ASTM F789-95a
(Specification)Standard Specification for Type PS-46 and Type PS-115 Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Plastic Gravity Flow Sewer Pipe and Fittings (Withdrawn 2004)
Standard Specification for Type PS-46 and Type PS-115 Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Plastic Gravity Flow Sewer Pipe and Fittings (Withdrawn 2004)
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers requirements and test methods for materials, dimensions, workmanship, flattening resistance, impact resistance, pipe stiffness, extrusion quality, joining systems, and a form of marking for Type PS-46 and Type PS-115 poly(vinyl chloride) (PVC) plastic, gravity flow sewer pipe having a minimum pipe stiffness of 46 psi (320 kPa) and 115 psi (790 kPa), respectively, and fittings.
1.2 Pipe and fittings produced to this specification shall be installed in accordance with Practice D2321.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are provided for information purposes only.
1.4 The following precautionary caveat pertains only to the test method portion, Section 8, of this specification: This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
WITHDRAWN RATIONALE
This specification covers requirements and test methods for materials, dimensions, workmanship, flattening resistance, impact resistance, pipe stiffness, extrusion quality, joining systems, and a form of marking for Type PS-46 and Type PS-115 poly(vinyl chloride) (PVC) plastic, gravity flow sewer pipe having a minimum pipe stiffness of 46 psi (320 kPa) and 115 psi (790 kPa), respectively, and fittings.
Formerly under the jurisdiction of Committee F17 on Plastic Piping Systems, this specification was withdrawn in July 2004. This specification was withdrawn in accordance with section 10.5.3.1 of the Regulations Governing ASTM Technical Committees, which requires that standards shall be updated by the end of the eighth year since the last approval date.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
An American National Standard
Designation: F 789 – 95a
Standard Specification for
Type PS-46 and Type PS-115 Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC)
Plastic Gravity Flow Sewer Pipe and Fittings
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F 789; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope D 2412 Test Method for Determination of External Loading
Characteristics of Plastic Pipe by Parallel-Plate Loading
1.1 This specification covers requirements and test methods
D 2444 Test Method for Impact Resistance of Thermoplas-
for materials, dimensions, workmanship, flattening resistance,
tic Pipe and Fittings by Means of a Tup (Falling Weight)
impact resistance, pipe stiffness, extrusion quality, joining
D 2564 Specification for Solvent Cements for Poly(Vinyl
systems, and a form of marking for Type PS-46 and Type
Chloride) (PVC) Plastic Piping Systems
PS-115 poly(vinyl chloride) (PVC) plastic, gravity flow sewer
D 2855 Practice for Making Solvent-Cemented Joints with
pipe having a minimum pipe stiffness of 46 psi (320 kPa) and
Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Pipe and Fittings
115 psi (790 kPa), respectively, and fittings.
D 3212 Specification for Joints for Drain and Sewer Plastic
1.2 Pipe and fittings produced to this specification shall be
Pipes Using Flexible Elastomeric Seals
installed in accordance with Practice D 2321.
F 402 Practice for Safe Handling of Solvent Cements,
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
Primers, and Cleaners Used for Joining Thermoplastic Pipe
as the standard. The values given in parentheses are provided
and Fittings
for information purposes only.
F 412 Terminology Relating to Plastic Piping Systems
1.4 The following precautionary caveat pertains only to the
F 477 Specification for Elastomeric Seals (Gaskets) for
test method portion, Section 8, of this specification: This
Joining Plastic Pipe
standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns,
2.2 Federal Standard:
if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user
Fed. Std. No. 123 Marking for Shipment (Civil Agencies)
of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health
2.3 Military Standard:
practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limita-
MIL-STD-129 Marking for Shipment and Storage
tions prior to use.
3. Terminology
2. Referenced Documents
3.1 Definitions:
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3.1.1 General—Definitions used in the specification are in
D 618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics and Electrical
accordance with Terminology F 412 unless otherwise indi-
Insulating Materials for Testing
cated. The abbreviation for poly(vinyl chloride) is PVC.
