ASTM D6436-14
(Guide)Standard Guide for Reporting Properties for Plastics and Thermoplastic Elastomers
Standard Guide for Reporting Properties for Plastics and Thermoplastic Elastomers
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 This guide is intended to provide ready access to the recommended property name, test method reference, maximum number of significant digits,4 and appropriate units for commonly used plastics and thermoplastic elastomer tests.
4.2 It is particularly useful for those involved in the writing and proofreading of documents containing data for a large number of tests since the need to go to each individual test method should be greatly minimized.
4.3 SI units are to be regarded as standard. U.S. Customary units and conversion factors are provided to accommodate those situations where it is necessary to report both. U.S. Customary refers to units commonly used in the United States and is not always the same as inch-pound units.
SCOPE
1.1 This guide provides recommendations for reporting the property values of plastics and thermoplastic elastomers in published literature, data sheets, presentations, comparative analysis, and so forth. It is intended to minimize confusion when comparing the data from several sources.
1.2 This standard is not intended to replace recommendations within the test methods for reporting data. Refer to the test method or use other guidance to determine the number of significant figures for reporting laboratory test results.Note 1—There is no known ISO equivalent to this standard.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D6436 − 14
Standard Guide for
Reporting Properties for Plastics and Thermoplastic
1
Elastomers
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6436; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* 2.3 NFPA Standard:
3
NFPA 99 Standard for Health Care Facilities
1.1 This guide provides recommendations for reporting the
property values of plastics and thermoplastic elastomers in
3. Terminology
published literature, data sheets, presentations, comparative
3.1 Definitions—The terminology used in this guide is in
analysis, and so forth. It is intended to minimize confusion
accordance with Terminologies D883, D1600, and IEEE/
when comparing the data from several sources.
ASTM SI-10.
1.2 This standard is not intended to replace recommenda-
4. Significance and Use
tions within the test methods for reporting data. Refer to the
4.1 This guide is intended to provide ready access to the
test method or use other guidance to determine the number of
recommendedpropertyname,testmethodreference,maximum
significant figures for reporting laboratory test results.
4
number of significant digits, and appropriate units for com-
NOTE 1—There is no known ISO equivalent to this standard.
monly used plastics and thermoplastic elastomer tests.
1.3 This international standard was developed in accor-
4.2 It is particularly useful for those involved in the writing
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
and proofreading of documents containing data for a large
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
number of tests since the need to go to each individual test
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
method should be greatly minimized.
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
4.3 SI units are to be regarded as standard. U.S. Customary
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
units and conversion factors are provided to accommodate
those situations where it is necessary to report both. U.S.
2. Referenced Documents
Customary refers to units commonly used in the United States
2.1 Because of the large number of ASTM test methods
and is not always the same as inch-pound units.
referenced in this guide, they will not be identified individually
in this section. 5. Procedure
2
5.1 RefertoTable1fortherecommendednomenclatureand
2.2 ASTM Standards:
units for physical properties and the recommended number of
D883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
significant digits for test data associated with each property.
D1600 Terminology forAbbreviatedTerms Relating to Plas-
tics
5.2 Abbreviations not shown in Table 1 that may be
IEEE/ ASTM SI-10 Standard for Use of the International
necessary to further clarify the conditions of testing, such as
System of Units (SI): The Modern Metric System
MHz and kHz for electrical tests, can be found in IEEE/ASTM
SI-10.
6. Keywords
1
This guide is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D20 on Plastics and
is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.15 on Thermoplastic Materials.
6.1 conversion factors; decimal places; properties reporting;
Current edition approved March 1, 2014. Published March 2014. Originally
reporting guide; significant figures
approved in 1999. Last previous edition approved in 2008 as D6436 - 08. DOI:
10.1520/D6436-14.
2 3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or Available from National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), 1 Batterymarch
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Park, Quincy, MA 02169-7471, http://www.nfpa.org.
