ASTM A600-92a(2016)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Tool Steel High Speed
Standard Specification for Tool Steel High Speed
ABSTRACT
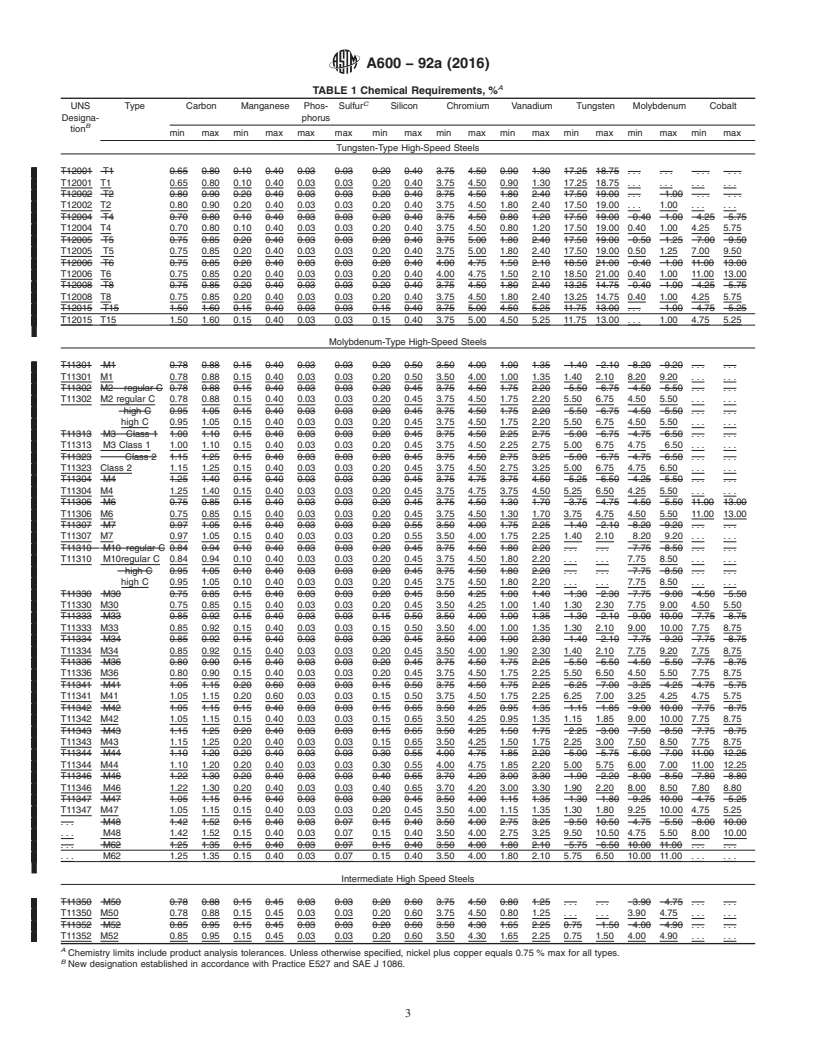
This specification covers seven tungsten-type (types T1, T2, T4, T5, T6, T8, and T15) and nineteen molybdenum-type high-speed steels (types M1, M2, M3, M4, M6, M7, M10, M30, M33, M34, M36, M41, M42, M43, M44, M46, M47, M48, and M62) in the form of annealed, hot-rolled bars, forgings, plate, sheet, or strip, and annealed, cold-finished bars or forgings used primarily in the fabrication of tools. Two intermediate high speed tool steels designated as M50 and M52 are also covered. Unless otherwise specified, material shall be made by an electric melting process. A chemical analysis of each heat of steel shall be made to determine the percentage of the elements specified (including carbon, manganese, phosphorus, sulfur, silicon, chromium, vanadium, tungsten, molybdenum, and cobalt) and these values shall conform to the requirements as to the prescribed chemical composition. Requirements for: (1) heat treatment such as austenitizing, quenching, and tempering, (2) hardness testing (3) macrostructure and macroetch standard for porosity and ingot pattern, and (4) decarburization determination are detailed. The maximum Brinell hardness and minimum Rockwell C hardness for the tool steels are given.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers tungsten-type and molybdenum-type high-speed steels available as annealed, hot-rolled bars, forgings, plate, sheet, or strip, and annealed, cold-finished bars or forgings used primarily in the fabrication of tools.
1.2 Seven types of tungsten high-speed tool steels designated T1, T2, etc., seventeen types of molybdenum high-speed tool steels designated M1, M2, etc., and two intermediate high speed steels designated as M50 and M52 are covered. Selection will depend upon design, service conditions, and mechanical properties.
1.3 The term “high-speed steel” is described and its minimum requirements are covered in the Annex.
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation:A600 −92a (Reapproved 2016)
Standard Specification for
1
Tool Steel High Speed
This standard is issued under the fixed designation A600; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
3
1. Scope Open-Hearth Iron, and Wrought Iron (Withdrawn 1995)
E45Test Methods for Determining the Inclusion Content of
1.1 This specification covers tungsten-type and
Steel
molybdenum-type high-speed steels available as annealed,
E59Practice for Sampling Steel and Iron for Determination
hot-rolled bars, forgings, plate, sheet, or strip, and annealed,
3
of Chemical Composition (Withdrawn 1996)
cold-finished bars or forgings used primarily in the fabrication
2.2 Military Standard:
of tools.
