ASTM F429-01(2007)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Shock-Attenuation Characteristics of Protective Headgear for Football
Standard Test Method for Shock-Attenuation Characteristics of Protective Headgear for Football
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
Maximum acceleration and time duration data obtained by the specified procedures are intended to determine the shock attenuation characteristics of a headgear.
Note 1—These data can be used at a later date to assess the protection afforded to the head when blows are delivered to the helmet.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the shock-attenuation characteristics of protective headgear for football.
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
An American National Standard
Designation:F429–01 (Reapproved 2007)
Standard Test Method for
Shock-Attenuation Characteristics of Protective Headgear
for Football
ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationF429;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginal
adoptionor,inthecaseofrevision,theyearoflastrevision.Anumberinparenthesesindicatestheyearoflastreapproval.Asuperscript
epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the shock-
attenuation characteristics of protective headgear for football.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
F717 Specification for Football Helmets
2.2 SAE Document:
J221 JUN 80 Instrumentation for Impact Tests, Require-
ments for Channel Class 1000
2.3 ISO Standard:
ISO/DIS 6220 Headforms For Use in the Testing of Protec-
tive Helmets
3. Terminology
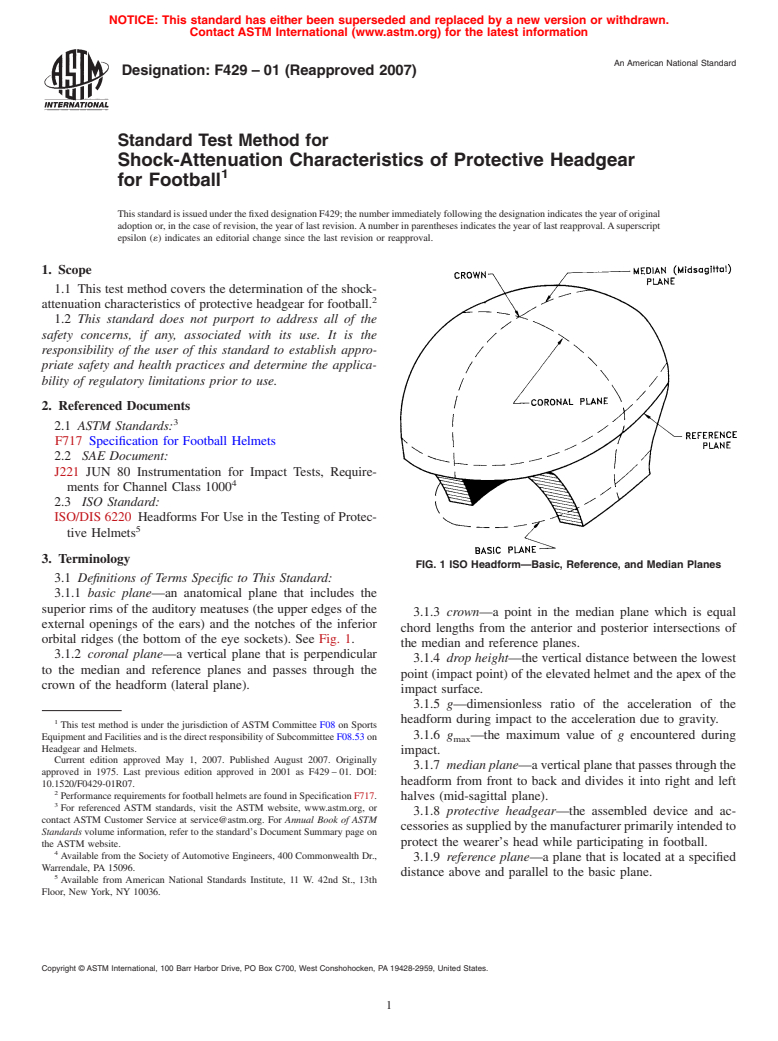
FIG. 1 ISO Headform—Basic, Reference, and Median Planes
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.1.1 basic plane—an anatomical plane that includes the
superior rims of the auditory meatuses (the upper edges of the
3.1.3 crown—a point in the median plane which is equal
external openings of the ears) and the notches of the inferior
chord lengths from the anterior and posterior intersections of
orbital ridges (the bottom of the eye sockets). See Fig. 1.
the median and reference planes.
