ASTM F1642-12
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Glazing and Glazing Systems Subject to Airblast Loadings
Standard Test Method for Glazing and Glazing Systems Subject to Airblast Loadings
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This test method provides a structured procedure to establish the hazard rating of glazing and glazing systems subjected to an airblast loading. Knowing the hazard rating provides the ability to assess the risk of personal injury and facility damage.
5.2 The hazard rating for a glazing or glazing material does not imply that a single specimen will resist the specific airblast for which it is rated with a probability of 1.0. The probability that a single glazing or glazing construction specimen will resist the specific airblast for which it is rated increases proportionally with the number of test specimens that successfully resist the given level of airblast to the hazard level for which it is rated.
SCOPE
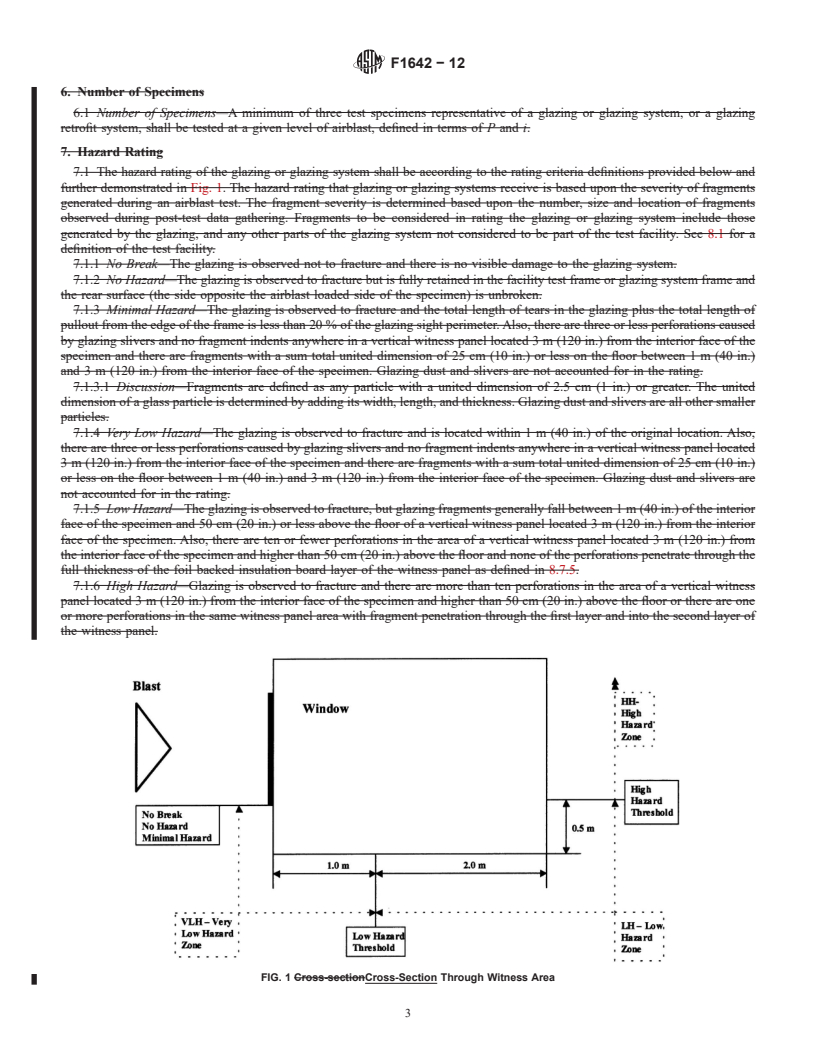
1.1 This test method sets forth procedures for the evaluation of hazards of glazing or glazing systems against airblast loadings. The specifying authority shall provide the airblast loading parameters.
1.2 The data obtained from testing under this method shall be used to determine the glazing or glazing system hazard rating using Specification F2912.
1.3 This test method allows for glazing to be tested and rated with or without framing systems.
1.4 This test method is designed to test and rate all glazing, glazing systems, and glazing retrofit systems including, but not limited to, those fabricated from glass, plastic, glass-clad plastics, laminated glass, glass/plastic glazing materials, and film-backed glass.
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. Values given in parentheses are for information only. For conversion of quantities in various systems of measurements to SI units, see E699.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. See Section 7 for specific hazards statements.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: F1642 − 12
Standard Test Method for
1
Glazing and Glazing Systems Subject to Airblast Loadings
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F1642; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
INTRODUCTION
Historical records show that fragments from glazing that has failed as the result of intentional or
accidental explosions present a serious threat of personal injury. Glazing failure also allows blast
pressure to enter the interior of buildings thus resulting in additional threat of personal injury and
facilitydamage.Theserisksincreaseindirectproportiontotheamountofglazingusedonthebuilding
facade. This test method addresses only glazing and glazing systems. It assumes that the designer has
verified that other structural elements have been adequately designed to resist the anticipated airblast
pressures.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
2
1.1 This test method sets forth procedures for the evaluation 2.1 ASTM Standards:
of hazards of glazing or glazing systems against airblast E699 Practice for Evaluation of Agencies Involved in
Testing, Quality Assurance, and Evaluating of Building
loadings. The specifying authority shall provide the airblast
loading parameters. Components
E997 Test Method for Evaluating Glass Breakage Probabil-
1.2 The data obtained from testing under this method shall
ity Under the Influence of Uniform Static Loads by Proof
be used to determine the glazing or glazing system hazard
Load Testing
rating using Specification F2912.
