ASTM B194-96
(Specification)Standard Specification for Copper-Beryllium Alloy Plate, Sheet, Strip, and Rolled Bar
Standard Specification for Copper-Beryllium Alloy Plate, Sheet, Strip, and Rolled Bar
SCOPE
1.1 This specification establishes the requirements for copper-beryllium alloy plate, sheet, strip, and rolled bar. The following alloys are specified:Copper AlloyPreviously Used Commercial Nominal BerylliumUNS No. DesignationsContent, %C17000Alloy 1651.7C17200Alloy 251.9
1.2 Unless otherwise required, Copper Alloy UNS No. C17200 shall be the alloy furnished whenever Specification B 194 is specified without any alloy designation.
1.3 Units—With the exception of Grain Size values, the values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units, which are provided for information only and not considered standard.
1.4 The following hazard statement pertains only to the test method portions in the annex of this specification:
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: B 194 – 96
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR TESTING AND MATERIALS
100 Barr Harbor Dr., West Conshohocken, PA 19428
Reprinted from the Annual Book of ASTM Standards. Copyright ASTM
Standard Specification for
Copper-Beryllium Alloy Plate, Sheet, Strip, and Rolled Bar
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B 194; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope E 112 Test Methods for Determining Average Grain Size
E 527 Practice for Numbering Metals and Alloys (UNS)
1.1 This specification covers copper-beryllium alloy plate,
sheet, strip, and rolled bar. The following alloys are covered:
3. Ordering Information
Copper Alloy Previously Used Commercial Nominal Beryllium
3.1 Orders for material under this specification should
UNS No. Designations Content, %
C17000 Alloy 165 1.7
include the following information:
C17200 Alloy 25 1.9
3.1.1 Quantity,
1.2 Unless otherwise required, Copper Alloy UNS No. 3.1.2 Copper Alloy UNS number (1.1),
C17200 shall be the alloy furnished whenever Specification 3.1.3 Form of material: plate, sheet, strip, or rolled bar,
B 194 is specified without any alloy designation. 3.1.4 Temper (5.1),
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded 3.1.5 Dimensions: thickness and width, and length if appli-
as the standard. The values in parentheses are for information cable.
only. 3.1.6 How furnished: rolls, stock lengths with or without
1.4 The following hazard statement pertains only to the test ends, specific lengths with or without ends,
method portions in the annex of this specification: 3.1.7 Type of edge, if required: slit, sheared, sawed, square
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the corners, rounded corners, rounded edges, or full-rounded edges
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the (Section 12),
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro- 3.1.8 Type of width and straightness tolerances, if required:
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica- slit-metal tolerances, square-sheared-metal tolerances, sawed-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. metal tolerances, straightened or edge-rolled-metal tolerances
(Section 12),
2. Referenced Documents
3.1.9 Special thickness tolerances, if required (12.2),
2.1 The following documents of the issue in effect on date 3.1.10 Tension test or hardness as applicable (Section 6),
of material purchase form a part of this specification to the
3.1.11 Bend test, if required (Section 9),
extent referenced herein: 3.1.12 Grain size or grain count if required (Section 7 or 8),
2.2 ASTM Standards:
3.1.13 Certification if required (see Specification B 248,
B 248 Specification for General Requirements for Wrought Section 13),
Copper and Copper-Alloy Plate, Sheet, Strip, and Rolled
3.1.14 Mill Test Report, if required (see Specification
Bar
B 248, Section 14),
B 601 Practice for Temper Designations for Copper and 3.1.15 Specification number and year of issue, and
Copper Alloys—Wrought and Cast
3.1.16 Special tests or exceptions, if any.
E 8 Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials 3.2 When material is purchased for agencies of the U.S.
E 18 Test Methods for Rockwell Hardness and Rockwell
Government, this shall be specified in the contract or purchase
Superficial Hardness of Metallic Materials order, and the material shall conform to the Supplementary
requirements as defined in the current issue of Specification
B 248.
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B-5 on Copper
and Copper Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee B05.01 on Plate,
4. Chemical Composition
Sheet, and Strip.
4.1 The material shall conform to the chemical requirements
Current edition approved Sept. 10, 1996. Published November 1996. Originally
published as B 194 – 45 T. Last previous edition B 194 – 95.
specified in Table 1.
The UNS system for copper and copper alloys (see Practice E 527) is a simple
4.2 These specification limits do not preclude the presence
expansion of the former standard designation system accomplished by the addition
of other elements. Limits for unnamed elements may be
of a prefix “C” and a suffix “00.” The suffix can be used to accommodate
composition variations of the base alloy.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 02.01.
4 5
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.01. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.01.
