ASTM A1044/A1044M-05
(Specification)Standard Specification for Steel Stud Assemblies for Shear Reinforcement of Concrete
Standard Specification for Steel Stud Assemblies for Shear Reinforcement of Concrete
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers steel stud assemblies for shear reinforcement of concrete. Stud assemblies consist of either single-headed studs attached to a steel base rail by welding, or double-headed studs mechanically crimped into a steel shape.
Note 1&38212;The configuration of the studs for stud assemblies is much different than the configuration of the headed-type studs prescribed in Section 7, Figure 7.1 of AWS D1.1/D1.1M. Ratios of the cross-sectional areas of the head-to-shank of the AWS D1.1/D1.1M studs range from about 2.5 to 4. In contrast, this specification requires the area of the head of the studs for stud assemblies to be at least 10 times the area of the shank. Thus, the standard headed-type studs in Section 7, Figure 7.1 of AWS D1.1/D1.1M do not conform to the requirements of this specification for use as stud assemblies for shear reinforcement.
1.2 This specification is applicable for orders in either inch-pound units or in SI units.
1.3 The values stated either in inch-pound or SI units are to be regarded as standard. Within the text, the SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each system must be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in nonconformance with this specification.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: A1044/A1044M – 05
Standard Specification for
Steel Stud Assemblies for Shear Reinforcement of
Concrete
This standard is issued under the fixed designation A1044/A1044M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the
year of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last
reapproval. A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 2.3 U.S. Military Standards:
MIL-STD-129 Marking for Shipment and Storage
1.1 This specification covers steel stud assemblies for shear
MIL-STD-163 Steel Mill Products Preparation for Ship-
reinforcement of concrete. Stud assemblies consist of either
ment and Storage
single-headed studs attached to a steel base rail by welding, or
2.4 U.S. Federal Standard:
double-headed studs mechanically crimped into a steel shape.
Fed. Std. No. 123 Marking for Shipment (Civil Agencies)
NOTE 1—The configuration of the studs for stud assemblies is much
different than the configuration of the headed-type studs prescribed in
3. Terminology
Section 7, Figure 7.1 of AWS D1.1/D1.1M. Ratios of the cross-sectional
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
areas of the head-to-shank of the AWS D1.1/D1.1M studs range from
3.1.1 headed stud, n—a steel bar used in the reinforcement
about 2.5 to 4. In contrast, this specification requires the area of the head
of concrete that has a head formed at one or both ends.
of the studs for stud assemblies to be at least 10 times the area of the
shank. Thus, the standard headed-type studs in Section 7, Figure 7.1 of
3.1.2 base rail, n—the steel shape or plate that a group of
AWS D1.1/D1.1M do not conform to the requirements of this specifica-
headed studs is attached to by welding or other means.
tion for use as stud assemblies for shear reinforcement.
3.1.2.1 Discussion—Stud assemblies comprised of single-
1.2 This specification is applicable for orders in either headedstudsrequireabaserail;thebaserailactsasastructural
inch-pound units or in SI units. element to provide anchorage to the concrete. For stud assem-
1.3 The values stated either in inch-pound or SI units are to blies in which double-headed studs are mechanically crimped
beregardedasstandard.Withinthetext,theSIunitsareshown into a base rail, for example, into a steel channel, the base rail
in brackets. The values stated in each system are not exact is not required to provide anchorage to the concrete; the
equivalents; therefore, each system must be used indepen- purpose of the base rail is to hold the studs in the appropriate
dently of the other. Combining values from the two systems location, direction, and spacing until the concrete is cast.
may result in nonconformance with this specification.