F2912 Specification for Glazing and Glazing Systems Sub-
1.3 This test method allows for glazing to be tested and
ject to Airblast Loadings
rated with or without framing systems.
2.2 ISO Standard:
1.4 This test method is designed to test and rate all glazing,
ISO/IEC International Standard 17025 General Require-
glazing systems, and glazing retrofit systems including, but not
ments for the Competence of Testing and Calibration
limited to, those fabricated from glass, plastic, glass-clad
Laboratories
plastics, laminated glass, glass/plastic glazing materials, and
2.3 ANSI Standard:
film-backed glass.
SI 10 American National Standard for Use of the Interna-
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the tional System of Units (SI): The Modern Metric System
standard. Values given in parentheses are for information only.
3. Terminology
For conversion of quantities in various systems of measure-
ments to SI units, see E699.
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 airblast pressure—the pressure increase that a sur-
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the face experiences due to the detonation of a high explosive
charge.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica- 3.1.1.1 Discussion—The airblast pressure history, as mea-
sured at a point on the surface, consists of two separate phases.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. See Section 7 for
specific hazards statements. The positive phase is characterized by a nearly instantaneous
rise to a maximum pressure followed by an exponential decay
to ambient pressure. In the negative phase, which follows
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee F12 on Security
Systems and Equipmentand is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F12.10 on
2
Systems Products and Services. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved Nov. 15, 2012. Published January 2013. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approved in 1995. Last previous edition approved in 2010 as F1642 – 04(2010). Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
DOI: 10.1520/F1642-12. the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F1642 − 12
immediately the positive phase, the pressure decreases below 6. Apparatus
ambient for a period of time before returning to ambient.
6.1 Test Facility—Test facilities shall be accredited for this
3.1.2 ambient temperature—24 6 11°C (75 6 20°F).
method to the requirements of ISO/IEC 17025 or qualified
according to Practice E699. The test facility shall consist of
3.1.3 blast mat—a steel or concrete pad upon which high
eitherashocktubeoranopen-airarenafromwhichtheairblast
explosive may be detonated to reduce the incidence of ejecta.
loading is generated.The test facili
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: F1642 − 04 (Reapproved 2010) F1642 − 12
Standard Test Method for
1
Glazing and Glazing Systems Subject to Airblast Loadings
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F1642; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
INTRODUCTION
Historical records show that fragments from glazing that has failed as the result of intentional or
accidental explosions present a serious threat of personal injury. Glazing failure also allows blast
pressure to enter the interior of buildings thus resulting in additional threat of personal injury and
facility damage. These risks increase in direct proportion to the amount of glazing used on the building
facade. This test method addresses only glazing and glazing systems. It assumes that the designer has
verified that other structural elements have been adequately designed to resist the anticipated airblast
pressures.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method sets forth procedures for the evaluation of hazards of glazing or glazing systems against airblast loadings.
The specifying authority shall provide the airblast loading parameters.
1.2 The data obtained from testing under this method shall be used to determine the glazing or glazing system hazard rating
using Specification F2912.
1.3 This test method allows for glazing to be tested and rated with or without framing systems.
1.4 This test method is designed to test and rate all glazing, glazing systems, and glazing retrofit systems including, but not
limited to, those fabricated from glass, plastic, glass-clad plastics, laminated glass, glass/plastic glazing materials, and film-backed
glass.
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. Values given in parentheses are for information only. For
conversion of quantities in various systems of measurements to SI units, see SI 10E699.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use. See Section 97 for specific hazards statements.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
E699 Practice for Evaluation of Agencies Involved in Testing, Quality Assurance, and Evaluating of Building Components
E997 Test Method for Structural Performance of Glass in Exterior Windows, Curtain Walls, and Doors Under the Influence of
Uniform Static Loads by Destructive Methods
SI 10F2912 American National Standard for Use of the International System of Units (SI): The Modern Metric SystemSpeci-
fication for Glazing and Glazing Systems Subject to Airblast Loadings
2.2 ISO Standard:
ISO/IEC International Standard 17025 General Requirements for the Competence of Testing and Calibration Laboratories
2.3 ANSI Standard:
SI 10 American National Standard for Use of the International System of Units (SI): The Modern Metric System
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F12 on Security Systems and Equipmentand is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F12.10 on
Systems Products and Services.
Current edition approved May 1, 2010Nov. 15, 2012. Published May 2010January 2013. Originally approved in 1995. Last previous edition approved in 20042010 as
F1642 – 04.F1642 – 04(2010). DOI: 10.1520/F1642-04R10.10.1520/F1642-12.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F1642 − 12
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 airblast pressure—the pressure increase that a surface experiences due to the detonation of a high explosive charge.
3.1.1.1 Discussion—
The airblast pressure history, as measured at a point on the surface, consists of two separate phases. The positive phase is
characterized by a nearly instantaneous rise to a maximum pressure followed by an exponential decay to ambient pressure. In the
negative phase, which follows immediately the positive phase, the pressure decrease
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.