ASTM D2444-21
(Practice)Standard Practice for Determination of the Impact Resistance of Thermoplastic Pipe and Fittings by Means of a Tup (Falling Weight)
Standard Practice for Determination of the Impact Resistance of Thermoplastic Pipe and Fittings by Means of a Tup (Falling Weight)
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 The impact resistance of thermoplastic pipe and fittings relates to suitability for service and to quality of processing. Impact resistance may also provide a relative measure of a material's resistance to breakage during handling and installation and, for non-buried applications, to in-service breakage. See Appendix X5 for guidelines for selecting testing combinations.
4.2 Results obtained by use of this practice can be used in three ways:
4.2.1 As the basis for establishing impact test requirements in product standards,
4.2.2 To measure the effect of changes in materials or processing, and
4.2.3 To measure the effect of the environment.
SCOPE
1.1 This practice covers the determination of the impact resistance of thermoplastic pipe and fittings under specified conditions of impact by means of a tup (falling weight). Three interchangeable striking noses are used on the tup, differing in geometrical configuration. Two specimen holders are described.
Note 1: Appendix X1 shows the procedure to determine impact strength.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D2444 − 21
Standard Practice for
Determination of the Impact Resistance of Thermoplastic
1
Pipe and Fittings by Means of a Tup (Falling Weight)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D2444; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* F412 Terminology Relating to Plastic Piping Systems
F725 Practice for Drafting Impact Test Requirements In
1.1 This practice covers the determination of the impact
Thermoplastic Pipe And Fittings Standards
resistance of thermoplastic pipe and fittings under specified
conditions of impact by means of a tup (falling weight). Three
3. Terminology
interchangeable striking noses are used on the tup, differing in
3.1 Definitions—Definitions are in accordance with Termi-
geometrical configuration. Two specimen holders are de-
nology F412, and abbreviations are in accordance with Termi-
scribed.
nology D1600, unless otherwise specified.
NOTE 1—Appendix X1 shows the procedure to determine impact
strength.
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
3.2.1 tup—Thestrikingpartofafallinghammerlikemecha-
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
nism.
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
4. Significance and Use
and are not considered standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the 4.1 The impact resistance of thermoplastic pipe and fittings
relates to suitability for service and to quality of processing.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro- Impact resistance may also provide a relative measure of a
material’s resistance to breakage during handling and installa-
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. tion and, for non-buried applications, to in-service breakage.
See Appendix X5 for guidelines for selecting testing combi-
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard- nations.
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
4.2 Results obtained by use of this practice can be used in
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
three ways:
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
4.2.1 As the basis for establishing impact test requirements
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
in product standards,
4.2.2 To measure the effect of changes in materials or
2. Referenced Documents
processing, and
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
4.2.3 To measure the effect of the environment.
D618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
5. Apparatus
D1600 Terminology forAbbreviatedTerms Relating to Plas-
tics
5.1 General—One type of impact tester is illustrated in Fig.
D2122 Test Method for Determining Dimensions of Ther-
1.
moplastic Pipe and Fittings
5.2 Tup:
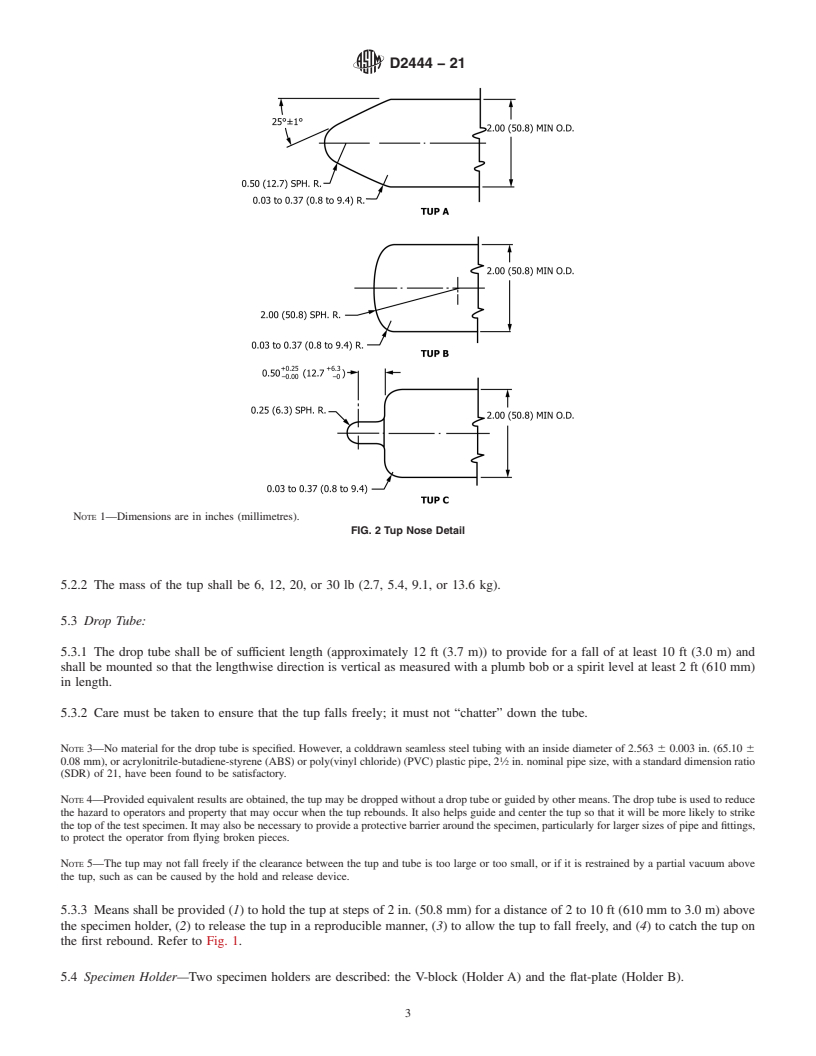
5.2.1 The tup nose shall be as shown in Fig. 2. When used
