ASTM D4367-99
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Benzene in Hydrocarbon Solvents by Gas Chromatography
Standard Test Method for Benzene in Hydrocarbon Solvents by Gas Chromatography
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination by gas chromatography of benzene at levels from 0.01 to 1 volume% in hydrocarbon solvents.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.3 For hazard information and guidance, see the supplier's Material Safety Data Sheet. For specific hazard statements, see Section 7.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: D 4367 – 99
Standard Test Method for
Benzene in Hydrocarbon Solvents by Gas Chromatography
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 4367; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope * components then pass through a column with the highly polar
phase, 1,2,3-tris(2-cyanoethoxy)propane, that separates the
1.1 This test method covers the determination by gas
aromatic and nonaromatic compounds. The eluted components
chromatography of benzene at levels from 0.01 to 1 volume %
are detected by a conventional detector and recorded on a strip
in hydrocarbon solvents.
chart. The peak areas are measured and the concentration of
NOTE 1—For benzene levels lower than 0.01 volume %, use Test
each component is calculated by reference to the internal
Method D 6229.
standard.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
4. Significance and Use
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
4.1 Benzene is classed as a toxic and carcinogenic material.
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
A knowledge of the concentration of this compound may be an
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
aid in evaluating the possible health hazards to persons
1.3 For hazard information and guidance, see the supplier’s
handling and using hydrocarbon solvents, but this test method
Material Safety Data Sheet. For specific hazard statements, see
is not intended to evaluate such hazards.
Section 7.
5. Apparatus
2. Referenced Documents
5.1 Chromatograph—Any gas chromatographic instrument
2.1 ASTM Standards:
that has a backflush system and flame ionization detector and
D 3606 Test Method for the Determination of Benzene and
that can be operated at the conditions given in Table 1. The
Toluene in Finished Motor and Aviation Gasoline by Gas
detector-recorder combination must produce a 4-mm deflection
Chromatography
for a 1-μL specimen containing 0.05 volume % MEK when
D 6229 Test Method for Trace Benzene in Hydrocarbon
operated at maximum sensitivity.
Solvents by Capillary Gas Chromatography
5.2 Columns, one 0.8-m (2.5-ft) length of 3.2-mm ( ⁄8-in.)
E 260 Practice for Packed Column Gas Chromatography
outside diameter stainless steel tubing and one 4.6-m (15-ft)
E 300 Practice for Sampling Industrial Chemicals
length of 3.2-mm ( ⁄8-in.) outsider diameter stainless steel
tubing.
3. Summary of Test Method
5.3 Recorder, Strip Chart—Potentiometer with a full-scale
3.1 An internal standard, methyl ethyl ketone (MEK), is
deflection of 1 mV, a full-scale response time of2sor less, and
added to the material and then introduced into a gas chromato-
a maximum noise level of 60.3 % of full scale.
graph equipped with two columns connected in series. The
5.4 Microsyringe, 5-μL capacity.
specimen passes first through a column packed with the
5.5 Pipets, measuring 1 and 2 mL, graduated in 0.01 mL; 5,
nonpolar phase, methyl silicone, which separates the compo-
10, and 20-mL capacity.
nents by boiling point. After octane has eluted, the flow
5.6 Flasks, volumetric, 25 and 100-mL capacity.
through the nonpolar column is reversed, flushing out the
5.7 Vibrator, electric.
components heavier than octane. The octane and lighter
5.8 Vacuum Source.
5.9 Evaporator, vacuum, rotary.
5.10 Flask, boiling, round-bottom, short-neck, with 24/40 T
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D-1 on Paint
joint, 500-mL capacity. Suitable for use with the evaporator
and Related Coatings, Materials, and Applications and is the direct responsibility of
(see 5.9).
Subcommittee D01.35 on Solvents, Plasticizers, and Chemical Intermediates.
Current edition approved June 10, 1999. Published August 1999. Originally
5.11 Lamp, infrared.
published as D 4367 – 84. Last previous edition D 4367 – 94a.
5.12 Burets, automatic, with integral reservoir, 25-mL ca-
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 05.02.
3 pacity.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 06.04.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.02.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 15.05.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
D4367–99
TABLE 1 Instrument Conditions Found Satisfactory for
ylene chloride, acetone, methyl ethyl ketone, benzene (see
Measuring Low Concentrations of Benzene in
6.11.1), and n-nonane are hazardous.
