ASTM D4216-22
(Specification)Standard Specification for Rigid Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) and Related PVC and Chlorinated Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (CPVC) Building Products Compounds
Standard Specification for Rigid Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) and Related PVC and Chlorinated Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (CPVC) Building Products Compounds
ABSTRACT
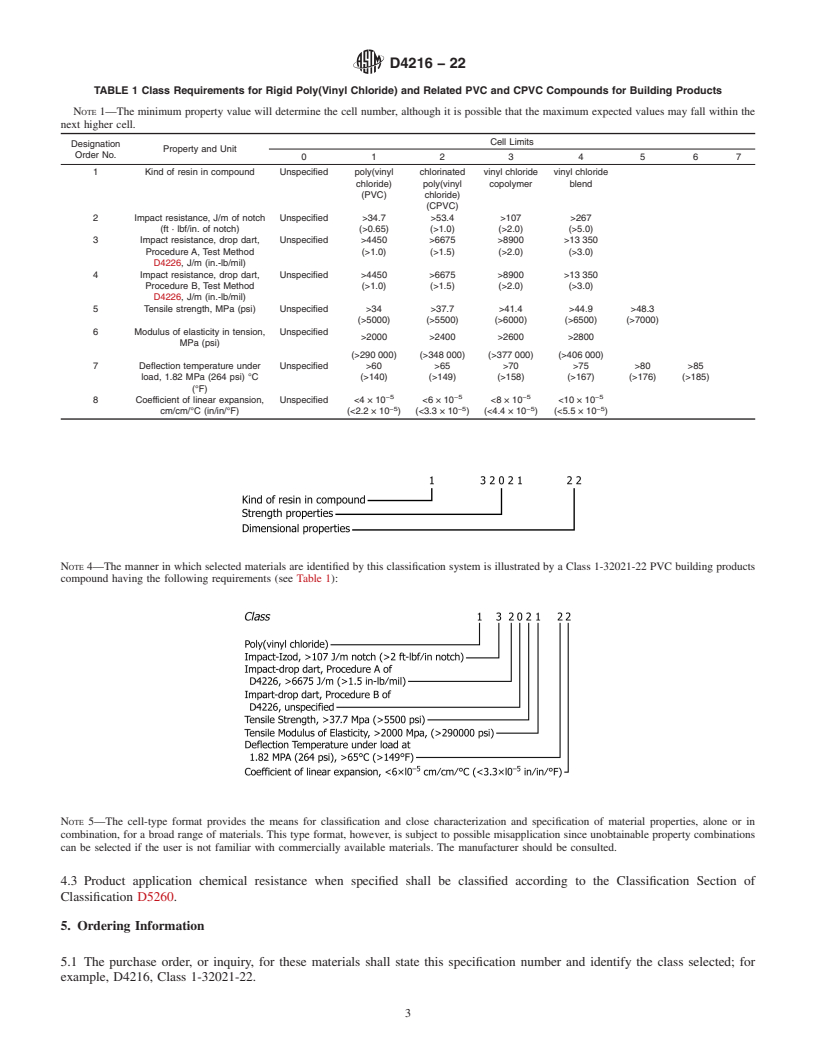
This specification covers rigid plastic PVC and CPVC exterior compounds composed of poly (vinyl chloride), chlorinated poly (vinyl chloride), vinyl chloride copolymers or vinyl chloride blends, and the necessary compound ingredients intended for use in making building products. The compounding ingredients may consist of lubricants, stabilizers, nonpoly-(vinyl chloride) resin modifiers, colorants or pigments, or both, and inorganic fillers. It is intended to provide classification of base compounds used to manufacture PVC and CPVC exterior building products. The means for classifying and identifying rigid PVC building products compounds are provided as follows: kind of resin in compound, impact resistance, tensile strength, modulus of elasticity in tension, deflection temperature under a specific load and coefficient of linear expansion. PVC compound shall be in the form of cubes, pellets, granules, free-flowing powder blends, or compacted powder blends. Materials shall be of uniform composition and size and shall be free of foreign matter to a level that is not expected to affect processability, serviceability, or finished product appearance adversely.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers rigid plastic PVC and CPVC Exterior compounds composed of poly(vinyl chloride), chlorinated poly(vinyl chloride), vinyl chloride copolymers or vinyl chloride blends, and the necessary compound ingredients intended for use in making building products. The compounding ingredients are permitted to consist of lubricants, stabilizers, nonpoly(vinyl chloride) resin modifiers, colorants or pigments, or both, and inorganic fillers.
1.2 This specification is intended to provide classification of base compounds used to manufacture PVC and CPVC exterior building products. It is acceptable to determine physical properties by evaluating compounds of any color.
Note 1: Two year weathering studies, without specific requirements for color change and physical property change, are recommended for all colors of new compounds and compounds for new applications to provide the basis for agreement between producer and buyer on the suitability of the compound for the intended application.
1.3 The requirements in this specification are intended for qualification, as well as for quality control of compounds used to manufacture building products. They are not applicable to finished building products.
1.4 It will be necessary, in special cases, to select specific compounds for unusual applications that require consideration of other properties not covered in this specification.
1.5 The rate of burning test, Test Method D635, is used in this specification only as a screening test for identification of certain properties of the PVC compound; there is no flammability test or flammability requirement for the compound.
1.6 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.7 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the test methods portion, Section 11, of this specification:This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Note 2: There is no known ISO equivalent to this standard.
1.8 The text of this standard references notes and footnotes, which provide explanatory material. These notes and footnotes (excluding those in tables and figures) shall not be considered as requirements of this standard.