with the 0.50 in. (12.7 mm) radius nose, it is designated as Tup
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F17 on Plastic
A. When used with the 2.00 in. (51 mm) radius nose, it is
Piping Systems and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F17.40 on Test
Methods. designated as Tup B. When used with the 0.25 in. (6.3 mm)
Current edition approved Feb. 1, 2021. Published February 2021. Originally
radius nose, it is designated as Tup C.
approved in 1965. Last previous edition approved in 2019 as D2444 – 19. DOI:
10.1520/D2444-21.
NOTE 2—It is suggested that tups be made of scratch-resistant steel to
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
reduce damage to the nose. Badly scarred noses may affect test results.
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
5.2.2 The mass of the tup shall be 6, 12, 20, or 30 lb (2.7,
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. 5.4, 9.1, or 13.6 kg).
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D2444 − 21
5.3 Drop Tube:
5.3.1 The drop tube shall be of sufficient length (approxi-
mately 12 ft (3.7 m)) to provide for a fall of at least 10 ft (3.0
m) and
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D2444 − 19 D2444 − 21
Standard Practice for
Determination of the Impact Resistance of Thermoplastic
1
Pipe and Fittings by Means of a Tup (Falling Weight)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D2444; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 This practice covers the determination of the impact resistance of thermoplastic pipe and fittings under specified conditions
of impact by means of a tup (falling weight). Three interchangeable striking noses are used on the tup, differing in geometrical
configuration. Two specimen holders are described.
NOTE 1—Appendix X1 shows the procedure to determine impact strength.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of
regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
D1600 Terminology for Abbreviated Terms Relating to Plastics
D2122 Test Method for Determining Dimensions of Thermoplastic Pipe and Fittings
F412 Terminology Relating to Plastic Piping Systems
F725 Practice for Drafting Impact Test Requirements In Thermoplastic Pipe And Fittings Standards
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions—Definitions are in accordance with Terminology F412, and abbreviations are in accordance with Terminology
D1600, unless otherwise specified.
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F17 on Plastic Piping Systems and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F17.40 on Test Methods.
Current edition approved Aug. 1, 2019Feb. 1, 2021. Published September 2019February 2021. Originally approved in 1965. Last previous edition approved in 20172019
as D2444 – 17.D2444 – 19. DOI: 10.1520/D2444-19.10.1520/D2444-21.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D2444 − 21
3.2.1 tup—The striking part of a falling hammer like mechanism.
4. Significance and Use
4.1 The impact resistance of thermoplastic pipe and fittings relates to suitability for service and to quality of processing. Impact
resistance may also provide a relative measure of a material’s resistance to breakage during handling and installation and, for
non-buried applications, to in-service breakage. See Appendix X5 for guidelines for selecting testing combinations.
4.2 Results obtained by use of this practice can be used in three ways:
4.2.1 As the basis for establishing impact test requirements in product standards,
4.2.2 To measure the effect of changes in materials or processing, and
4.2.3 To measure the effect of the environment.
5. Apparatus
5.1 General—One type of impact tester is illustrated in Fig. 1.
5.2 Tup:
5.2.1 The tup nose shall be as shown in Fig. 2. When used with the 0.50 in. (12.7 mm) radius nose, it is designated as Tup A. When
used with the 2.00 in. (51 mm) radius nose, it is designated as Tup B. When used with the 0.25 in. (6.3 mm) radius nose, it is
designated as Tup C.
NOTE 2—It is suggested that tups be made of scratch-resistant steel to reduce damage to the nose. Badly scarred noses may affect test results.
FIG. 1 One Type of Tup Impact Tester
2
---------------
...










Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.