ASTM A723/A723M-08
(Specification)Standard Specification for Alloy Steel Forgings for High-Strength Pressure Component Application
Standard Specification for Alloy Steel Forgings for High-Strength Pressure Component Application
ABSTRACT
This specification covers the standard requirements for high-strength quenched and tempered alloy steel forgings for pressure vessels, isostatic presses, shock tubes, and similar components. These materials are not intended for welded construction. Three grades of nickel-chromium-molybdenum steels and six classes of increasing tensile strength are included. The strength class, section size, and configuration of the forging will largely dictate the applicable type of steel. Materials shall be manufactured by steel melting processes, rough machining, and final heat treatment, which shall consist of normalizing, reaustenitization, liquid quenching, and tempering. Conformance of the forging specimens to chemical composition requirements shall be analyzed by heat and product analyses. Proper sampling methods for mechanical properties testing shall be done by any of four possible ways, as judged appropriate. Steel specimens shall also undergo straight-beam and angle-beam ultrasonic examination, and magnetic particle examination procedures to evaluate nondestructive examination requirements. Repair welding of the forgings shall not be permitted.
SCOPE
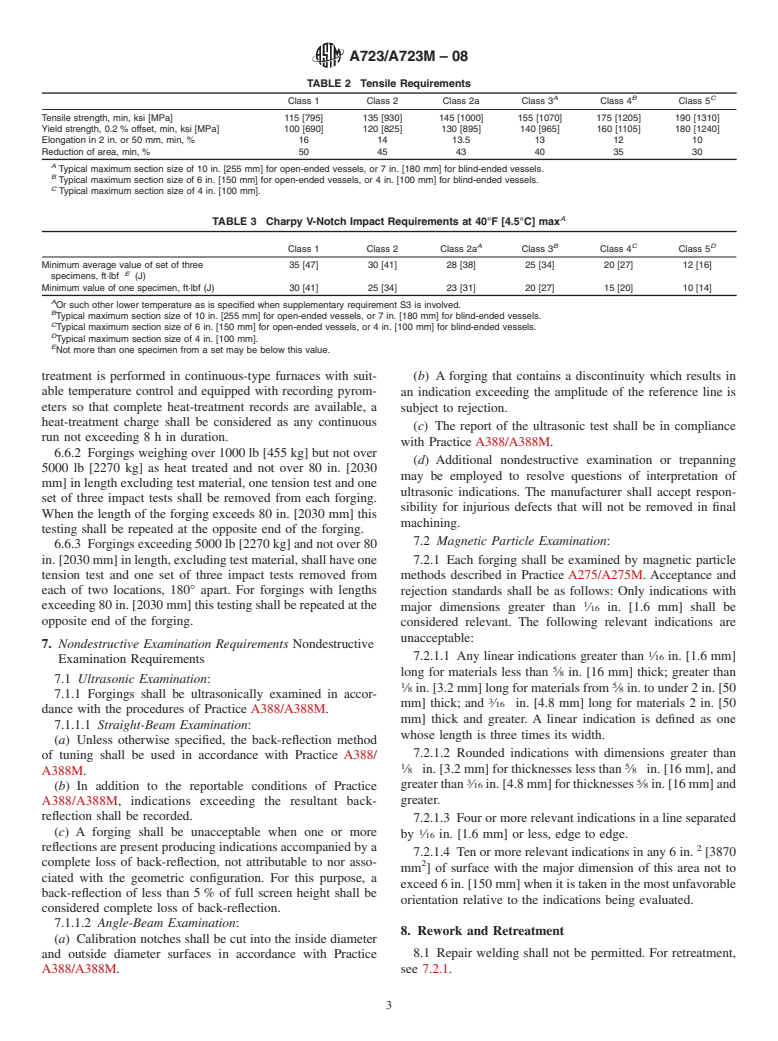
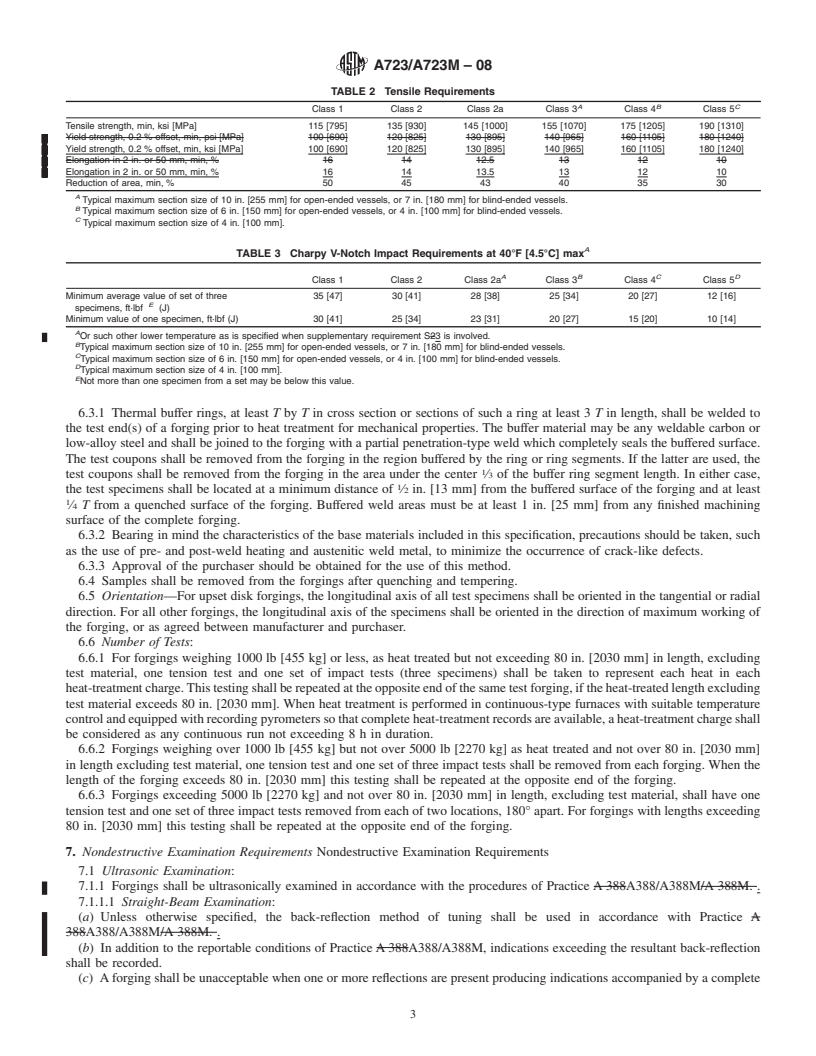
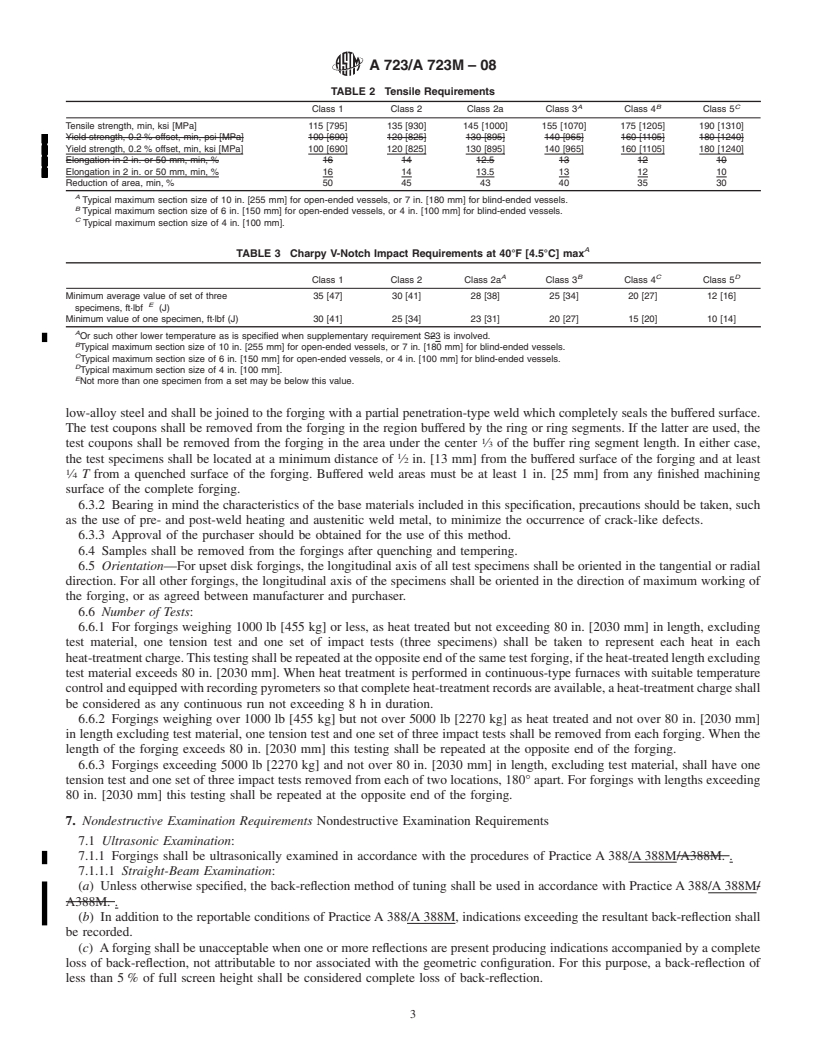