4. Ordering Information
2. Referenced Documents
4.1 It shall be the responsibility of the purchaser to specify
2.1 ASTM Standards: all requirements that are necessary for material ordered to this
A29/A29M Specification for Steel Bars, Carbon andAlloy, specification. Such requirements shall include but are not
Hot-Wrought, General Requirements for limited to the following:
A36/A36M Specification for Carbon Structural Steel 4.1.1 Name of product: stud assemblies for shear reinforce-
A370 Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing ment of concrete,
of Steel Products 4.1.2 Quantity of studs by diameter,
2.2 AWS Standard: 4.1.3 Number of heads per stud,
AWS D1.1/D1.1M-2004 Structural Welding Code—Steel 4.1.4 Dimensions of base rail, if included,
4.1.5 Overall height of stud assembly,
4.1.6 Number of studs per each assembly and their spacing
This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM CommitteeA01 on Steel,
(see Note 2),
Stainless Steel and RelatedAlloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
4.1.7 Packaging, and
A01.05 on Steel Reinforcement.
Current edition approved June 1, 2005. Published July 2005. DOI: 10.1520/
4.1.8 ASTM designation and year of issue.
A1044_A1044M-05.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or NOTE 2—Inthecaseoforderingstudsratherthanassemblies,thelength
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website.
3 4
Available from TheAmerican Welding Society (AWS), 550 NW LeJeune Rd., Available from Standardization Documents Order Desk, DODSSP, Bldg. 4,
Miami, FL 33126. Section D, 700 Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA 19111-5098.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
A1044/A1044M – 05
A
ofthestudsshouldbespecifiedsuchthattheappropriateheightofthestud TABLE 2 Tensile Requirements—Base Rail Material
assembly is achieved.
Tensile strength, min, psi [MPa] 65 000 [450]
Yield strength, min, psi [MPa] 44 000 [300]
5. Materials and Manufacture
Elongation in 8 in. [200 mm], min, % 20
A
Studs welded to base rail.
5.1 Headedstudsshallbemanufacturedfromsteelconform-
ing to Specification A29/A29M, Grades 1010 through 1020.
The stud material shall conform to the requirements for tensile
conducted by the assembly manufacturer, or an inspection
properties prescribed in Table 1.
agency, or the stud supplier.
5.2 Base Rails:
6.2 Tensile testing shall be performed in accordance with
5.2.1 For stud assemblies in which the studs are welded to
the requirements described in Test Methods and Definitions
a base rail, the base rail material shall conform to 5.2.1.1,
A370.Tensile testing of headed studs shall be performed using
5.2.1.2,or 5.2.1.3.
a test fixture as described in Section 7.3.2 of AWS D1.1/
5.2.1.1 The base rail material, except for tensile properties,
D1.1M.
shall conform to Specification A36/A36M or equivalent. The
base rail material shall conform to the requirements for tensile
7. Acceptance Criteria
properties prescribed in Table 2.
7.1 In addition to meeting the strength requirements of 5.1
5.2.1.2 Base rail material conforming to the minimum
and 5.2, no observed partial or total fracture of the head, the
required tensile properties in SpecificationA36/A36M shall be
studweld,orotherstud-baserailconnectionshallbepermitted.
permitted provided the base rail thickness is increased by a
Thefailureshalloccureitherinthestudmaterialaminimumof
factorequaltotheminimumyieldstrengthspecifiedinTable2
one-half shank diameter from the head-to-shank or stud-to-
divided by the minimum yield strength required by Specifica-
base rail connection, or by tearing a hole in the base rail.
tion A36/A36M.
Failure of the head or stud-to-base rail connection within the
5.2.1.3 Baserailmaterialselectedbythemanufacturershall
attachmentregionshallbecauseforrejection.Thetensileforce
be permitted subject to agreement with the purchaser. The
at which failure occurs shall exceed the minimum yield
manufacturer shall furnish documentation to the purchaser in
strength of the stud.
the form of test reports that confirms the suitability of the
selected base rail material for: (1) manufacturing stud assem-
8. Number of Tests
blies;and (2)structuraladequacyofthestudassembliesforthe
intended application. 8.1 A minimum of two tensile tests shall be conducted
5.2.2 For stud assemblies in which double-headed studs are during a production shift or period. It shall be permissible to
mechanically crimped into a steel shape, the steel shape shall test separate base rail material of the same thickness, chemical
composition, and configuration of the base rails used in
be sufficiently stiff to hold the studs in appropriate location,
direction, and spacing. production. One test at the start and one test at the end of each
8-h production shift or less than 8-h production period, or at
5.3 For stud assemblies in which the studs are attached to
base rails by stud welding, the stud welding shall conform to random intervals during the production period, shall be con-
AWS D1.1/D1.1M, including the provisions for production ducted.