MIL-STD-163 Steel Mill Products, Preparation for Ship-
4
1.2 Seven types of tungsten high-speed tool steels desig-
ment and Storage
natedT1,T2, etc., seventeen types of molybdenum high-speed
2.3 Federal Standards:
4
tool steels designated M1, M2, etc., and two intermediate high
Fed. Std. No. 123Marking for Shipment (Civil Agencies)
speedsteelsdesignatedasM50andM52arecovered.Selection Fed. Std. No. 183Continuous Identification Marking of Iron
4
will depend upon design, service conditions, and mechanical
and Steel Products
properties.
3. Classification
1.3 The term “high-speed steel” is described and its mini-
3.1 Material in accordance with this specification is classi-
mum requirements are covered in the Annex.
fied by chemical composition. Types correspond to respective
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
AISI designations.
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
3.1.1 Types T1, T2, T4, T5, T6, T8, and T15 are character-
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
ized by a controlled high tungsten content along with other
and are not considered standard.
alloying elements.
3.1.2 Types M1, M2, M3, M4, M6, M7, M10, M30, M33,
2. Referenced Documents
M34, M36, M41, M42, M43, M44, M46, M47, M48, and M62
are characterized by a controlled high molybdenum content
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
along with other alloying elements.
A370Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing
3.1.3 Types M2, M3, and M10 are further classified accord-
of Steel Products
ing to carbon range. Type M3 is further classified according to
A388/A388MPractice for Ultrasonic Examination of Steel
vanadium range.
Forgings
3.1.4 Types M50 and M52 are considered intermediate high
A561Practice for Macroetch Testing of Tool Steel Bars
speed steels in view of their lower total alloy content than the
A700Guide for Packaging, Marking, and Loading Methods
standard types. These leaner alloy grades normally are limited
for Steel Products for Shipment
to less severe service conditions.
E3Guide for Preparation of Metallographic Specimens
E30TestMethodsforChemicalAnalysisofSteel,CastIron,
4. Ordering Information
4.1 Ordersformaterialunderthisspecificationshallinclude
the following information, as required to describe adequately
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee A01 on Steel,
the desired material:
Stainless Steel and RelatedAlloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
4.1.1 Name of material (high-speed tool steel),
A01.29 on Tool Steels.
4.1.2 Type,
Current edition approved March 1, 2016. Published June 2016. Originally
approved in 1969. Last previous edition approved in 2010 as A600–92a (2010).
DOI: 10.1520/A0600-92AR16.
2 3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM www.astm.org.
4
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from DLA Document Services, Building 4/D, 700 Robbins Avenue,
the ASTM website. Philadelphia, PA 19111-5094, http://quicksearch.dla.mil.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
A600−92a (2016)
4.1.3 Shape (sheet, strip, plate, flat bar, round bar, square to chemical composition specified in Table 1. If requested or
bar, hexagon bar, octagon, special shapes), required, the chemical composition shall be reported to the
4.1.4 Dimensions (thickness, width, diameter, length).
...
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: A600 − 92a (Reapproved 2016)
Standard Specification for
1
Tool Steel High Speed
This standard is issued under the fixed designation A600; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
3
1. Scope Open-Hearth Iron, and Wrought Iron (Withdrawn 1995)
E45 Test Methods for Determining the Inclusion Content of
1.1 This specification covers tungsten-type and
Steel
molybdenum-type high-speed steels available as annealed,
E59 Practice for Sampling Steel and Iron for Determination
hot-rolled bars, forgings, plate, sheet, or strip, and annealed,
3
of Chemical Composition (Withdrawn 1996)
cold-finished bars or forgings used primarily in the fabrication
2.2 Military Standard:
of tools.
MIL-STD-163 Steel Mill Products, Preparation for Ship-
4
1.2 Seven types of tungsten high-speed tool steels desig- ment and Storage
nated T1, T2, etc., seventeen types of molybdenum high-speed
2.3 Federal Standards:
4
tool steels designated M1, M2, etc., and two intermediate high Fed. Std. No. 123 Marking for Shipment (Civil Agencies)
speed steels designated as M50 and M52 are covered. Selection
Fed. Std. No. 183 Continuous Identification Marking of Iron
4
will depend upon design, service conditions, and mechanical and Steel Products
properties.
3. Classification
1.3 The term “high-speed steel” is described and its mini-
3.1 Material in accordance with this specification is classi-
mum requirements are covered in the Annex.
fied by chemical composition. Types correspond to respective
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
AISI designations.
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
3.1.1 Types T1, T2, T4, T5, T6, T8, and T15 are character-
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
ized by a controlled high tungsten content along with other
and are not considered standard.
alloying elements.
3.1.2 Types M1, M2, M3, M4, M6, M7, M10, M30, M33,
2. Referenced Documents
M34, M36, M41, M42, M43, M44, M46, M47, M48, and M62
2 are characterized by a controlled high molybdenum content
2.1 ASTM Standards:
along with other alloying elements.