1.9 It is possible that rigid PVC recycle plastic meeting the requirements of this specification will be usable in some applications. Refer to the specific requirements in the Materials and Manufacture Section of the applicable product standard.
1.10 This international standard was developed in accorda...
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation:D4216 −22
Standard Specification for
Rigid Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) and Related PVC and
Chlorinated Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (CPVC) Building Products
1
Compounds
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4216; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope* 1.7 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the
test methods portion, Section 11, of this specification:This
1.1 This specification covers rigid plastic PVC and CPVC
standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns,
Exterior compounds composed of poly(vinyl chloride), chlori-
if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user
nated poly(vinyl chloride), vinyl chloride copolymers or vinyl
of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and
chloride blends, and the necessary compound ingredients
environmental practices and determine the applicability of
intended for use in making building products. The compound-
regulatory limitations prior to use.
ing ingredients are permitted to consist of lubricants,
stabilizers, nonpoly(vinyl chloride) resin modifiers, colorants
NOTE 2—There is no known ISO equivalent to this standard.
or pigments, or both, and inorganic fillers.
1.8 The text of this standard references notes and footnotes,
1.2 Thisspecificationisintendedtoprovideclassificationof whichprovideexplanatorymaterial.Thesenotesandfootnotes
base compounds used to manufacture PVC and CPVC exterior (excluding those in tables and figures) shall not be considered
building products. It is acceptable to determine physical as requirements of this standard.
properties by evaluating compounds of any color.
1.9 It is possible that rigid PVC recycle plastic meeting the
requirements of this specification will be usable in some
NOTE 1—Two year weathering studies, without specific requirements
for color change and physical property change, are recommended for all
applications.RefertothespecificrequirementsintheMaterials
colorsofnewcompoundsandcompoundsfornewapplicationstoprovide
and Manufacture Section of the applicable product standard.
the basis for agreement between producer and buyer on the suitability of
1.10 This international standard was developed in accor-
the compound for the intended application.
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
1.3 The requirements in this specification are intended for
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
qualification, as well as for quality control of compounds used
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
to manufacture building products. They are not applicable to
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
finished building products.
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
1.4 It will be necessary, in special cases, to select specific
compounds for unusual applications that require consideration
2. Referenced Documents
of other properties not covered in this specification.
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
1.5 The rate of burning test, Test Method D635, is used in
D256Test Methods for Determining the Izod Pendulum
this specification only as a screening test for identification of
Impact Resistance of Plastics
certain properties of the PVC compound; there is no flamma-
D618Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
bility test or flammability requirement for the compound.
D635Test Method for Rate of Burning and/or Extent and
Time of Burning of Plastics in a Horizontal Position
1.6 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
D638Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
D648Test Method for Deflection Temperature of Plastics
only.
Under Flexural Load in the Edgewise Position
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D20 on
Plastics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.15 on Thermoplastic
2
Materials (Section D20.15.08). For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved May 1, 2022. Published May 2022. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approved in 1983. Last previous edition approved in 2017 as D4216–17. DOI: Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
10.1520/D4216-22. the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appe
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D4216 − 17 D4216 − 22
Standard Specification for
Rigid Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) and Related PVC and
Chlorinated Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (CPVC) Building Products
1
Compounds
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4216; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope*
1.1 This specification covers rigid plastic PVC and CPVC Exterior compounds composed of poly(vinyl chloride), chlorinated
poly(vinyl chloride), vinyl chloride copolymers or vinyl chloride blends, and the necessary compound ingredients intended for use
in making building products. The compounding ingredients are permitted to consist of lubricants, stabilizers, nonpoly(vinyl
chloride) resin modifiers, colorants or pigments, or both, and inorganic fillers.
1.2 This specification is intended to provide classification of base compounds used to manufacture PVC and CPVC exterior
building products. It is acceptable to determine physical properties by evaluating compounds of any color.
NOTE 1—Two year weathering studies, without specific requirements for color change and physical property change, are recommended for all colors of
new compounds and compounds for new applications to provide the basis for agreement between producer and buyer on the suitability of the compound
for the intended application.
1.3 The requirements in this specification are intended for qualification, as well as for quality control of compounds used to
manufacture building products. They are not applicable to finished building products.
1.4 It will be necessary, in special cases, to select specific compounds for unusual applications that require consideration of other
properties not covered in this specification.
1.5 The rate of burning test, Test Method D635, is used in this specification only as a screening test for identification of certain
properties of the PVC compound; there is no flammability test or flammability requirement for the compound.
1.6 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.7 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the test methods portion, Section 11, of this specification:This standard
does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this
standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D20 on Plastics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.15 on Thermoplastic Materials
(Section D20.15.08).
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2017May 1, 2022. Published January 2018May 2022. Originally approved in 1983. Last previous edition approved in 20132017 as
D4216 – 13.D4216 – 17. DOI: 10.1520/D4216-17.10.1520/D4216-22.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D4216 − 22
NOTE 2—There is no known ISO equivalent to this standard.
1.8 The text of this standard references notes and footnotes, which provide explanatory material. These notes and footnotes
(excluding those in tables and figures) shall not be considered as requirements of this standard.
1.9 It is possible that rigid PVC recycle plastic meeting the requirements of this specification will be usable in some applications.
Refer to the specific requirements in the Materials and Manufacture Section of the applicable product standard.
1.10 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D256 Test Methods for Determining the Izod Pendulum Impact Resistance of Plastics
D618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
D635 Test Method for Rate of Burning and/or Extent and Time of Bur
...










Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.