ASTM D1560-92(2005)
(Test Method)Standard Test Methods for Resistance to Deformation and Cohesion of Bituminous Mixtures by Means of Hveem Apparatus
Standard Test Methods for Resistance to Deformation and Cohesion of Bituminous Mixtures by Means of Hveem Apparatus
SCOPE
1.1 These test methods cover the determination of (1) the resistance to deformation of compacted bituminous mixtures by measuring the lateral pressure developed when applying a vertical load by means of the Hveem stabilometer and (2) the cohesion of compacted bituminous mixtures by measuring the force required to break or bend the sample as a cantilever beam by means of the Hveem cohesiometer.
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.2 The values stated in acceptable metric units are to be regarded as the standard.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D1560–92 (Reapproved 2005)
Standard Test Methods for
Resistance to Deformation and Cohesion of Bituminous
Mixtures by Means of Hveem Apparatus
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 1560; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope cohesion test is sometimes used for fine mixes such as sand
mixes wherein cohesion, or tensile strength, is of major or
1.1 These test methods cover the determination of (1) the
primary importance. The cohesion test is also sometimes used
resistance to deformation of compacted bituminous mixtures
for the design of cold mixes containing emulsified asphalt.
by measuring the lateral pressure developed when applying a
vertical load by means of the Hveem stabilometer and (2) the
RESISTANCE TO DEFORMATION
cohesion of compacted bituminous mixtures by measuring the
force required to break or bend the sample as a cantilever beam
4. Apparatus
by means of the Hveem cohesiometer.
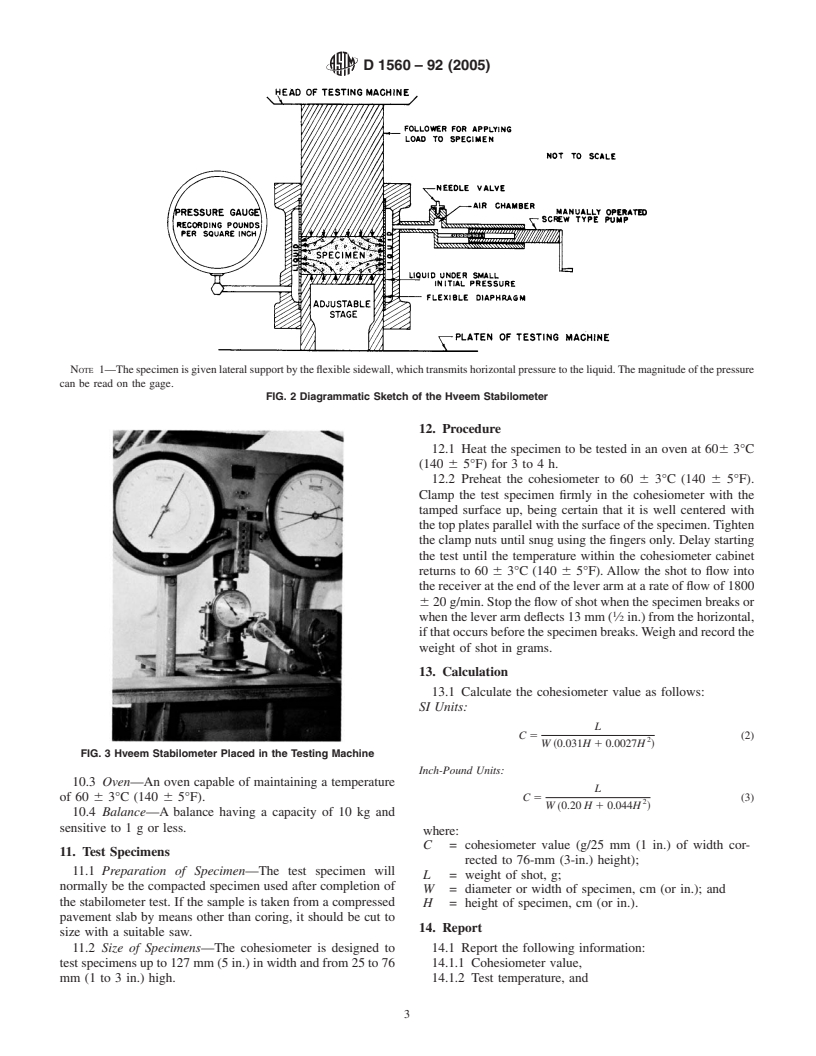
4.1 Stabilometer—TheHveemstabilometer(Fig.1andFig.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
2) is a triaxial testing device consisting essentially of a rubber
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
sleeve within a metal cyclinder containing a liquid which
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
registers the horizontal pressure developed by a compacted test
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
specimen as a vertical load is applied.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
4.2 Testing Machine—Acompression testing machine hav-
1.3 The values stated in acceptable metric units are to be
ing a minimum capacity of 44.5 kN (10 000 lbf). Fig. 3 shows
regarded as the standard.
the stabilometer in a testing machine. The 22-kN (50 000-lbf)
capacity compression testing machine specified in Practice
2. Referenced Documents
D 1561, is normally used to perform the stabilometer test.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
4.3 Test Specimen Push-Out Device—A device, to push the
D 1561 Practice for Preparation of Bituminous MixtureTest
specimen out of the mold (see Fig. 4 for an example).