4
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on The recommended maximum number of significant digits is based on experi-
the ASTM website. ence of experts in the plastics industry.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright ©ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D6436 − 14
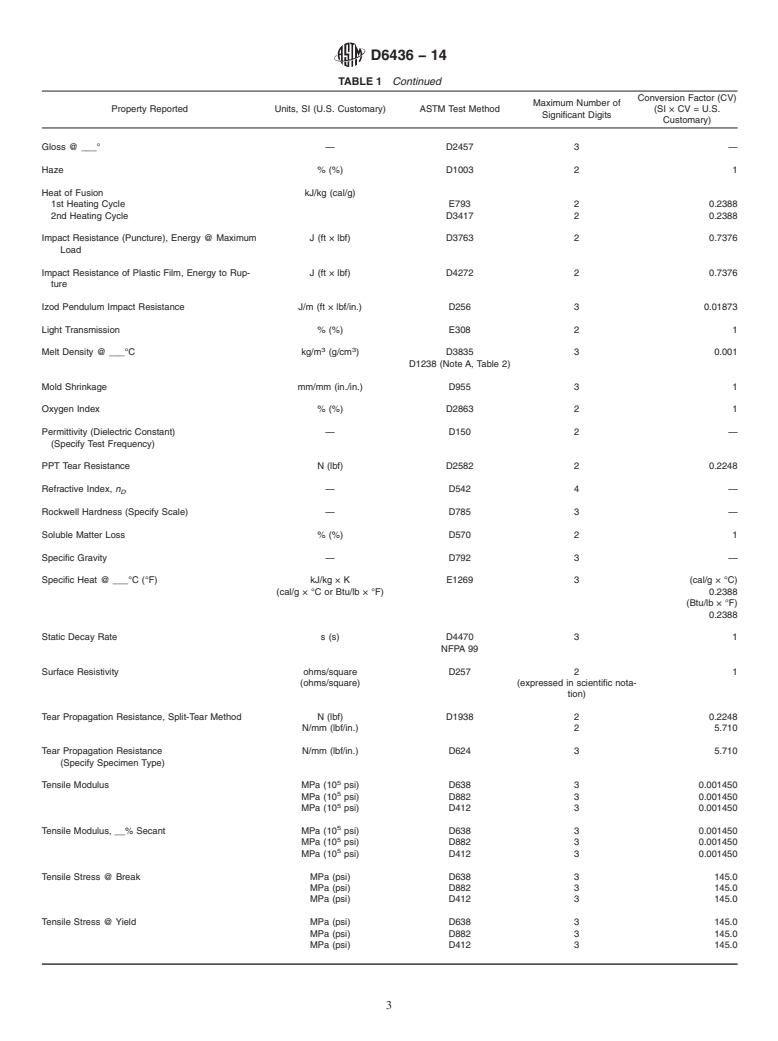
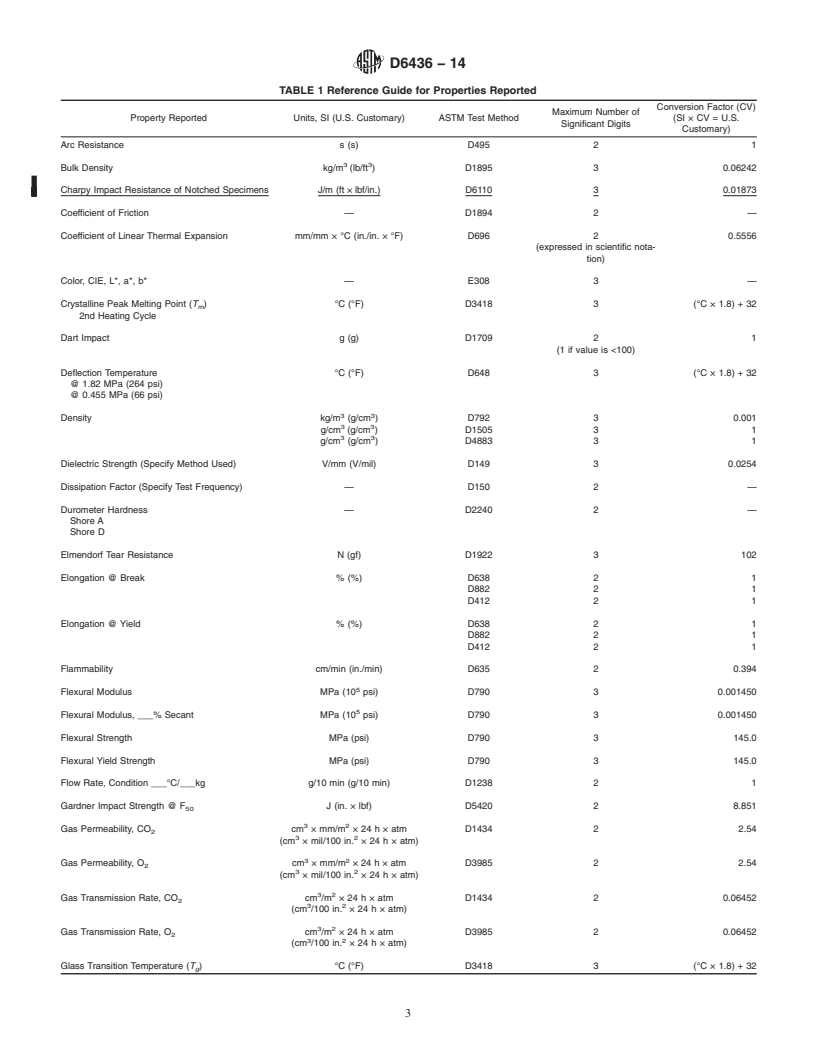
TABLE 1 Reference Guide for Properties Reported
Conversion Factor (CV)
Maximum Number of
Property Reported Units, SI (U.S. Customary) ASTM Test Method (SI × CV = U.S.