1.1 This specification covers requirements for high-strength quenched and tempered alloy steel forgings for pressure vessels, isostatic presses, shock tubes, and similar components.
1.2 These materials are not intended for welded construction.
1.3 Three grades of nickel-chromium-molybdenum steels and six classes of increasing tensile strength are included. The strength class, section size, and configuration of the forging will largely dictate the applicable type(s) of steel.
1.4 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI (metric) units are to be regarded separately as the standard. Within the text and tables, the SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each system must be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in nonconformance with the specification.
1.5 Unless the order specifies the applicable “M” specification designation, the material shall be furnished to the inch-pound units.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: A723/A723M – 08
Standard Specification for
Alloy Steel Forgings for High-Strength Pressure Component
1
Application
This standard is issued under the fixed designationA723/A723M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* 3. Ordering Information and General Requirements
2
1.1 This specification covers requirements for high- 3.1 In addition to the ordering information required by
strength quenched and tempered alloy steel forgings for pres- Specification A788/A788M, the purchaser shall include with
sure vessels, isostatic presses, shock tubes, and similar com- the inquiry and order a detailed drawing, sketch, or written
ponents. description of the forging and the method of selecting test
1.2 These materials are not intended for welded construc- location (see 6.2). When appropriate, the areas of significant
tion. loading in the forging shall be designated. The purchaser may
1.3 Three grades of nickel-chromium-molybdenum steels also include appropriate supplementary requirements from
and six classes of increasing tensile strength are included. The Specification A788/A788M as well as from this specification.
strength class, section size, and configuration of the forging 3.2 Material supplied to this specification shall conform to
will largely dictate the applicable type(s) of steel. the requirements of Specification A788/A788M, which out-
1.4 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI lines additional ordering information, manufacturing require-
(metric) units are to be regarded separately as the standard. ments, testing and retesting methods and procedures, marking,
Within the text and tables, the SI units are shown in brackets. certification,productanalysisvariations,andadditionalsupple-
The values stated in each system are not exact equivalents; mentary requirements.
therefore,eachsystemmustbeusedindependentlyoftheother. 3.3 If the requirements of this specification are in conflict
Combining values from the two systems may result in noncon- with the requirements of Specification A788/A788M, the
formance with the specification. requirements of this specification shall prevail.
