ASTM F481-97(2019)
(Practice)Standard Practice for Installation of Thermoplastic Pipe and Corrugated Pipe in Septic Tank Leach Fields
Standard Practice for Installation of Thermoplastic Pipe and Corrugated Pipe in Septic Tank Leach Fields
ABSTRACT
This practice describes procedures for handling and installing thermoplastic pipe and corrugated pipe in septic tank leach fields, curtain drains, and from the septic tank to the leach field. Proper installation ensures that the pipe will satisfactorily convey and distribute partially treated waste water to a leaching field for additional treatment and disposal by soil absorption. The curtain or perimeter drain will function to protect the soil absorption capacity of the leach field. Pipe should be stored with support from a flat surface to prevent the pipe from developing a permanent set. Care should be exercised during loading, unloading, and in transit because pipe may be damaged by abrasion and sharp edges. Because thermoplastics are temporarily softened by high temperatures, care should be taken under these conditions to avoid damage during handling operations. Coiled pipe is not recommended for use in leach fields because it is difficult to install at the proper grade and alignment; it is acceptable with special equipment installation. Pipe can reach comparatively high temperatures when exposed to the sun and this reduces the pipe stiffness appreciably. Therefore, precautions must be taken to prevent the impact of sharp or heavy objects, the sudden imposition of heavy overburden or excessive pull on such pipe. The pipe regains full strength and stiffness as the temperature decreases to that of the soil; this will normally require about five minutes. Care in handling and installation should be exercised under low-temperature conditions to avoid damage. As temperatures decrease, some types of pipe tend to become more brittle and less flexible.
SCOPE
1.1 This practice describes procedures for handling and installing thermoplastic pipe and corrugated pipe in septic tank leach fields, curtain drains, and from the septic tank to the leach field. Proper installation ensures that the pipe will satisfactorily convey and distribute partially treated waste water to a leaching field for additional treatment and disposal by soil absorption. The curtain or perimeter drain will function to protect the soil absorption capacity of the leach field.
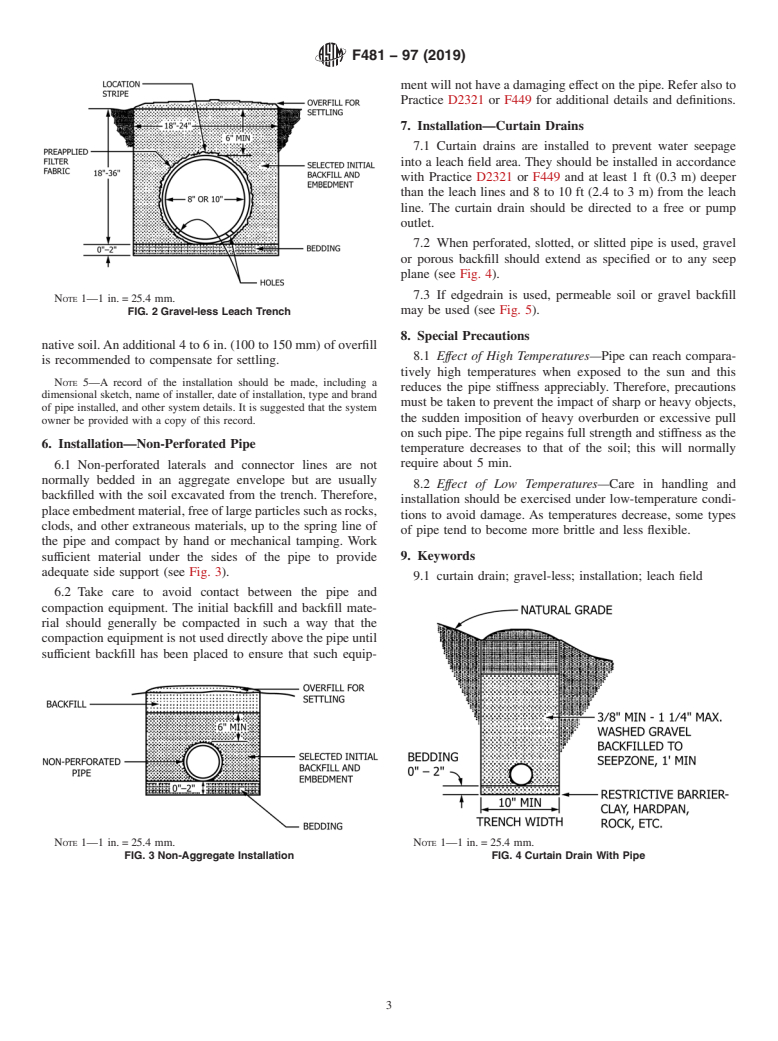
1.2 To ensure compliance with local regulatory provisions, the local approving authority (local health departments and so forth) should be contacted regarding specific requirements for leach field design materials and installation.
1.3 This practice applies to pipe and fittings made under each of the following ASTM specifications:
1.3.1 For transport from tank to leach field: Specifications D2680, D2729, D2751, D2852, D3034, F405, F758, F789, F810, F891, F892, and F949.
1.3.2 Perforated, for use in leach field or curtain drain: Specifications D2729, D2751, F405, F810, F891, and F892.
1.4 Pipe intended for installation in accordance with this practice should have a minimum pipe stiffness as specified in the appropriate product standard referenced in 1.3.1 or 1.3.2.
1.5 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific precautionary statements, see Section 7.
