ASTM D6710-17
(Guide)Standard Guide for Evaluation of Hydrocarbon-Based Quench Oil
Standard Guide for Evaluation of Hydrocarbon-Based Quench Oil
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 The significance and use of each test method will depend on the system in use and the purpose of the test method listed under Section 6. Use the most recent editions of the test methods.
SCOPE
1.1 This guide covers information without specific limits, for selecting standard test methods for testing hydrocarbon-based quench oils for quality and aging.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard.
1.2.1 Exception—The units given in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D6710 − 17
Standard Guide for
1
Evaluation of Hydrocarbon-Based Quench Oil
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6710; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* andOpaqueLiquids(andCalculationofDynamicViscos-
ity)
1.1 This guide covers information without specific limits,
D482Test Method for Ash from Petroleum Products
for selecting standard test methods for testing hydrocarbon-
D524Test Method for Ramsbottom Carbon Residue of
based quench oils for quality and aging.
Petroleum Products
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
D664Test Method for Acid Number of Petroleum Products
standard.
by Potentiometric Titration
1.2.1 Exception—The units given in parentheses are for
D974Test Method for Acid and Base Number by Color-
information only.
Indicator Titration
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the D1298Test Method for Density, Relative Density, or API
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
Gravity of Crude Petroleum and Liquid Petroleum Prod-
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro- ucts by Hydrometer Method
priate safety, health and environmental practices and deter-
D4052Test Method for Density, Relative Density, and API
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Gravity of Liquids by Digital Density Meter
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
D4530Test Method for Determination of Carbon Residue
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard- (Micro Method)
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
D6200Test Method for Determination of Cooling Charac-
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom- teristics of Quench Oils by Cooling Curve Analysis
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
D6304Test Method for Determination of Water in Petro-
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee. leum Products, Lubricating Oils, and Additives by Cou-
lometric Karl Fischer Titration
2. Referenced Documents
D7042Test Method for Dynamic Viscosity and Density of
2
Liquids by Stabinger Viscometer (and the Calculation of
2.1 ASTM Standards:
Kinematic Viscosity)
D91Test Method for Precipitation Number of Lubricating
3
Oils 2.2 ISO Standards:
D92Test Method for Flash and Fire Points by Cleveland ISO 9950Industrial Quenching Oils—Determination of
Open Cup Tester Cooling Characteristics—Nickel-Alloy Probe Test
D94Test Methods for Saponification Number of Petroleum Method, 1995-95-01
Products
D95Test Method for Water in Petroleum Products and 3. Terminology
Bituminous Materials by Distillation
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
D189Test Method for Conradson Carbon Residue of Petro-
leum Products Quench Processing
D445Test Method for Kinematic Viscosity of Transparent 3.1.1 austenitization, n—heatingasteelcontaininglessthan
the eutectoid concentration of carbon (about 0.8 mass %) to a
temperaturejustabovetheeutectoidtemperaturetodecompose
1
This guide is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum the pearlite microstructure to produce a face-centered cubic
Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcom-
(fcc) austenite-ferrite mixture.
mittee D02.L0.06 on Non-Lubricating Process Fluids.
3.1.2 dragout, n—solutioncarriedoutofabathonthemetal
Current edition approved Aug. 1, 2017. Published August 2017. Originally
approved in 2001. Last previous edition approved in 2012 as D6710–02(2012).
being quenched and associated handling equipment.