A370 Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing
3.1.3 Types M2, M3, and M10 are further classified accord-
of Steel Products
ing to carbon range. Type M3 is further classified according to
A388/A388M Practice for Ultrasonic Examination of Steel
vanadium range.
Forgings
3.1.4 Types M50 and M52 are considered intermediate high
A561 Practice for Macroetch Testing of Tool Steel Bars
speed steels in view of their lower total alloy content than the
A700 Guide for Packaging, Marking, and Loading Methods
standard types. These leaner alloy grades normally are limited
for Steel Products for Shipment
to less severe service conditions.
E3 Guide for Preparation of Metallographic Specimens
E30 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Steel, Cast Iron,
4. Ordering Information
4.1 Orders for material under this specification shall include
the following information, as required to describe adequately
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A01 on Steel,
the desired material:
Stainless Steel and Related Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
4.1.1 Name of material (high-speed tool steel),
A01.29 on Tool Steels.
4.1.2 Type,
Current edition approved March 1, 2016. Published June 2016. Originally
approved in 1969. Last previous edition approved in 2010 as A600 – 92a (2010).
DOI: 10.1520/A0600-92AR16.
2 3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM www.astm.org.
4
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from DLA Document Services, Building 4/D, 700 Robbins Avenue,
the ASTM website. Philadelphia, PA 19111-5094, http://quicksearch.dla.mil.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
A600 − 92a (2016)
4.1.3 Shape (sheet, strip, plate, flat bar, round bar, square to chemical composition specified in Table 1. If requested or
bar, hexagon bar, octagon, special shapes), required, the chemical composition shall be reported to the
4.1.4 Dimensions (thickness, width, diameter, length). (For purchaser or his representative.
coils, include the minimum inside diameter or inside dia
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: A600 − 92a (Reapproved 2010) A600 − 92a (Reapproved 2016)
Standard Specification for
1
Tool Steel High Speed
This standard is issued under the fixed designation A600; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope
1.1 This specification covers tungsten-type and molybdenum-type high-speed steels available as annealed, hot-rolled bars,
forgings, plate, sheet, or strip, and annealed, cold-finished bars or forgings used primarily in the fabrication of tools.
1.2 Seven types of tungsten high-speed tool steels designated T1, T2, etc., seventeen types of molybdenum high-speed tool
steels designated M1, M2, etc., and two intermediate high speed steels designated as M50 and M52 are covered. Selection will
depend upon design, service conditions, and mechanical properties.
1.3 The term “high-speed steel” is described and its minimum requirements are covered in the Annex.
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
A370 Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing of Steel Products
A388/A388M Practice for Ultrasonic Examination of Steel Forgings
A561 Practice for Macroetch Testing of Tool Steel Bars
A700 Guide for Packaging, Marking, and Loading Methods for Steel Products for Shipment
E3 Guide for Preparation of Metallographic Specimens
3
E30 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Steel, Cast Iron, Open-Hearth Iron, and Wrought Iron (Withdrawn 1995)
E45 Test Methods for Determining the Inclusion Content of Steel
3
E59 Practice for Sampling Steel and Iron for Determination of Chemical Composition (Withdrawn 1996)
2.2 Military Standard:
4
MIL-STD-163 Steel Mill Products, Preparation for Shipment and Storage
2.3 Federal Standards:
4
Fed. Std. No. 123 Marking for Shipment (Civil Agencies)
4
Fed. Std. No. 183 Continuous Identification Marking of Iron and Steel Products
3. Classification
3.1 Material in accordance with this specification is classified by chemical composition. Types correspond to respective AISI
designations.
3.1.1 Types T1, T2, T4, T5, T6, T8, and T15 are characterized by a controlled high tungsten content along with other alloying
elements.
3.1.2 Types M1, M2, M3, M4, M6, M7, M10, M30, M33, M34, M36, M41, M42, M43, M44, M46, M47, M48, and M62 are
characterized by a controlled high molybdenum content along with other alloying elements.
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A01 on Steel, Stainless Steel and Related Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee A01.29
on Tool Steels.
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2010March 1, 2016. Published December 2010June 2016. Originally approved in 1969. Last previous edition approved in 20042010 as
A600 – 92a (2010). (2004). DOI: 10.1520/A0600-92AR10.10.1520/A0600-92AR16.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on www.astm.org.
4
Available from Standardization Documents Order Desk, DODSSP, Bldg. 4, Section D, 700 Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA 19111-5098, http://dodssp.daps.dla.mil.DLA
Document Services, Building 4/D, 700 Robbins Avenue, Philadelphia, PA 19111-5094, http://quicksearch.dla.mil.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
A600 − 92a (2016)
3.1.3 Types M2, M3, and M10 are further classified according to carbon range. Type M3 is further classified according to
vanadium range.
3.1.4 Types M50 and M52 are considered intermediate high speed steels in view of their lower total alloy content than the
standard types. These leaner alloy grades normally are limited to less severe service conditions.
4. Ordering Information
4.1 Orders for material under this specification shall include the following information, as required t
...











Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.