accor-
3.2.3 heating tool—a device used to heat the heater faces.
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
3.2.4 fitting heater face or adapter—A block of heat con-
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
ducting material that attaches to the heating tool and is
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
dimensioned to melt the internal surface of the fitting socket.
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
3.2.5 pipe heater face or adapter— A block of heat con-
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
ducting material that attaches to the heating tool and is
dimensioned to melt the external surface of the pipe.
2. Referenced Documents
2
NOTE1—Thefittingheaterfaceandpipeheaterfacecanbeinoneblock
2.1 ASTM Standards:
of heat conducting material.
D1600 Terminology forAbbreviatedTerms Relating to Plas-
3.2.6 rounding clamp or cold ring—a device that is clamped
tics
aroundthepipetoroundthepipeandlimitthedistancethepipe
D2513 Specification for Polyethylene (PE) Gas Pressure
end goes into the pipe heater face and the socket fitting.
Pipe, Tubing, and Fittings
D2683 Specification for Socket-Type Polyethylene Fittings
4. Materials and Manufacture
for Outside Diameter-Controlled Polyethylene Pipe and
4.1 Heater faces may be manufactured from aluminum,
Tubing
steel, or other suitable heat conducting material.
D3035 SpecificationforPolyethylene(PE)PlasticPipe(DR-
PR) Based on Controlled Outside Diameter
NOTE 2—Polyethylene may stick to hot metal heating surfaces. This
F412 Terminology Relating to Plastic Piping Systems
sticking may be minimized by covering the heating surfaces with a
stick-resistant coating such as polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) or polyphe-
nylene sulfide (PPS). Copper or copper alloys are not suitable without
coating because some polyolefins react with copper.
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee F17 on Plastic
Piping Systems and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F17.20 on Joining.
5. Dimensions, Mass, and Permissible Variations
Current edition approved Feb. 1, 2018. Published March 2018. Originally
5.1 Heaterfacedimensionsandtolerancesshallbeasshown
approved in 1987. Last previous edition approved in 2011 as F1056 – 04(2011).
DOI: 10.1520/F1056-18.
in Table 1.The dimensions in Table 1 are for heater faces at the
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
commonly used operating temperature of 500°F (260°C).
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Annex A1 contains Table A1.1 which gives dimensions to
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. measure for coated aluminum faces at 73.4°F (23°C).
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: F1056 − 04 (Reapproved 2011) F1056 − 18 An American National Standard
Standard Specification for
Socket Fusion Tools for Use in Socket Fusion Joining
1
Polyethylene Pipe or Tubing and Fittings
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F1056; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope Scope*
1.1 This specification covers socket fusion tools for use in making socket fusion joints between polyethylene pipe or tubing and
fittings as specified by Specifications D3035, D2513, D2447, and D2683. This specification covers newly manufactured heater
faces and used heater faces which have been recoated. Requirements for materials, workmanship, and dimensions are included.
Where applicable on this specification, “pipe” shall mean “pipe” and “tubing.”
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.3 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D1248 Specification for Polyethylene Plastics Extrusion Materials for Wire and Cable
D1600 Terminology for Abbreviated Terms Relating to Plastics
D2122 Test Method for Determining Dimensions of Thermoplastic Pipe and Fittings
3
D2447 Specification for Polyethylene (PE) Plastic Pipe, Schedules 40 and 80, Based on Outside Diameter (Withdrawn 2010)
D2513 Specification for Polyethylene (PE) Gas Pressure Pipe, Tubing, and Fittings
D2657 Practice for Heat Fusion Joining of Polyolefin Pipe and Fittings
D2683 Specification for Socket-Type Polyethylene Fittings for Outside Diameter-Controlled Polyethylene Pipe and Tubing
D3035 Specification for Polyethylene (PE) Plastic Pipe (DR-PR) Based on Controlled Outside Diameter
D3350 Specification for Polyethylene Plastics Pipe and Fittings Materials
F412 Terminology Relating to Plastic Piping Systems
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 General—Definitions are in accordance with Terminology F412 and abbreviations are in accordance with Terminology
D1600, unless otherwise specified.
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.2.1 chamfer tool—a device that is used to chamfer the outside edge of the pipe. The chamfer allows the pipe end to easily
1
enter the pipe heater face and easily enter the heated fitting. Chamfering is optional for all sizes but commonly done for 1 ⁄4-in.
IPS and larger sizes.
3.2.2 depth gage—a device that is used to locate the rounding clamp a prescribed distance from the end of the pipe.
3.2.3 heating tool—a device used to heat the heater faces.
3.2.4 fitting heater face or adapter—A block of heat conducting material that attaches to the heating tool and is dimensioned
to melt the internal surface of the fitting socket.
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F17 on Plastic Piping Systems and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F17.20 on Joining.
Current edition approved Feb. 1, 2011Feb. 1, 2018. Published March 2011March 2018. Originally approved in 1987. Last previous edition approved in 20042011 as
F1056 – 04.F1056 – 04(2011). DOI: 10.1520/F1056-04R11.10.1520/F1056-18.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F1056 − 18
3.2.5 pipe heater face or adapter— A block of heat conducting material that attaches to the heating tool and is dimensioned to
melt the external surface of the pipe.
NOTE 1—The fitting heater face and pipe heater face can be in one block of heat conducting material.
3.2.6 rounding clamp or cold ring—a device that is clamped around the pipe to r
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.