Specimens by Means of California Kneading Compactor
4.4 Oven—An oven capable of maintaining a temperature
D 3666 Specification for Minimum Requirements forAgen-
of 60 6 3°C (140 6 5°F).
cies Testing and Inspecting Road and Paving Materials
4.5 Calibration Cylinder—A hollow metal cylinder 101.6
2.2 California Department of Transportation Standards:
6 0.13 mm (4 6 0.005 in.) in outside diameter by 140 6 6.4
Test 306 Method of Test for Cohesiometer Value
mm (5.5 6 0.25 in.) high (for calibration purposes).
Test 366 Method of Test for Stabilometer Value
4.6 Rubber Bulb—For introducing air into the stabilometer.
4.7 Follower—One solid wall metal follower 101.2 mm
3. Significance and Use
(3.985in.)indiameterby140mm(5 ⁄2in.)high(seeFig.5and
3.1 The results of the deformation and cohesion tests can be
Fig. 6).
used for specification purposes or for mix design purposes or
both. For example, these values can be used for specification
5. Test Specimens
compliance testing of aggregate properties. They can also be
5.1 Test specimens shall be mixed and compacted in accor-
used for specification compliance testing of the mix. The
dance with those procedures normally used. The procedure
described in Practice D 1561 is a suitable procedure.
These methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D04 on Road
6. Adjustment of Stabilometer
and Paving Materials and are the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D04.20 on
Mechanical Tests of Bituminous Mixtures.
6.1 Adjust the stabilometer base so that the distance from
Current edition approved Jan. 1, 2005. Published January 2005. Originally
the bottom of the upper tapered ring (see Fig. 1) to the top of
approved in 1958. Last previous edition approved in 2000 as D 1560 – 92 (2000).
2 the base is 89 mm (3.5 in.).
A more detailed description of the procedures for performing the tests is
available on request from the California Dept. of Transportation, 5900 Folsom 6.2 Place the calibration cylinder (preheated to 60°C
Blvd., Sacramento, CA 95819. Also available is a procedure containing details
(140°F))inplaceinthestabilometer.Seatitfirmlyonthestage,
regarding the operation and calibration of the stabilometer and the replacement of
hold it in place with either the hand or a vertical load of 0.45
the stabilometer diaphragm.
kN (100 lbf) in the testing machine, and apply a horizontal
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 04.03.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
D1560–92 (2005)
TABLE 1
seated type of upper head, the locking shims used during the
fabrication of the test specimen must be removed before
performing the stabilometer test. Start the vertical movement
of the press (speed of 1.3 mm (0.05 in.)/min) and record the
stabilometer gage readings when the vertical load is 13.4, 22.3,
and 26.7 kN (3000, 5000, and 6000 lbf). Stop the vertical
movement of the press when the total load reaches 26.7 kN
(6000 lbf). Immediately reduce the vertical load to 4.45 6 0.45
kN (1000 6 100 lbf), and then adjust the horizontal pressure to
34.5 kPa (5 psi). This will result in a further reduction of the
vertical load to less than 4.45 kN (1000 lbf).This is normal and
no compensation need be made. Measure the number of turns
of the pump handle required to raise the horizontal pressure
from 34.5 to 689 kPa (5 to 100 psi) with the specimen in place.
Turn the pump handle at approximately two turns per second
when applying this pressure. The number of turns measured is
the displacement reading, D. In measuring the displacement,
the vertical load will increase and at times exceed 4.45 kN
(1000 lbf). As before, these changes in load are characteristic
and no adjustment or compensation is required.
8. Calculation
A—Air cell.
8.1 Determine the stabilometer value of the specimen as
B—Displacement pump.
follows:
C—200-psi pressure gage.
D—Ames dial.
22.2
E—Base adjustment nut.
S 5 (1)
@~P ·D!/~P 2P !# 1 0.222
F—Bottom of upper tapered ring.
h v h
FIG. 1 Hveem Stabilometer
where:
S = stabilometer value,
P = horizontal pressure for corresponding P in kPa (or
h v
pressure of exactly 34.5 kPa (5 psi). When applying the
psi),
34.5-kPa pressure, always start below or drop below this value,
D = displacement of specimen, and
then bring the pressure up to 34.5 kPa (5 psi) and gently tap the
P = vertical pressure (typically the 2800 kPa (400 psi)
v
dial to remove any slack in the system. Adjust the turns
being applied when the vertical load is 22.3 kN (5000
indicator dial to zero. Turn the pump handle at an approximate
lbf).
rate of two turns per second until the stabilometer dial reads
NOTE
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.