D 1784 Specification for Rigid Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC)
3.1.2 The terms PS-46 and PS-115 are not abbreviations but
Compounds and Chlorinated Poly(Vinyl Chloride)
,
3 4 rather arbitrary designations for products having minimum
(CPVC) Compounds
pipe stiffnesses, at 5 % deflection, of 46 psi (320 kPa) and 115
D 2122 Test Method for Determining Dimensions of Ther-
4 psi (790 kPa) when tested in accordance with Test Method
moplastic Pipe and Fittings
D 2412.
D 2152 Test Method for Degree of Fusion of Extruded
Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Pipe and Molded Fittings by
4. Significance and Use
Acetone Immersion
4.1 The requirements of this specification are intended to
D 2321 Practice for Underground Installation of Thermo-
provide pipe and fittings suitable for nonpressure drainage of
plastic Pipe for Sewers and Other Gravity–Flow Applica-
sewage and surface water.
tions
NOTE 1—Industrial waste disposal lines should be installed only with
specific approval of the cognizant code authority since chemicals not
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F-17 on Plastic
commonly found in drains and sewers and temperatures in excess of
Piping Systems and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F17.62 on Sewer.
140°F (60°C) may be encountered.
Current edition approved Oct. 10, 1995. Published December 1995. Originally
published as F 789 – 82. Last previous edition F 789 – 95.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.01.
3 5
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.02. Available from Standardization Documents Order Desk, Bldg. 4 Section D, 700
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.04. Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA 19111-5094, Attn: NPODS.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
F 789 – 95a
5. Materials 7.3 Socket Dimensions for Solvent Cemented Joints and
Fittings:
5.1 Basic Materials—The pipe shall be made of PVC
7.3.1 Socket Diameter—The inside diameter of the tapered
having a minimum cell classification of 12164-B as defined in
socket shall comply with the dimensions listed in Table 2 when
Specification D 1784 with a minimum tensile strength of 4000
determined in accordance with 8.5.1.
psi (28 MPa). The fittings shall be made of PVC plastic having
7.3.2 Socket Depth—The socket depth shall comply with
a cell classification of 12454-C or 13343-C as defined in
the dimensions listed in Table 2 when measured in accordance
Specification D 1784. Compounds that have different cell
with 8.5.2.
classifications because one or more properties are superior to
those of the specified compound are also acceptable. 7.4 Molded Fittings Dimensions:
5.2 Rework Material—Clean rework material generated
7.4.1 Wall Thickness of Molded Fittings—The wall thick-
from the manufacturer’s own pipe or fittings production may
ness of the waterway and socket or bell of molded fittings shall
be used by the same manufacturer provided that the pipe or
be no less than the minimum thickness listed for that nominal
fittings produced meet all the requirements of this specifica-
size in Table 2. For reducing fittings or those with small inlets,
tion. the minimum wall thickness of each inlet shall be no less than
5.3 Gaskets—Elastomeric seals (gaskets) shall comply with
the minimum wall thickness for that nominal size in Table 2.
the requirements of Specification F 477.
The thickness shall be determined in accordance with Test
5.4 Lubricant—The lubricant used for assembly shall have
Method D 2122 and 8.5.3.
no detrimental effect on the gasket or on the pipe or fittings.
7.4.2 Laying Length—The laying length of fittings shall
5.5 Solvent Cement—The PVC solvent cement used in
meet the requirements of Table 3, Table 4, Table 5, Table 6, and
joining of pipe and fittings for solvent cement joints shall
Table 7.
comply with the requirements of Specification D 2564.
7.4.3 Other Dimensions—Certain other fitting dimensions
are given in Table 8, Table 9, Table 10, and Table 11.
6. Joining Systems
7.5 Pipe Flattening—There shall be no evidence of split-
6.1 Gasketed Joints—The joint shall be designed so that
ting, cracking, or breaking when pipe is tested in accordance
when assembled, the gasket inside the bell will be compressed
with 8.6.
radially on the pipe spigot to form a watertight seal.