1.7 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: F481 − 97 (Reapproved 2019)
Standard Practice for
Installation of Thermoplastic Pipe and Corrugated Pipe in
Septic Tank Leach Fields
ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationF481;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginal
adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.Asuperscript
epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
1.1 This practice describes procedures for handling and
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
installing thermoplastic pipe and corrugated pipe in septic tank
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
leachfields,curtaindrains,andfromtheseptictanktotheleach
field. Proper installation ensures that the pipe will satisfactorily
2. Referenced Documents
convey and distribute partially treated waste water to a
2.1 ASTM Standards:
leaching field for additional treatment and disposal by soil
D1600 Terminology forAbbreviatedTerms Relating to Plas-
absorption. The curtain or perimeter drain will function to
tics
protect the soil absorption capacity of the leach field.
D2321 PracticeforUndergroundInstallationofThermoplas-
1.2 To ensure compliance with local regulatory provisions,
tic Pipe for Sewers and Other Gravity-Flow Applications
the local approving authority (local health departments and so
D2680 Specification for Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene
forth) should be contacted regarding specific requirements for
(ABS) and Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Composite Sewer
leach field design materials and installation.
Piping
1.3 This practice applies to pipe and fittings made under
D2729 Specification for Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Sewer
each of the following ASTM specifications:
Pipe and Fittings
1.3.1 For transport from tank to leach field: Specifications
D2751 Specification for Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene
D2680, D2729, D2751, D2852, D3034, F405, F758, F789,
(ABS) Sewer Pipe and Fittings (Withdrawn 2014)
F810, F891, F892, and F949.
D2852 Specification for Styrene-Rubber (SR) Plastic Drain
1.3.2 Perforated, for use in leach field or curtain drain:
Pipe and Fittings
Specifications D2729, D2751, F405, F810, F891, and F892.
D3034 Specification for Type PSM Poly(Vinyl Chloride)
(PVC) Sewer Pipe and Fittings
1.4 Pipe intended for installation in accordance with this
F405 Specification for Corrugated Polyethylene (PE) Pipe
practice should have a minimum pipe stiffness as specified in
and Fittings (Withdrawn 2015)
the appropriate product standard referenced in 1.3.1 or 1.3.2.
F412 Terminology Relating to Plastic Piping Systems
1.5 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
F449 Practice for Subsurface Installation of Corrugated
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
Polyethylene Pipe for Agricultural Drainage or Water
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
Table Control
and are not considered standard.
F758 Specification for Smooth-Wall Poly(Vinyl Chloride)
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the
(PVC) Plastic Underdrain Systems for Highway, Airport,
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
and Similar Drainage
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
F789 Specification for Type PS-46 and Type PS-115 Poly-
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Plastic Gravity Flow Sewer Pipe
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
and Fittings (Withdrawn 2004)
For specific precautionary statements, see Section 7.
F810 Specification for Smoothwall Polyethylene (PE) Pipe
1.7 This international standard was developed in accor-
for Use in Drainage andWaste DisposalAbsorption Fields
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
1 2
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F17 on Plastic For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Piping Systems and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F17.65 on Land contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Drainage. Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Current edition approved Aug. 1, 2019. Published August 2019. Originally the ASTM website.
approvedin1976.Lastpreviouseditionapprovedin2014asF481 – 97(2014).DOI: The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
10.1520/F0481-97R19. www.astm.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
F481 − 97 (2019)
F891 Specification for Coextruded Poly(Vinyl Chloride)
(PVC) Plastic Pipe With a Cellular Core
F892 Specification for Polyethylene (PE) Corrugated Pipe
With a Smooth Interior and Fittings (Withdrawn 2001)
F949 Specification for Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Corru-
gated Sewer Pipe With a Smooth Interior and Fittings
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions are in accordance with Terminology F412 NOTE 1—1 in. = 25.4 mm.
and abbreviations are in accordance with Terminology D1600, FIG. 1 Gravel Leach Trench
unless otherwise specified.
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
should not be compacted; for example, by tamping or walking,
3.2.1 dual-wall pipe—pipe with corrugated exterior and
as this may damage the soil interface.
smooth interior.
5.4 Fittings recommended by the pipe manufacturer should
3.2.2 pipe—smooth or corrugated interior wall thermoplas-
be used at all joints and for changes of direction except that
tic pipe.
pipe may be bent to a radius of not less than 5 times the
diameter.
4. General Requirements
5.5 Unless otherwise specified, pipe should be laid true to
4.1 Storage—Pipe should be stored with support from a flat
grade and aligned in the center of the trench, with the top print
surface to prevent the pipe from developing a permanent set.
line or location stripe at the 12 o’clock position so that holes
4.2 Handling—Care should be exercised during loading,
are placed down. It should be held in place by alignment
unloading, and in transit because pipe may be damaged by
supports, such as wooden stakes or steel rods.
abrasion and sharp edges. Because thermoplastics are tempo-
rarily softened by high temperatures, care should be taken NOTE 3—Some authorities require the covering of the line with
untreated building paper or a geotextile to prevent entry of aggregate,
under these conditions to avoid damage during handling
prior to the next step.This is usually required only in areas that require the
operations.
perforations to be oriented on the top instead of the bottom of the pipe.
4.3 If contact with chemicals not ordinarily present in
5.6 For gravel systems, place aggregate around the pipe
sanitary sewage is anticipated, the approval of the regulatory
until only the top center is still visible. Make a final check of
authority to install pipe should be obtained.
grade and alignment. It is particularly important that the side
walls be given uniform and continuous support to provide
NOTE 1—The manufactu
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.