ASTM D6565-00(2005)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determination of Water (Moisture) Content of Soil by the Time-Domain Reflectometry (TDR) Method (Withdrawn 2014)
Standard Test Method for Determination of Water (Moisture) Content of Soil by the Time-Domain Reflectometry (TDR) Method (Withdrawn 2014)
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
The determination of the water-content, or moisture content, of soil is one of the fundamental needs in the soil physics and hydrology disciplines. The need arises from requirements for defining the optimal time for irrigation, the infiltration rate, the soil-moisture flux, contaminant transport rates, and evaluating the potential for leakage from a waste site or a surface or subsurface barrier.
The TDR application covered in this test method is that used for point measurements of moisture content in soil. The application is either through manual insertion into the soil or by burying a probe in the subsurface to acquire moisture content data at a specific location. In addition, core samples may be tested with TDR at a drill site to acquire real-time soil moisture data.
SCOPE
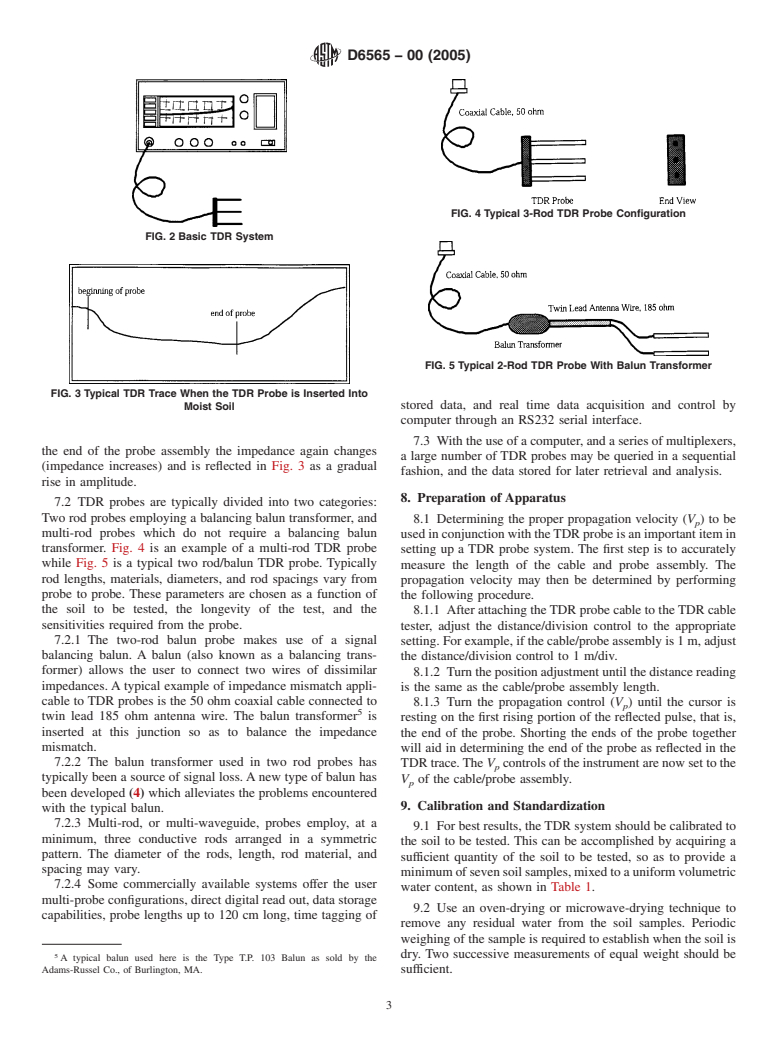
1.1 This test method covers the determination of water content (or moisture content) in soil by the use of the electromagnetic technique called Time-Domain Reflectometry (TDR).
1.2 This test method was written to detail the procedure for conventional TDR measurements of soil. Other TDR applications exist for the purpose of quantifying water content in soil and are not covered here, such as flat probe technologies and wetting front advance methods.
1.3 Commercial TDR applications exist which automate the TDR methodology and are not detailed in this test method. It is likely that overlap exists in the automated commercial systems versus this applied method, and the user is encouraged to adhere to this test method when applicable.