7.6 Pipe Impact Strength—The impact strength of the pipe
6.1.1 The joint shall be designed to avoid displacement of
at the time of manufacture shall not be less than the values
the gasket when installed in accordance with the manufactur-
given in Table 12 when tested in accordance with 8.7.
er’s recommendations.
6.1.2 The assembly of joints shall be in accordance with the NOTE 3—This test is intended only for use as a quality control test, not
as a simulated service test. As aged impact data is developed, the
pipe manufacturer’s recommendations.
applicable aged impact values will be included to reflect long-term
6.2 Solvent Cement Joints—In the solvent cement joint, the
performance needs.
pipe spigot wedges into the tapered socket and the surfaces
fuse together. The tapered socket may be a portion of a molded
7.7 Pipe Stiffness—Pipe stiffness values for the pipe shall
fitting or it may be a belled end of a pipe section.
equal or exceed 46 psi (320 kPa) or 115 psi (790 kPa) when
6.2.1 The assembly of joints shall be in accordance with
tested in accordance with 8.8.
Practice D 2855 and taking cognizance of Practice F 402.
7.8 Solvent Cement—The cement shall meet the require-
ments of Specification D 2564.
7. Requirements
7.9 Elastomeric Seals (Gaskets).
7.1 Workmanship—The pipe and fittings shall be homoge-
7.9.1 All gaskets shall meet the requirements of Specifica-
neous throughout and free of visible cracks, holes, foreign
tion F 477.
inclusions, or other injurious defects. The pipe shall be uniform
7.10 Joint Tightness:
in color, opacity, density, and other physical properties.
7.10.1 Elastomeric Seal (Gasketed) Joints—Joints made
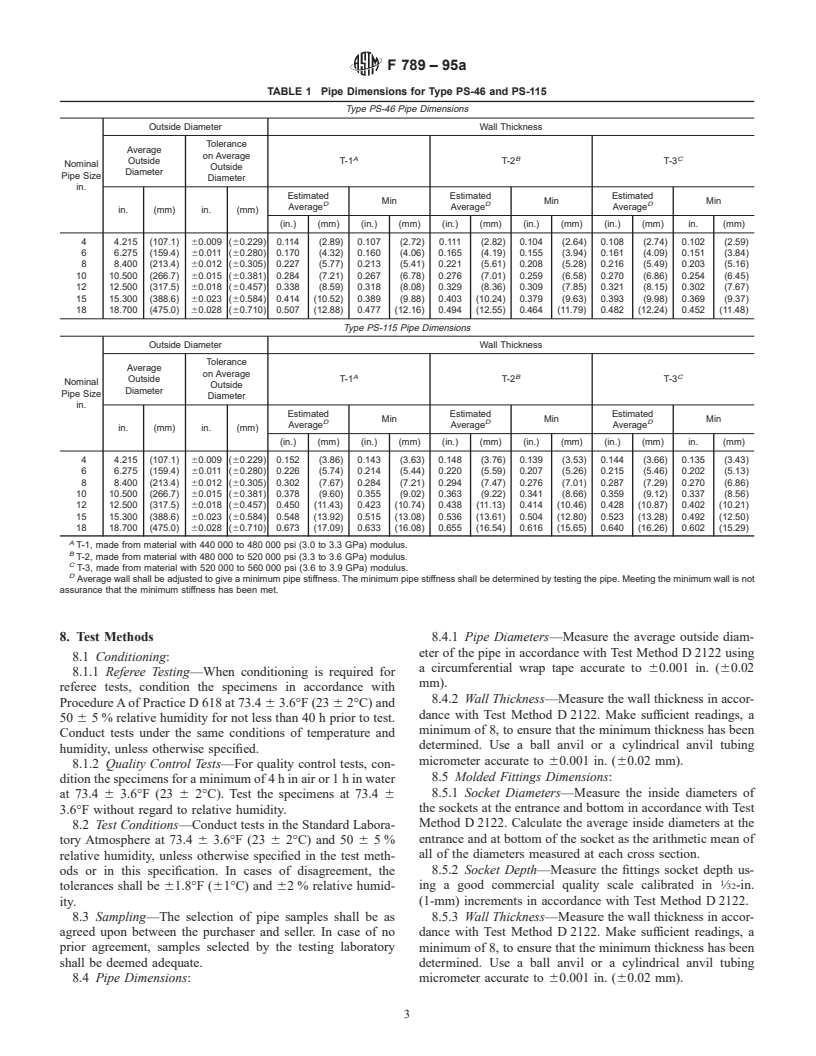
7.2 Pipe Dimensions:
with pipe and fittings having elastomeric seals show no sign of
7.2.1 Diameter—The average outside diameter shall meet
leakage when tested in accordance with Specification D 3212.