Hydrocarbon Solvents (Note 2)
7.2 Benzene is volatile and highly flammable. Exercise care
Detector flame ionization
to prevent accidental ignition. Benzene is also carcinogenic
Columns two, stainless steel
and toxic; acute or chronic poisoning may result from inhala-
Length, m (A) 0.8; (B) 4.6
Outside diameter, mm 3.2
tion of benzene vapor, absorption of benzene through the skin,
Stationary phases (A) methyl silicone, 10 weight %
or drinking benzene.
(B) TCEP, 25 weight %
Support (A) acid-washed calcined diatomite, 60 to
80-mesh 8. Sampling
(B) acid-washed pink diatomaceous
8.1 Take samples of solvents to be analyzed by this test
earth, 80 to 100-mesh
Reference column any column or restriction may be used method using the procedures described in Practice E 300.
Temperature, °C
Injection port 150
9. Preparation of Columns
Column, isothermal 100
Detector block 150
9.1 Column Packing Preparation—Prepare the two packing
Carrier gas helium
materials, one containing 10 % methyl silicone and the other
Flow rate, mL/min approximately 30
25 % TCEP, as follows:
Recorder range, mV 0 to 1
Chart speed, mm/min 10
9.1.1 Weigh 45 g of the acid-washed calcined diatomite
Specimen size, μL 1.0
support 60 to 80 mesh, into a 500-mL flask (see 5.10). Dissolve
Time to backflush, min approximately 2
5 g of the methyl silicone in approximately 50 mL of
Total cycle time, min approximately 30
chloroform. (Warning—See Note 3.) Pour the methyl sili-
cone–chloroform solution into the flask containing the support.
Attach the flask to the evaporator (see 5.9), connect the
NOTE 2—Suppliers of stationary phases and supports can be found in
Research Report RR:D01-1038, available from ASTM Headquarters.
vacuum, and start the motor. Turn on the infrared lamp and
allow the packing to mix thoroughly until dry.
6. Reagents and Materials
NOTE 3—Warning: Chloroform is a toxic material and inhalation must
6.1 Purity of Reagents—Reagent grade chemicals shall be
be avoided.
used in all tests. Unless otherwise indicated, it is intended that
9.1.2 Weigh 75 g of acid-washed pink diatomaceous earth,
all reagents shall conform to the specifications of the Commit-
80 to 100 mesh, into a 500-mL flask (see 5.10). Dissolve 25 g
tee on Analytical Reagents of the American Chemical Society,
of TCEP in 200 mL of methanol and pour into the flask
where such specifications are available. Other grades may be
containing the support. Attach the flask to the evaporator (see
used, provided it is first ascertained that the reagent is of
5.9), connect the vacuum, and start the motor. Turn on the
sufficiently high purity to permit its use without lessening the
infrared lamp and allow the packing to mix thoroughly until
accuracy of the determination.
dry, but do not heat the packing above 180°C.
6.2 Acetone.
9.2 Column Preparation:
6.3 Chloroform.
9.2.1 Clean the stainless steel tubing as follows: Attach a
6.4 Diatomaceous Earth —Acid-washed, 60 to 80 mesh
metal funnel to one end of the steel tubing. Hold or mount the
and 80 to 100 mesh.
stainless steel tubing in an upright position and place a beaker
6.5 Helium, 99.99 % pure.
under the outlet end of the tubing. Pour about 50 mL of
6.6 Methanol.
methylene chloride into the funnel and allow it to drain through
6.7 Methylene Chloride.
the steel tubing into the beaker. Repeat the washing with 50 mL
6.8 Methyl Ethyl Ketone (MEK), 99.9 mol %.
of acetone. Remove the funnel and connect the steel tubing to
6.9 Methyl Silicone.
an air line, by means of vinyl tubing. Remove all solvent from
6.10 1,2,3-Tris(2-Cyanoethoxy) Propane (TCEP).
the steel tubing by blowing filtered, oil-free air through or
6.11 Calibration Standards.
+
applying a vacuum.
6.11.1 Benzene,99 mol %.
+
9.2.2 Pack the 0.8-m (2.5-ft) tubing (Column A) with the
6.11.2 Isooctane,99 mol %.
+
methyl silicone packing (see 9.1.1) and the 4.6-m (15-ft) tubing
6.11.3 n-Nonane,99 mol %.