1.4 This test method is one of a series on vadose zone characterization methods. Other standards have been prepared on vadose zone characterization techniques.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
WITHDRAWN RATIONALE
This test method covered the determination of water content (or moisture content) in soil by the use of the electromagnetic technique called Time-Domain Reflectometry (TDR).
Formerly under the jurisdiction of Committee D18 on Soil and Rock, this test method was withdrawn in July 2014 in accordance with section 10.6.3 of the Regulations Governing ASTM Technical Committees, which requires that standards shall be updated by the end of the eighth year since the last approval date.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D6565 −00(Reapproved 2005)
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Water (Moisture) Content of Soil by the
1
Time-Domain Reflectometry (TDR) Method
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6565; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope (Moisture) Content of Soil and Rock by Mass
D4643 Test Method for Determination of Water (Moisture)
1.1 This test method covers the determination of water
Content of Soil by Microwave Oven Heating
content (or moisture content) in soil by the use of the
D4700 Guide for Soil Sampling from the Vadose Zone
electromagnetic technique called Time-Domain Reflectometry
D4944 TestMethodforFieldDeterminationofWater(Mois-
(TDR).
ture)ContentofSoilbytheCalciumCarbideGasPressure
1.2 This test method was written to detail the procedure for
Tester
conventional TDR measurements of soil. Other TDR applica-
D5220 Test Method for Water Mass per Unit Volume of Soil
tions exist for the purpose of quantifying water content in soil
and Rock In-Place by the Neutron Depth Probe Method
and are not covered here, such as flat probe technologies and
wetting front advance methods.
3. Terminology
1.3 Commercial TDR applications exist which automate the 3.1 Definitions:
TDR methodology and are not detailed in this test method. It is
3.1.1 time domain reflectometry (TDR)—an electromagnetic
likely that overlap exists in the automated commercial systems method used in the determination of water content of soil.
versus this applied method, and the user is encouraged to
3.1.2 Definitions of other terminology used in this guide
adhere to this test method when applicable.
may be found in Terminology D653.
1.4 This test method is one of a series on vadose zone
4. Summary of Test Method
characterization methods. Other standards have been prepared
on vadose zone characterization techniques.
4.1 Aspeciallyconstructed,multi-wave-guideTDRprobeis
inserted into the soil. The electronic cable tester (or automated
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
commercial TDR electronics) is used to send a pulsed wave-
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
form to the probe.The cable tester then receives a return signal
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
which was influenced by the dielectric constant of the soil,
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
which in turn is a function of water content.An analysis of the
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
waveform trace supplies the necessary information to calculate
2. Referenced Documents the water content of the soil.
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
5. Significance and Use
D653 Terminology Relating to Soil, Rock, and Contained
5.1 The determination of the water-content, or moisture
Fluids
content, of soil is one of the fundamental needs in the soil
D1452 Practice for Soil Exploration and Sampling byAuger
physics and hydrology disciplines. The need arises from
Borings
requirements for defining the optimal time for irrigation, the
D2216 Test Methods for Laboratory Determination of Water
infiltration rate, the soil-moisture flux, contaminant transport
rates, and evaluating the potential for leakage from a waste site
or a surface or subsurface barrier.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D18 on Soil and
Rock and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D18.21.02 on Vadose Zone
5.2 The TDR application covered in this test method is that
Monitoring.
used for point measurements of moisture content in soil. The
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2005. Published December 2005. Originally
applicationiseitherthroughmanualinsertionintothesoilorby
approved in 2000. Last previous edition approved in 2000 as D6565 – 00. DOI:
10.1520/D6565-00R05.
burying a probe in the subsurface to acquire moisture content
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
data at a specific location. In addition, core samples may be
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
tested withTDR at a drill site to acquire real-time soil moisture
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. data.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D6565−00 (2005)
Fig. 1(a ) Properly installed probe Fig. 1(b) Improperly installed probe
FIG. 1Properly and Improperly Installed TDR Probes
6. Interferences 6.5 A static charge on the coaxial cab
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.