the requirements given in Table 1 when measured in accor-
All surfaces of the joint, upon which the gasket bears, shall be
dance with 8.4.1.
smooth and free of imperfections, ridges, fractures, or cracks
7.2.2 Wall Thickness—Pipe wall thickness shall meet the
that could adversely affect the seal.
requirements given in Table 1 when measured in accordance
7.10.2 Solvent Cement Joints—Joints made with solvent
with 8.4.2. In the case of belled pipe for solvent or gasket
cement joining shall show no sign of leakage when tested in
joining and fittings fabricated from pipe sections, the thickness
accordance with 8.9.2.
of the wall in the bell shall be considered satisfactory if it was
7.11 Acetone Immersion—The pipe shall not show flaking
formed from pipe meeting the above requirements.
or disintegration when tested in accordance with 8.10.
NOTE 2—Fabricated fittings with solvent-cemented components should
be made in accordance with Practice D 2855 and taking cognizance of NOTE 4—This test is intended only for use as a quality control test and
Practice F 402. Currently there are only fabricated fittings for 18-in. pipe. is not for use as a simulated service test.
F 789 – 95a
TABLE 1 Pipe Dimensions for Type PS-46 and PS-115
Type PS-46 Pipe Dimensions
Outside Diameter Wall Thickness
Tolerance
Average
on Average
A B C
Outside T-1 T-2 T-3
Nominal
Outside
Diameter
Pipe Size
Diameter
in.
Estimated Estimated Estimated
Min Min Min
D D D
Average Average Average
in. (mm) in. (mm)
(in.) (mm) (in.) (mm) (in.) (mm) (in.) (mm) (in.) (mm) in. (mm)
4 4.215 (107.1) 60.009 (60.229) 0.114 (2.89) 0.107 (2.72) 0.111 (2.82) 0.104 (2.64) 0.108 (2.74) 0.102 (2.59)
6 6.275 (159.4) 60.011 (60.280) 0.170 (4.32) 0.160 (4.06) 0.165 (4.19) 0.155 (3.94) 0.161 (4.09) 0.151 (3.84)
8 8.400 (213.4) 60.012 (60.305) 0.227 (5.77) 0.213 (5.41) 0.221 (5.61) 0.208 (5.28) 0.216 (5.49) 0.203 (5.16)
10 10.500 (266.7) 60.015 (60.381) 0.284 (7.21) 0.267 (6.78) 0.276 (7.01) 0.259 (6.58) 0.270 (6.86) 0.254 (6.45)
12 12.500 (317.5) 60.018 (60.457) 0.338 (8.59) 0.318 (8.08) 0.329 (8.36) 0.309 (7.85) 0.321 (8.15) 0.302 (7.67)
15 15.300 (388.6) 60.023 (60.584) 0.414 (10.52) 0.389 (9.88) 0.403 (10.24) 0.379 (9.63) 0.393 (9.98) 0.369 (9.37)
18 18.700 (475.0) 60.028 (60.710) 0.507 (12.88) 0.477 (12.16) 0.494 (12.55) 0.464 (11.79) 0.482 (12.24) 0.452 (11.48)
Type PS-115 Pipe Dimensions
Outside Diameter Wall Thickness
Tolerance
Average
on Average
A B C
Outside T-1 T-2 T-3
Nominal
Outside
Diameter
Pipe Size
Diameter
in.