B 194
TABLE 1 Chemical Requirements
6.2.2 The referee product rejection criteria shall be tensile
Composition, % test results when tested in accordance with Test Method E 8.
Element 6.2.3 Rockwell hardness and tensile strength requirements
Copper Alloy UNS Copper Alloy UNS
No. C17000 No. C17200
are given in Table 2, Table 3, and Table 4.
6.3 Product, as specified in 5.1 shall conform to the require-
Beryllium 1.60–1.79 1.80–2.00
Additive elements:
ments specified in Table 2 in the solution heat treated, or
Nickel + cobalt, min 0.20 0.20
solution heat treated and cold worked conditions, and in Table
Nickel + cobalt + iron, max 0.6 0.6
Aluminum, max 0.20 0.20 3 after precipitation heat treatment or Table 4 in the mill
Silicon, max 0.20 0.20
hardened condition. Precipitation heat treatment parameters for
Copper remainder remainder
Table 2 and Table 3 are shown in Section 10.
7. Grain Size
established, by agreement between manufacturer or supplier
7.1 Material over 0.010 in. (0.254 mm) in thickness shall
and purchaser. Copper may be given as remainder, and may be
have an average grain size in accordance with Test Method
taken as the difference between the sum of all elements
E 112, not exceeding the limits specified in Table 5. The
analyzed and 100 %. When all elements in Table 1 are
determinations are made on the separate samples and in a plane
analyzed, their sum shall be 99.5 % minimum.
perpendicular to the surface and perpendicular to the direction
of rolling.
5. Temper
5.1 Tempers available under this specification are defined in
8. Grain Count
Practice B 601. The standard tempers of product are as
8.1 The grain count of a sample of material, in any temper,
designated in Table 2, Table 3, and Table 4. Plate is generally
over 0.004 to 0.010 in. (0.102 to 0.254 mm), inclusive, in
available in the TB00 (A), TD04 (H), TF00 (AT), and TH04
thickness shall not be less than the limits specified in Table 6.
(HT) tempers.
8.2 Grain count is the number of grains per stock thickness,
averaged for five locations one stock thickness apart. Grain
NOTE 1—Plate is generally available in the TB00 (solution-heat treated)
and TD04 (hard) tempers. count shall be determined in a plane perpendicular to the
surface and perpendicular to the direction of rolling.
6. Mechanical Properties
9. Bend Test Requirements
6.1 Product less than 0.050 in. (0.127 mm) in thickness.
6.1.1 Tensile test results shall be the product acceptance 9.1 The optional bend test is a method for evaluating the
criteria when tested in accordance with Test Method E 8. ductility of precipitation heat treated copper-beryllium strip in
6.1.2 The tensile strength requirements are given in Table 2,
thin gages.
Table 3 and Table 4. 9.2 When specified in the order (see 3.1.6), material in any
6.2 Product 0.050 in. (1.270 mm) and greater in thickness.
temper 0.004 to 0.020 in. (0.102 to 0.508 mm), inclusive, in
6.2.1 Rockwell hardness is the product acceptance criteria thickness shall conform to the requirements specified in Table
when tested in accordance with Test Method E 18.
7 when tested in accordance with 11.2.
TABLE 2 Mechanical Property Requirements for Material in The Solution-Heat-Treated or Solution-Heat-Treated and Cold-Worked
Condition
A E
D
Temper Designation Material Thickness, in. Rockwell Hardness
Tensile Strength, Elongation in 2 in. or
B C
ksi (MPa) 50 mm, min,%
Standard Former Over Incl B Scale 30T Scale 15T Scale
TB00 A . . 60–78 35 45–78 46–67 75–85
(410–540)
TD01 ⁄4 H . 0.188 75–88 15 68–90 62–75 83–89
(520–610)
TD02 ⁄2 H . 0.188 85–100 9 88–96 74–79 88–91
(590–690)
TD04 H . 0.188 100–130 2 96–104 79–83 91–94
(690–900)
TD04 H 0.188 0.375 90–130 . 91–103 77 90
(660–900)
TD04 H 0.375 1.000 90–120 . 90–102 . .
(620–830)
TD04 H over 1.000 85–115 8 88–102 . .
(590–800)
A
Standard designations defined in Practice B 601.
B
ksi 5 100 psi.
C
See Appendix X1.
D
Elongation requirement applies to material 0.004 in. (0.102 mm) and thicker.
E
The thickness of material that may be tested by use of the Rockwell hardness scales is as follows:
B Scale.0.040 in. (1.016 mm) and over
30T Scale.0.020 to 0.040 in. (0.508 to 1.016 mm), excl.
15T Scale.0.015 to 0.020 in. (0.381 to 0.508 mm), excl.
Hardness values shown apply only to direct determinations, not converted values.