Significant Digits
Customary)
Arc Resistance s (s) D495 2 1
3 3
Bulk Density kg/m (lb/ft ) D1895 3 0.06242
Charpy Impact Resistance of Notched Specimens J/m (ft×lbf ⁄in.) D6110 3 0.01873
Coefficient of Friction — D1894 2 —
Coefficient of Linear Thermal Expansion mm/mm × °C (in./in. × °F) D696 2 0.5556
(expressed in scientific nota-
tion)
Color, CIE, L*, a*, b* — E308 3 —
Crystalline Peak Melting P
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D6436 − 08 D6436 − 14
Standard Guide for
Reporting Properties for Plastics and Thermoplastic
1
Elastomers
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6436; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 This guide provides recommendations for reporting the results of property values forof plastics and thermoplastic elastomers
in published literature, data sheets, presentations, comparative analysis, and so forth. It is intended to minimize confusion when
comparing the data from several sources.
1.2 This standard is not intended to replace recommendations within the test methods for reporting data. Refer to the test method
or use other guidance to determine the number of significant figures for reporting laboratory test results.
NOTE 1—There is no similar or equivalent ISO known ISO equivalent to this standard.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 Due toBecause of the large number of ASTM test methods referenced in this guide, they will not be identified individually
in this section.
2
2.2 ASTM Standards:
D883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
D1600 Terminology for Abbreviated Terms Relating to Plastics
IEEE/ ASTM SI-10 Standard for Use of the International System of Units (SI): The Modern Metric System
2.3 NFPA Standard:
3
NFPA 99 Standard for Health Care Facilities
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions—The terminology used in this guide is in accordance with Terminologies D883, D1600, and IEEE/ ASTM SI-10.
4. Significance and Use
4.1 This guide is intended to provide ready access to the recommended property name, test method reference, maximum number
4
of significant digits, and appropriate units for commonly used plastics and thermoplastic elastomer tests.
4.2 It is particularly useful for those involved in the writing and proofreading of documents containing data for a large number
of tests since the need to go to each individual test method should be greatly minimized.
4.3 SI units are to be regarded as the standard. U.S. Customary units and conversion factors are provided to accommodate those
situations where it is necessary to report both. U.S. Customary refers to units commonly used in the United States and is not always
the same as inch-pound units.
5. Procedure
5.1 Refer to Table 1 for the recommended nomenclature and units for physical properties and the recommended number of
significant digits for test data associated with each property.
1
This guide is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D20 on Plastics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.94 on Government/Industry
Standardization.
Current edition approved Aug. 1, 2008March 1, 2014. Published September 2008March 2014. Originally approved in 1999. Last previous edition approved in 20022008
as D6436 - 02.D6436 - 08. DOI: 10.1520/D6436-08.10.1520/D6436-14.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Available from National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), 1 Batterymarch Park, Quincy, MA 02169-7471, http://www.nfpa.org.
4
The recommended maximum number of significant digits is based on experience of experts in the plastics industry.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D6436 − 14
5.2 Abbreviations not shown in Table 1 that may be necessary to further clarify the conditions of testing, such as MHz and kHz
for electrical tests, can be found in IEEE/ ASTM SI-10.
6. Keywords
6.1 conversion factors; decimal places; properties reporting; reporting guide; significant figures
2
---------------------- Page: 2 ----------------------
D6436 − 14
TABLE 1 Reference Guide for Properties Reported
Conversion Factor (CV)
Maximum Number of
Property Reported Units, SI (U.S. Customary) ASTM Test Method (SI × CV = U.S.
Significant Digits
Customary)
Arc Resistance s (s) D495 2 1
3 3
Bulk Density kg/m (lb/ft ) D1895 3 0.06242
Charpy Impact Resistance of Notched Specimens J/m (ft × lbf/in.) D6110 3 0.01873
Coefficient of Friction — D1894 2 —
Coefficient
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.