3.1.2 coronal plane—a vertical plane that is perpendicular
3.1.4 drop height—the vertical distance between the lowest
to the median and reference planes and passes through the
point (impact point) of the elevated helmet and the apex of the
crown of the headform (lateral plane).
impact surface.
3.1.5 g—dimensionless ratio of the acceleration of the
1 headform during impact to the acceleration due to gravity.
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee F08 on Sports
3.1.6 g —the maximum value of g encountered during
EquipmentandFacilitiesandisthedirectresponsibilityofSubcommitteeF08.53on
max
Headgear and Helmets.
impact.
Current edition approved May 1, 2007. Published August 2007. Originally
3.1.7 median plane—averticalplanethatpassesthroughthe
approved in 1975. Last previous edition approved in 2001 as F429–01. DOI:
headform from front to back and divides it into right and left
10.1520/F0429-01R07.
PerformancerequirementsforfootballhelmetsarefoundinSpecificationF717. halves (mid-sagittal plane).
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
3.1.8 protective headgear—the assembled device and ac-
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
cessoriesassuppliedbythemanufacturerprimarilyintendedto
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
protect the wearer’s head while participating in football.
the ASTM website.
Available from the Society ofAutomotive Engineers, 400 Commonwealth Dr.,
3.1.9 reference plane—a plane that is located at a specified
Warrendale, PA 15096.
distance above and parallel to the basic plane.
Available from American National Standards Institute, 11 W. 42nd St., 13th
Floor, New York, NY 10036.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
F429–01 (2007)
slide on vertical guides. If wires are used they must be placed
under at least 190-lbf (845-N) tension (see 12.4 for guide
assembly specifications and allowable weight of drop assem-
bly).
6.2 Recording Equipment —The recording equipment shall
meet the following criteria:
6.2.1 Acceleration Transducer—The acceleration trans-
ducer is mounted at the center of gravity of the combined test
headformandcarriageassemblywiththesensitiveaxisaligned
to within 5° of the vertical when the helmet and headform are
in the impact position. The acceleration data channel complies
with SAE Recommended Practice J211 JUN 80 (a low pass
filter having a 4-pole Butterworth transfer function and a
corner frequency of 1650 Hz meets this requirement). Digital
filtering at 1650 Hz can be substituted.
6.2.2 System Accuracy—The impact recording system shall
be capable of measuring shocks of up to 500- g peak
acceleration with an accuracy of 65%.
6.2.3 Impact Recording—The impact shall be recorded on
single- or dual-trace storage oscilloscope with 0.1-mVto 20-V
deflectionfactor,1to5-mssweepspeed-division,and500-kHz
bandwidth.
6.2.4 Headforms—Standard headforms as described in 12.4
will be used for helmet impact testing.
6.2.5 Height Measuring Rod—A metal rod accurate to 6
0.10 in. (6 2.5 mm) shall be used for measuring drop heights.
6.2.6 Impact Surfaces—The impact surface for the instru-
ment system check (see Section 10) shall be a flat, Modular
NOTE—Rail-guided drop assemblies are also permissible.
Elastomer Programmer (MEP), 152 mm in diameter and 25
FIG. 2 Schematic of Typical Drop Assembly
mm in thickness. The MEP shall have a durometer of 60 6 2
Shore “A.” The MEP is mounted on an aluminum mounting
4. Summary of Test Method
platewithaminimumthicknessof0.220in.aftergrinding.The
MEP (including aluminum mounting plate) shall be firmly
4.1 Aheadgearismountedonaheadformthatisorientedin
affixed to the top surface of a flat metal anvil. The base shall
different positions and is dropped at a specific velocity onto an
consist of a rigid slab weighing at least 136 kg. For helmet
impactsurface.Alinearaccelerometermountedatthecenterof
impacts, the instrument system check MEP is replaced with a
gravity of the headform monitors the acceleration and the time
MEP 13 mm in thickness, 152 mm in diameter, and a
history of impact which are recorded with appropriate instru-
mentation. durometer of 38 6 5 Shore “A.”