DOI: 10.1520/D6710-17.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
3
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available fromAmerican National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
the ASTM website. 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D6710 − 17
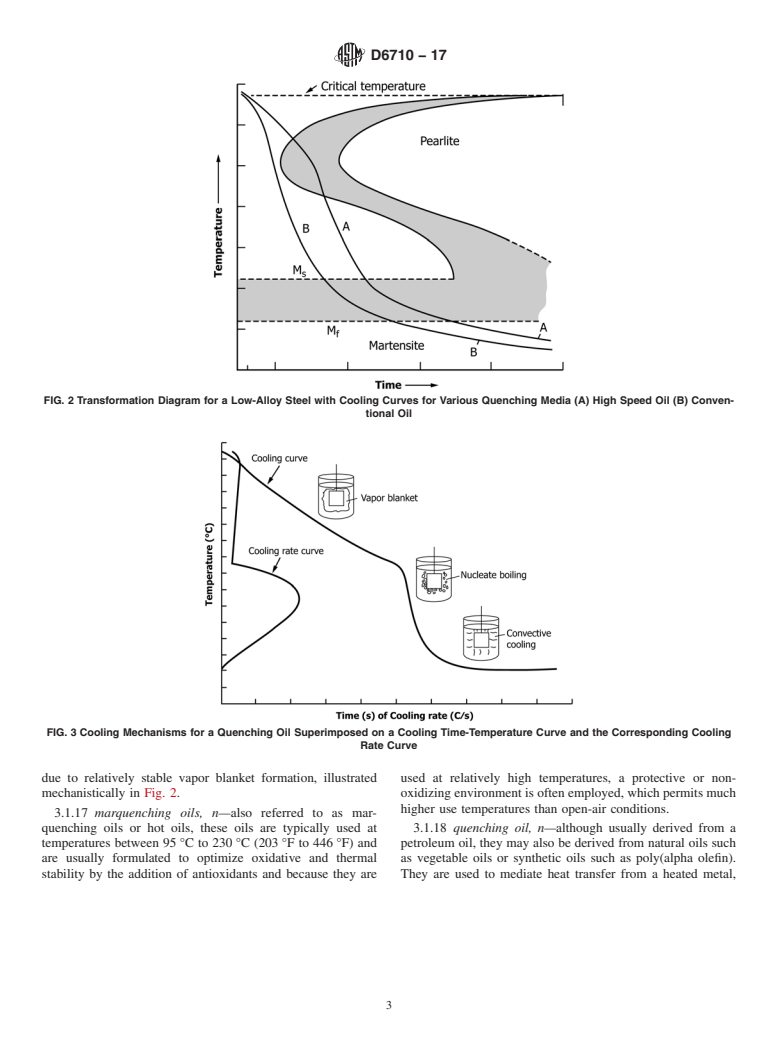
FIG. 1 (a) Conventional Quenching Cycle; (b) Martempering
3.1.3 martempering, n—cooling steel from the austenitiza- Cooling Mechanisms
tion temperature to a temperature just above the start of
3.1.9 convective cooling, n—after continued cooling, the
mertensite transformation (M ) for a time sufficient for the
s
interfacial temperature between the cooling metal surface and
temperature to eq
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D6710 − 02 (Reapproved 2012) D6710 − 17
Standard Guide for
1
Evaluation of Hydrocarbon-Based Quench Oil
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6710; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope Scope*
1.1 This guide covers information without specific limits, for selecting standard test methods for testing hydrocarbon-based
quench oils for quality and aging.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard.
1.2.1 Exception—The units given in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health and healthenvironmental practices and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to its use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D91 Test Method for Precipitation Number of Lubricating Oils
D92 Test Method for Flash and Fire Points by Cleveland Open Cup Tester
D94 Test Methods for Saponification Number of Petroleum Products
D95 Test Method for Water in Petroleum Products and Bituminous Materials by Distillation
D189 Test Method for Conradson Carbon Residue of Petroleum Products
D445 Test Method for Kinematic Viscosity of Transparent and Opaque Liquids (and Calculation of Dynamic Viscosity)
D482 Test Method for Ash from Petroleum Products
D524 Test Method for Ramsbottom Carbon Residue of Petroleum Products
D664 Test Method for Acid Number of Petroleum Products by Potentiometric Titration
D974 Test Method for Acid and Base Number by Color-Indicator Titration
D1298 Test Method for Density, Relative Density, or API Gravity of Crude Petroleum and Liquid Petroleum Products by
Hydrometer Method
D4052 Test Method for Density, Relative Density, and API Gravity of Liquids by Digital Density Meter
D4530 Test Method for Determination of Carbon Residue (Micro Method)
D6200 Test Method for Determination of Cooling Characteristics of Quench Oils by Cooling Curve Analysis
D6304 Test Method for Determination of Water in Petroleum Products, Lubricating Oils, and Additives by Coulometric Karl
Fischer Titration
D7042 Test Method for Dynamic Viscosity and Density of Liquids by Stabinger Viscometer (and the Calculation of Kinematic
Viscosity)
3
2.2 ISO Standards:
ISO 9950 Industrial Quenching Oils—Determination of Cooling Characteristics—Nickel-Alloy Probe Test Method, 1995-95-01
1
This guide is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
D02.L0.06 on Non-Lubricating Process Fluids.
Current edition approved April 15, 2012Aug. 1, 2017. Published May 2012August 2017. Originally approved in 2001. Last previous edition approved in 20072012 as
D6710–02(2007).D6710 – 02 (2012). DOI: 10.1520/D6710-02R12.10.1520/D6710-17.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Available from American National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St., 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D6710 − 17
FIG. 1 (a) Conventional Quenching Cycle; (b) Martempering
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
Quench Processing
3.1.1 austenitization, n—heating a steel containing less than the eutectoid concentration of carbon (about 0.8 mass %) to a
temperature just above the eutectoid temperature to decompose the pearlite microstructure to produce a face-centered cubic (fcc)
austenite-ferrite mixture.
3.1.2 dragout, n—solution ca
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.