B 194
A
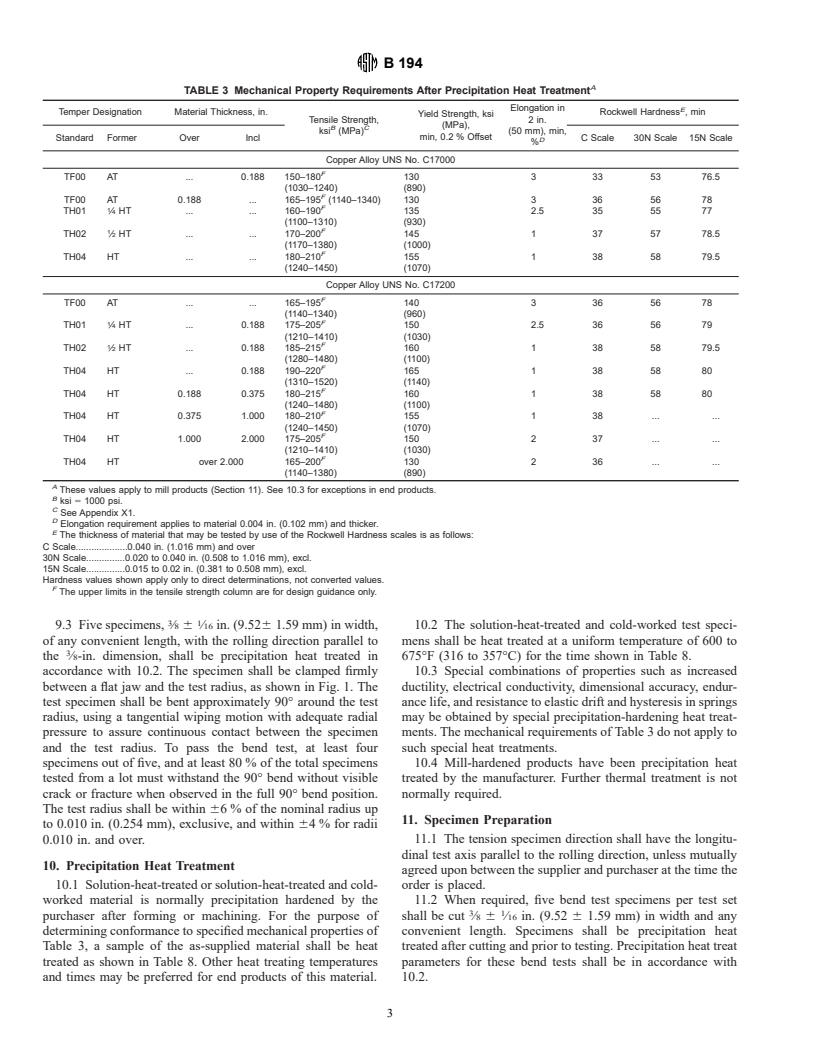
TABLE 3 Mechanical Property Requirements After Precipitation Heat Treatment
Elongation in E
Temper Designation Material Thickness, in. Rockwell Hardness , min
Yield Strength, ksi
Tensile Strength, 2 in.
(MPa),
B C
ksi (MPa) (50 mm), min,
min, 0.2 % Offset
Standard Former Over Incl C Scale 30N Scale 15N Scale
D
%
Copper Alloy UNS No. C17000
F
130 3 33 53 76.5
TF00 AT . 0.188 150–180
(1030–1240) (890)
F
TF00 AT 0.188 . 165–195 (1140–1340) 130 3 36 56 78
F
TH01 ⁄4 HT . . 160–190 135 2.5 35 55 77
(1100–1310) (930)
F
TH02 ⁄2 HT . . 170–200 145 1 37 57 78.5
(1170–1380) (1000)
F
TH04 HT . . 180–210 155 1 38 58 79.5
(1240–1450) (1070)
Copper Alloy UNS No. C17200
F
TF00 AT . . 165–195 140 336 56 78
(1140–1340) (960)
F
TH01 ⁄4 HT . 0.188 175–205 150 2.5 36 56 79
(1210–1410) (1030)
F
TH02 ⁄2 HT . 0.188 185–215 160 1 38 58 79.5
(1280–1480) (1100)
F
TH04 HT . 0.188 190–220 165 138 58 80
(1310–1520) (1140)
F
TH04 HT 0.188 0.375 180–215 160 138 58 80
(1240–1480) (1100)
F
TH04 HT 0.375 1.000 180–210 155 1 38 . .
(1240–1450) (1070)
F
TH04 HT 1.000 2.000 175–205 150 2 37 . .
(1210–1410) (1030)
F
TH04 HT over 2.000 165–200 130 2 36 . .
(1140–1380) (890)
A
These values apply to mill products (Section 11). See 10.3 for exceptions in end products.