6.2.7 Spherical Impactor — A device made of low reso-
5. Significance and Use
nance material, for example, magnesium, aluminum alloy or
5.1 Maximum acceleration and time duration data obtained
stainless steel, that couples mechanically with the ball arm
bythespecifiedproceduresareintendedtodeterminetheshock
connector of the drop assembly in place of the impact test
attenuation characteristics of a headgear.
headform. When mounted, the device presents a spherically
machinedimpactfacewitharadiusof2.875in.(73mm)onits
NOTE 1—These data can be used at a later date to assess the protection
bottom surface. All radii from the center of curvature of the
afforded to the head when blows are delivered to the helmet.
impact face to its outer edge shall form angles of no less than
6. Apparatus
40° with the downward vertical axis. The center of curvature
6.1 Guide Assembly —The headform shall be attached to
shall be within 5 mm of the vertical axis drawn through the
the free-fall drop assembly carriage by an adjustable mounting
centeroftheballarm.Themassofthedropassemblyincluding
which will allow impacts to be delivered to any prescribed
the impactor shall meet the same requirements as those
point on the helmet (see Fig. 2). The carriage shall be free to
specified for the drop assembly incorporated with the test
headforms (see section 12.4).
The sole source of supply of the apparatus known to the committee at this time
7. Sampling
is the Research & Testing Co., 1415 Park Ave., Hoboken, NJ 07030. If you are
aware of alternative suppliers, please provide this information to ASTM Interna-
7.1 Submit at least three specimen helmets, one for test
tional Headquarters.Your comments will receive careful consideration at a meeting
of the responsible technical committee, which you may attend. under the various conditions as described in Section 11.
F429–01 (2007)
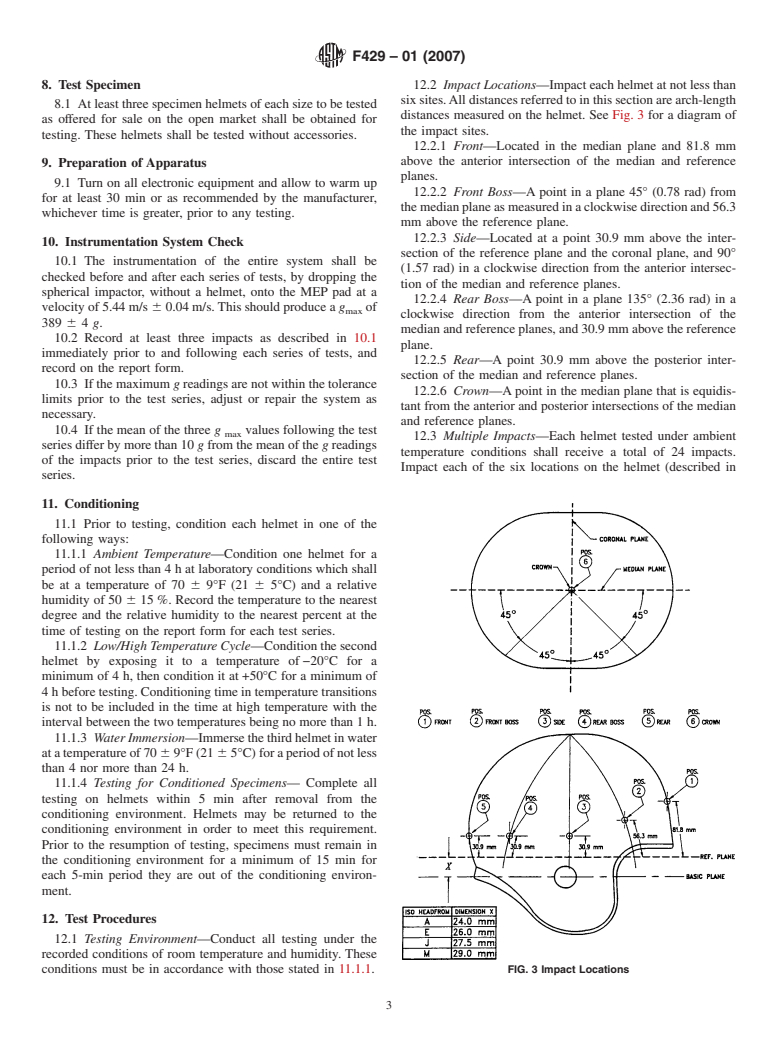
8. Test Specimen 12.2 Impact Locations—Impacteachhelmetatnotlessthan
sixsites.Alldistancesreferredtointhissectionarearch-length
8.1 Atleastthreespecimenhelmetsofeachsizetobetested
distances measured on the helmet. See Fig. 3 for a diagram of
as offered for sale on the open market shall be obtained for
the impact sites.
testing. These helmets shall be tested without accessories.
12.2.1 Front—Located in the median plan
...






Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.