(Column B) with the TCEP packing (see 9.1.2) as follows:
7. Hazards Preform Columns A and B separately to fit the chromato-
graphic instrument. Close one end of each tubing with a small,
7.1 Many hydrocarbon solvents are flammable and hazard-
glass wool plug and connect this end to a vacuum source by
ous; use special precautions when handling them. Of the
means of a glass-wool packed tube. To the other end connect a
reagents used in this procedure, methanol, chloroform, meth-
small polyethylene funnel by means of a short length of vinyl
tubing. Start the vacuum and pour the appropriate packing into
the funnel until the column is full. While filling each column,
“Reagent Chemicals, American Chemical Society Specifications,” Am. Chemi-
cal Soc., Washington, DC. For suggestions on the testing of reagents not listed by
vibrate the column with the electric vibrator to settle the
the American Chemical Society, see “Reagent Chemicals and Standards,” by Joseph
packing. Remove the funnel and shut off the vacuum source.
Rosin, D. Van Nostrand Co., Inc., New York, NY, and the “United States
Remove the top 6 mm ( ⁄4 in.) of packing and insert a glass
Pharmacopeia.”
See Note 2. wool plug in this end of the column.
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
D4367–99
9.3 Prepacked columns conforming to specifications listed
in Table 1, and in 5.2, 9.1, and 9.2 may be obtained from any
reputable chromatography supply company.
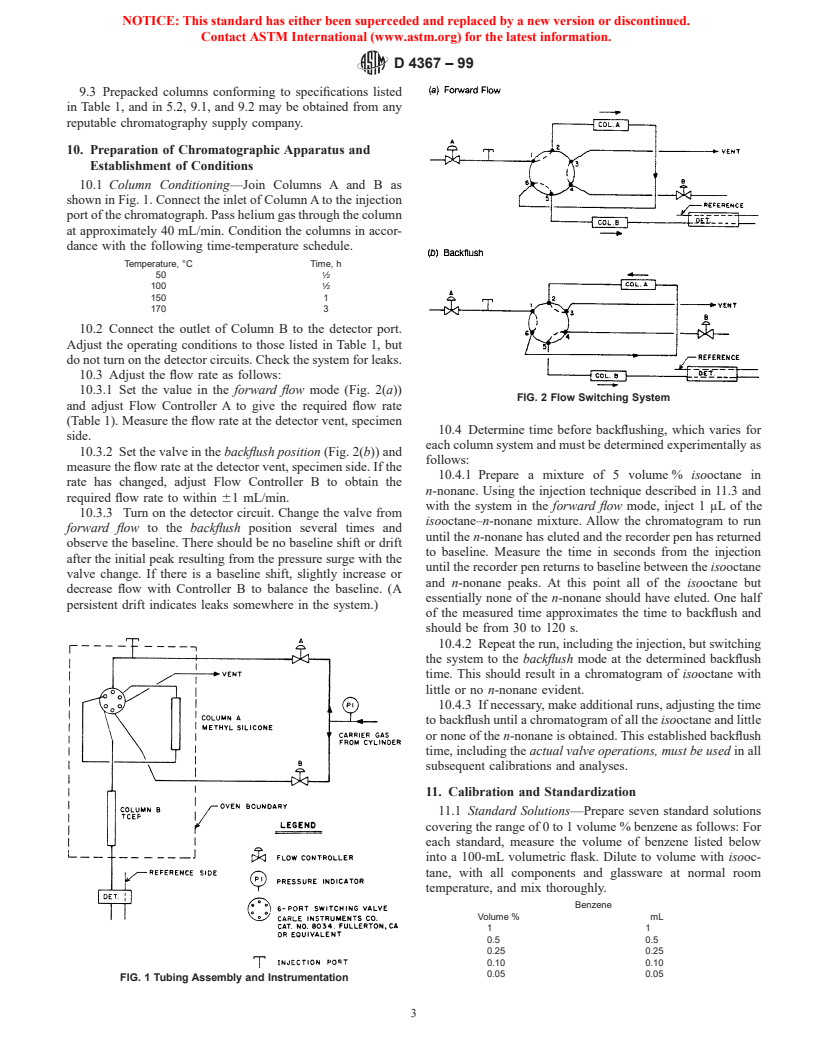
10. Preparation of Chromatographic Apparatus and
Establishment of Conditions
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.