ASTM F820-06
(Test Method)Test Method for Measuring Air Performance Characteristics of Central Vacuum Cleaning Systems
Test Method for Measuring Air Performance Characteristics of Central Vacuum Cleaning Systems
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
The test results allow the comparison of the maximum air power available when no dirt has been introduced into the vacuum cleaning system, that is, a completely clean filter or an empty, clean dirt container.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers procedures for determining air performance characteristics of household central vacuum cleaning systems, which use a flexible cleaning hose assembly and incorporates a series universal motor(s). This test method does not apply to the carpet cleaning mode of operation where dirt or debris is involved.
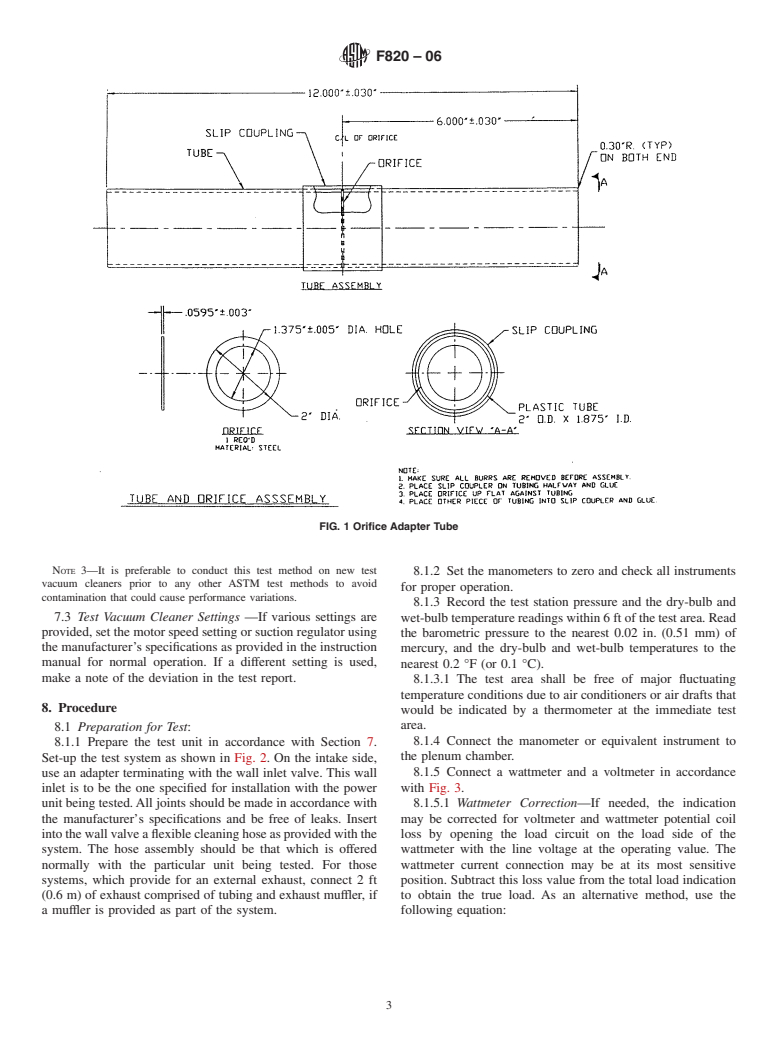
1.2 These tests and calculations include determination of suction, airflow, air power, maximum air power, and input power under standard operating conditions (see Note 0).Note 0
For more information on air performance characteristics, see Refs ().
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are provided for information only.
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. A specific precautionary statement is given in Note 0.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
An American National Standard
Designation: F820 – 06
Standard Test Method for
Measuring Air Performance Characteristics of Central
1
Vacuum Cleaning Systems
ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationF820;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginal
adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.Asuperscript
epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope F431 Specification for Air Performance Measurement Ple-
num Chamber for Vacuum Cleaners
1.1 This test method covers procedures for determining air
4
2.2 AMCA Standard:
performance characteristics of household central vacuum
210–85 Laboratory Methods of Testing Fans for Rating
cleaning systems, which use a flexible cleaning hose assembly
5
2.3 IEC Standard:
and incorporates a series universal motor(s). This test method
IEC 60312 Ed 3.2 Vacuum Cleaners for Household Use—
does not apply to the carpet cleaning mode of operation where
Methods of Measuring the Performance
dirt or debris is involved.
1.2 These tests and calculations include determination of
3. Terminology
suction, airflow, air power, maximum air power, and input
3.1 Definitions:
power under standard operating conditions (see Note 1).
3.1.1 air power,AP, W, n—inavacuumcleaner,thenettime
NOTE 1—For more information on air performance characteristics, see
rate of work performed by an air stream while expending
2
Refs (1-6).
energy to produce an airflow by a vacuum cleaner under
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
specified air resistance conditions.
as the standard. The values given in parentheses are provided
3.1.2 automatic bleed valve, n—any device a part of a
for information only.
vacuum cleaner’s design, which automatically introduces an
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
intentional leak within the vacuum cleaner’s system when
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
manufacturer specified conditions are met.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.1.3 corrected airflow, Q, cfm, n—in a vacuum cleaner, the
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
volume of air movement per unit of time under standard
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. A specific precau-
atmospheric conditions.
tionary statement is given in Note 4.
3.1.4 input power, W, n—the rate at which electrical energy
is absorbed by a vacuum cleaner.
2. Referenced Documents
3.1.5 model, n—the designation of a group of vacuum
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
cleaners having the same mechanical and electrical construc-
E1 Specification for ASTM Liquid-in-Glass Thermometers
tion with only cosmetic or nonfunctional differences.
E177 Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in
3.1.6 population, n—the total of all units of a particular
ASTM Test Methods
model vacuum cleaner being tested.
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
3.1.7 repeatability limit (r), n—the value below which the
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
absolutedifferencebetweentwoindividualtestresultsobtained
under repeatability conditions may be expected to occur with a
probability of approximately 0.95 (95 %).
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee F11 onVacuum
3.1.8 reproducibility limit (R), n—the value below which
Cleaners and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F11.22 on Air Perfor-
mance. the absolute difference between two test results obtained under
Current edition approved April 1, 2006. Published April 2006. Originally
reproducibility conditions may be expected to occur with a
approved in 1988. Last previous edition approved in 2003 as F820 – 03. DOI:
probability of approximately 0.95 (95 %).
10.1520/F0820-06.
2
The boldface numbers in parentheses refer to the list of references at the end of
this standard.
3 4
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or Available from Air Movement and Control Association, Inc., 30 West Univer-
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM sity Dr., Arlington Heights, IL 60004–1893.
5
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from the IEC Web store, webstore.iec.ch, or American National
the ASTM website. Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St., 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F820 – 06
3.1.9 repeatability standard deviation (S ), n—the standard value. These types of barometers generally have temperature
r
deviation of test results obtained under repeatability condi- compensation built into t
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.