B
ksi 5 1000 psi.
C
See Appendix X1.
D
Elongation requirement applies to material 0.004 in. (0.102 mm) and thicker.
E
The thickness of material that may be tested by use of the Rockwell Hardness scales is as follows:
C Scale.0.040 in. (1.016 mm) and over
30N Scale.0.020 to 0.040 in. (0.508 to 1.016 mm), excl.
15N Scale.0.015 to 0.02 in. (0.381 to 0.508 mm), excl.
Hardness values shown apply only to direct determinations, not converted values.
F
The upper limits in the tensile strength column are for design guidance only.
3 1
9.3 Five specimens, ⁄8 6 ⁄16 in. (9.526 1.59 mm) in width, 10.2 The solution-heat-treated and cold-worked test speci-
of any convenient length, with the rolling direction parallel to mens shall be heat treated at a uniform temperature of 600 to
the ⁄8-in. dimension, shall be precipitation heat treated in 675°F (316 to 357°C) for the time shown in Table 8.
accordance with 10.2. The specimen shall be clamped firmly 10.3 Special combinations of properties such as increased
between a flat jaw and the test radius, as shown in Fig. 1. The ductility, electrical conductivity, dimensional accuracy, endur-
test specimen shall be bent approximately 90° around the test ance life, and resistance to elastic drift and hysteresis in springs
radius, using a tangential wiping motion with adequate radial may be obtained by special precipitation-hardening heat treat-
pressure to assure continuous contact between the specimen ments. The mechanical requirements of Table 3 do not apply to
and the test radius. To pass the bend test, at least four such special heat treatments.
specimens out of five, and at least 80 % of the total specimens 10.4 Mill-hardened products have been precipitation heat
tested from a lot must withstand the 90° bend without visible treated by the manufacturer. Further thermal treatment is not
crack or fracture when observed in the full 90° bend position. normally required.
The test radius shall be within 66 % of the nominal radius up
11. Specimen Preparation
to 0.010 in. (0.254 mm), exclusive, and within 64 % for radii
0.010 in. and over. 11.1 The tension specimen direction shall have the longitu-
dinal test axis parallel to the rolling direction, unless mutually
10. Precipitation Heat Treatment
agreed upon between the supplier and purchaser at the time the
10.1 Solution-heat-treated or solution-heat-treated and cold- order is placed.
worked material is normally precipitation hardened by the 11.2 When required, five bend test specimens per test set
3 1
purchaser after forming or machining. For the purpose of shall be cut ⁄8 6 ⁄16 in. (9.52 6 1.59 mm) in width and any
determining conformance to specified mechanical properties of convenient length. Specimens shall be precipitation heat
Table 3, a sample of the as-supplied material shall be heat treated after cutting and prior to testing. Precipitation heat treat
treated as shown in Table 8. Other heat treating temperatures parameters for these bend tests shall be in accordance with
and times may be preferred for end products of this material. 10.2.
B 194
A
TABLE 4 Strip Mechanical Property Requirements—Mill Hardened Condition
E
Yield Strength, Elongation in 2
Temper Designation Rockwell Hardness , min
Tensile Strength,
ksi (MPa), in. (50 mm),
B C
B ksi (MPa)
D
Standard Former C Scale 30N Scale 15N Scale
0.2 % Offset min, %
Copper Alloy UNS No. C17000
F
TM00 AM 100–110 70–95 18 18 37 67.5
(690–760) (480–660)
F
TM01 ⁄4 HM 110–120 80–110 15 20 42 70
(760–830) (550–760)
1 F
TM02 ⁄2 HM 120–135 95–125 12 24 45 72
(830–930) (660–860)
F
TM04 HM 135–150 110–135 9 28 48 75
(930–1040) (760–930)
F
TM05 SHM 150–160 125–140 9 31 52 75.5
(1030–1100) (860–970)
F
TM06 XHM 155–175 135–165 3 32 52 76
(1070– 1210) (930–1140)
Copper Alloy UNS No. C17200
F
TM00 AM 100–110 70–95 16 R 95 37 67.5
B
(690–760) (480–660)
F
TM01 ⁄4 HM 110–120 80–110 15 20 42 70
(760–830) (550–760)
F
TM02 ⁄2 HM 120–135 95–125 12 23 44 72
(830–930) (660–860)
F
TM04 HM 135–150 110–135 9 28 48 75
(930–1030) (760–930)
F
TM05 SHM 150–160 125–140 9 31 52 75.5
(1030–1100) (860–970)
F
TM06 XHM 155–175 135–170 4 32 52 76
(1070–1210) (930–1170)
F
TM08 XHMS 175–190 150–180 3 33 53 76.5
(1210–1310) (1030–1240)
A
These
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.