control, and fabrication and verification requirements. 8.2 In the event different heats of stud or base rail material
5.4 Dimensions: withinthesamematerialspecificationareusedtoproducestud
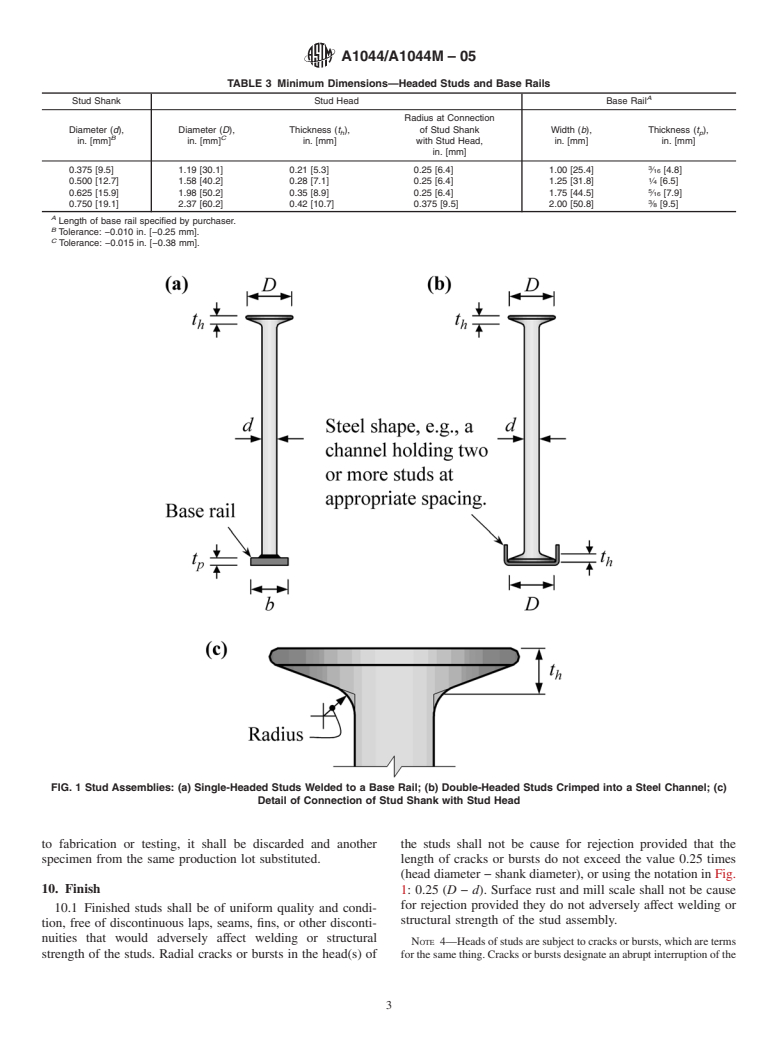
5.4.1 Minimum dimensions of headed studs and plate base assemblies during a production run, a minimum of two tensile
rails shall conform to Table 3. tests in accordance with Section 6 shall be conducted to verify
the production method, product quality, and weldability of the
NOTE 3—The configurations of stud assemblies are shown in Fig. 1.
heats of materials prior to continuing production.
5.4.2 Headed studs with heads that have variable thickness
8.3 Any identified procedural or performance deficiencies
shallbepermitted,providedtheymeetthetensilerequirements
shall be corrected and testing repeated until the tensile test
of this specification.
results meet the requirements of this specification.
6. Tensile Tests
9. Retests
6.1 At periodic intervals, tensile tests of the headed stud
9.1 If the tension test fails before meeting the specified
with a single or double head formed at one or both ends of the
minimum yield strength of the headed stud material per Table
shankorweldedtothebaserailshallbeperformedasspecified
1, but is within 2000 psi [14 MPa] of the required tensile
in the qu
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.