1.5 Unless the order specifies the applicable “M” specifica-
4. Materials and Manufacture
tion designation, the material shall be furnished to the inch-
pound units. 4.1 Melting Practice—The steel melting procedures of
Specification A788/A788M shall apply except that the open-
2. Referenced Documents
hearth process shall not be used, and that the steel shall be
3
2.1 ASTM Standards: vacuum degassed prior to or during the pouring of the ingot, in
A275/A275M Practice for Magnetic Particle Examination order to remove objectionable gases, particularly hydrogen.
of Steel Forgings 4.1.1 Use of secondary remelting or refining operations may
A370 Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing be considered for particularly demanding applications.
of Steel Products 4.2 Discard—Sufficient discard shall be taken from each
A388/A388M Practice for Ultrasonic Examination of Steel ingottosecurefreedomfrompipingandexcessivesegregation.
Forgings 4.3 Heat Treatment:
A788/A788M Specification for Steel Forgings, General Re- 4.3.1 Forgings shall be rough-machined prior to final heat
quirements treatment if it is necessary to reduce the mass to ensure full
hardening or to meet the requirements of 6.2. The risk of
cracking during heat treatment with high-hardenability steels
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A01 on Steel,
of the type covered by this specification should be borne in
Stainless Steel and Related Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
A01.06 on Steel Forgings and Billets. mind when deciding on the degree of surface preparation
Current edition approved March 1, 2008. Published March 2008. Originally
before heat treatment.
approved in 1975. Last previous edition approved in 2002 as A723/A723M – 02.
4.3.2 Heat Treatment for Mechanical Properties—Heat
DOI: 10.1520/A0723_A0723M-08.
2
treatment shall consist of normalizing (which may be part of
For ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code applications see related Specifi-
cation SA–723/SA–723M in Section II of that Code.
the preliminary treatment), reaustenitization, liquid quenching,
3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
and tempering. The forgings shall be quenched in a suitable
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
liquid medium by spraying or immersion. Quenching shall be
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
followed b
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:A 723/A 723M–02 Designation: A723/A723M – 08
Standard Specification for
Alloy Steel Forgings for High-Strength Pressure Component
1
Application
This standard is issued under the fixed designationA723/A723M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
2
1.1 This specification covers requirements for high-strength quenched and tempered alloy steel forgings for pressure vessels,
isostatic presses, shock tubes, and similar components.
1.2 These materials are not intended for welded construction.
1.3 Three grades of nickel-chromium-molybdenum steels and six classes of increasing tensile strength are included. The
strength class, section size, and configuration of the forging will largely dictate the applicable type(s) of steel.
1.4 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI (metric) units are to be regarded separately as the standard. Within the
text and tables, the SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each
system must be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in nonconformance with the
specification.
1.5 Unless the order specifies the applicable “M” specification designation, the material shall be furnished to the inch-pound
units.
2. Referenced Documents
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
A275/A275M Test Method Practice for Magnetic Particle Examination of Steel Forgings
A370 Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing of Steel Products
A388/A388M Practice for Ultrasonic Examination of Heavy Steel Forgings
A788788/A788M Specification for Steel Forgings, General Requirements
3. Ordering Information and General Requirements
3.1 In addition to the ordering information required by SpecificationA788A788A788/A788M, the purchaser shall include with
the inquiry and order a detailed drawing, sketch, or written description of the forging and the method of selecting test location (see
6.2). When appropriate, the areas of significant loading in the forging shall be designated.
3.2Material supplied to this specification shall conform to the requirements of SpecificationA788A788).When appropriate, the
areas of significant loading in the forging shall be designated. The purchaser may also include appropriate supplementary
requirements from Specification A788/A788M as well as from this specification.
3.2 Material supplied to this specification shall conform to the requirements of Specification A788/A788M, which outlines
additional ordering information, manufacturing requirements, testing and retesting methods and procedures, marking, certification,
product analysis variations, and additional supplementary requirements.
3.3 If the requirements of this specification are in conflict with the requirements of SpecificationA788A788A788/A788M, the
requirements of this specification shall prevail.