Estimated Estimated Estimated
Min Min Min
D D D
Average Average Average
in. (mm) in. (mm)
(in.) (mm) (in.) (mm) (in.) (mm) (in.) (mm) (in.) (mm) in. (mm)
4 4.215 (107.1) 60.009 (60.229) 0.152 (3.86) 0.143 (3.63) 0.148 (3.76) 0.139 (3.53) 0.144 (3.66) 0.135 (3.43)
6 6.275 (159.4) 60.011 (60.280) 0.226 (5.74) 0.214 (5.44) 0.220 (5.59) 0.207 (5.26) 0.215 (5.46) 0.202 (5.13)
8 8.400 (213.4) 60.012 (60.305) 0.302 (7.67) 0.284 (7.21) 0.294 (7.47) 0.276 (7.01) 0.287 (7.29) 0.270 (6.86)
10 10.500 (266.7) 60.015 (60.381) 0.378 (9.60) 0.355 (9.02) 0.363 (9.22) 0.341 (8.66) 0.359 (9.12) 0.337 (8.56)
12 12.500 (317.5) 60.018 (60.457) 0.450 (11.43) 0.423 (10.74) 0.438 (11.13) 0.414 (10.46) 0.428 (10.87) 0.402 (10.21)
15 15.300 (388.6) 60.023 (60.584) 0.548 (13.92) 0.515 (13.08) 0.536 (13.61) 0.504 (12.80) 0.523 (13.28) 0.492 (12.50)
18 18.700 (475.0) 60.028 (60.710) 0.673 (17.09) 0.633 (16.08) 0.655 (16.54) 0.616 (15.65) 0.640 (16.26) 0.602 (15.29)
A
T-1, made from material with 440 000 to 480 000 psi (3.0 to 3.3 GPa) modulus.
B
T-2, made from material with 480 000 to 520 000 psi (3.3 to 3.6 GPa) modulus.
C
T-3, made from material with 520 000 to 560 000 psi (3.6 to 3.9 GPa) modulus.
D
Average wall shall be adjusted to give a minimum pipe stiffness. The minimum pipe stiffness shall be determined by testing the pipe. Meeting the minimum wall is not
assurance that the minimum stiffness has been met.
8. Test Methods 8.4.1 Pipe Diameters—Measure the average outside diam-
eter of the pipe in accordance with Test Method D 2122 using
8.1 Conditioning:
a circumferential wrap tape accurate to 60.001 in. (60.02
8.1.1 Referee Testing—When conditioning is required for
mm).
referee tests, condition the specimens in accordance with
8.4.2 Wall Thickness—Measure the wall thickness in accor-
Procedure A of Practice D 618 at 73.4 6 3.6°F (23 6 2°C) and
dance with Test Method D 2122. Make sufficient readings, a
50 6 5 % relative humidity for not less than 40 h prior to test.
minimum of 8, to ensure that the minimum thickness has been
Conduct tests under the same conditions of temperature and
determined. Use a ball anvil or a cylindrical anvil tubing
humidity, unless otherwise specified.
micrometer accurate to 60.001 in. (60.02 mm).
8.1.2 Quality Control Tests—For quality control tests, con-
8.5 Molded Fittings Dimensions:
dition the specimens for a minimum of4hinairor1hin water
8.5.1 Socket Diameters—Measure the inside diameters of
at 73.4 6 3.6°F (23 6 2°C). Test the specimens at 73.4 6
the sockets at the entrance and bottom in accordance with Test
3.6°F without regard to relative humidity.
Method D 2122. Calculate the average inside diameters at the
8.2 Test Conditions—Conduct tests in the Standard Labora-
entrance and at bottom of the socket as the arithmetic mean of
tory Atmosphere at 73.4 6 3.6°F (23 6 2°C) and 50 6 5%
all of the diameters measured at each cross section.
relative humidity, unless otherwise specified in the test meth-
8.5.2 Socket Depth—Measure the fittings socket depth us-
ods or in this specification. In cases of disagreement, the
tolerances shall be 61.8°F (61°C) and 62 % relative humid- ing a good commercial quality scale calibrated in ⁄
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.