4. Materials and Manufacture
4.1 Melting Practice—The steel melting procedures of Specification A 788A 788A788/A788Mshall apply except that the
open-hearth process shall not be used, and that the steel shall be vacuum degassed prior to or during the pouring of the ingot, in
order to remove objectionable gases, particularly hydrogen.
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM CommitteeA01 on Steel, Stainless Steel and RelatedAlloys,Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
A01.06 on Steel Forgings and Billets.
Current edition approved September 10, 2002. Published January 2003. Originally approved in 1975. Last previous edition approved in 1994 as A 723–94(1999).
Current edition approved March 1, 2008. Published March 2008. Originally approved in 1975. Last previous edition approved in 2002 as A723/A723M – 02. DOI:
10.1520/A0723_A0723M-08.
2
For ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code applications see related Specification SA–723/SA–723M in Section II of that Code.
3
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. ForAnnualBookofASTMStandards
, Vol 01.05.volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:A 723/A 723M–02 Designation: A 723/A 723M – 08
Standard Specification for
Alloy Steel Forgings for High-Strength Pressure Component
1
Application
This standard is issued under the fixed designationA723/A723M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
2
1.1 This specification covers requirements for high-strength quenched and tempered alloy steel forgings for pressure vessels,
isostatic presses, shock tubes, and similar components.
1.2 These materials are not intended for welded construction.
1.3 Three grades of nickel-chromium-molybdenum steels and six classes of increasing tensile strength are included. The
strength class, section size, and configuration of the forging will largely dictate the applicable type(s) of steel.
1.4 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI (metric) units are to be regarded separately as the standard. Within the
text and tables, the SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each
system must be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in nonconformance with the
specification.
1.5 Unless the order specifies the applicable “M” specification designation, the material shall be furnished to the inch-pound
units.
2. Referenced Documents
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
A 275/A 275M Test Method Practice for Magnetic Particle Examination of Steel Forgings
A 370 Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing of Steel Products
A 388/A 388M Practice for Ultrasonic Examination of Heavy Steel Forgings
A 788/A 788M Specification for Steel Forgings, General Requirements
3. Ordering Information and General Requirements
3.1 InadditiontotheorderinginformationrequiredbySpecificationA 788/A 788M,thepurchasershallincludewiththeinquiry
and order a detailed drawing, sketch, or written description of the forging and the method of selecting test location (see 6.2).When
appropriate, the areas of significant loading in the forging shall be designated.
3.2Material supplied to this specification shall conform to the requirements of SpecificationA788). When appropriate, the areas
of significant loading in the forging shall be designated. The purchaser may also include appropriate supplementary requirements
from Specification A 788/A 788M as well as from this specification.
3.2 Material supplied to this specification shall conform to the requirements of Specification A 788/A 788M, which outlines
additional ordering information, manufacturing requirements, testing and retesting methods and procedures, marking, certification,
product analysis variations, and additional supplementary requirements.
3.3 If the requirements of this specification are in conflict with the requirements of Specification A788A 788/A 788M, the
requirements of this specification shall prevail.
4. Materials and Manufacture
4.1 Melting Practice—The steel melting procedures of Specification A788A 788/A 788Mshall apply except that the open-
hearth process shall not be used, and that the steel shall be vacuum degassed prior to or during the pouring of the ingot, in order
to remove objectionable gases, particularly hydrogen.
4.1.1 Use of secondary remelting or refining operations may be considered for particularly demanding applications.
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM CommitteeA01 on Steel, Stainless Steel and RelatedAlloys,Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
A01.06 on Steel Forgings and Billets.
Current edition approved September 10, 2002.March 1, 2008. Published January 2003.March 2008. Originally approved in 1975. Last previous edition approved in
19942002 as A723–94(1999).A 723/A 723M – 02.
2
For ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code applications see related Specification SA–723/SA–723M in Section II of that Code.
3
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. ForAnnualBookofASTMStandards
, Vol 01.05.volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
A 723/A 723M –
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.