ASTM C1346-96
(Practice)Standard Practice for Dissolution of UF6 from P-10 Tubes
Standard Practice for Dissolution of UF<sub>6</sub> from P-10 Tubes
SCOPE
1.1 This practice covers the dissolution of UF 6 from a P-10 tube to provide solutions for analysis.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific safeguard and safety precaution statements, see Section 8.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or
withdrawn. Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: C 1346 – 96
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR TESTING AND MATERIALS
100 Barr Harbor Dr., West Conshohocken, PA 19428
Reprinted from the Annual Book of ASTM Standards. Copyright ASTM
Standard Practice for
1
Dissolution of UF from P-10 Tubes
6
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C 1346; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This practice covers the dissolution of UF from a P-10
6
tube to provide solutions for analysis.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific
safeguard and safety precaution statements, see Section 8.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
C 761 Test Methods for Chemical, Mass Spectrometric,
Spectrochemical, Nuclear, and Radiochemical Analysis of
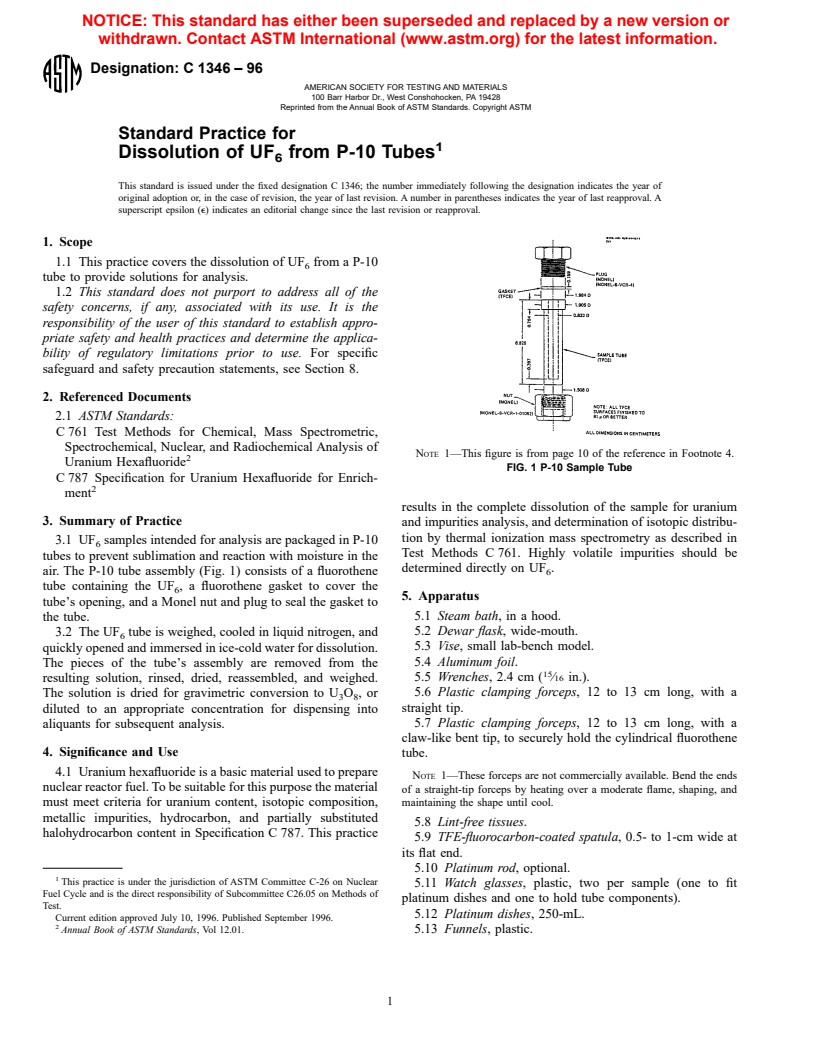
NOTE 1—This figure is from page 10 of the reference in Footnote 4.
2
Uranium Hexafluoride
FIG. 1 P-10 Sample Tube
C 787 Specification for Uranium Hexafluoride for Enrich-
2
ment
results in the complete dissolution of the sample for uranium
3. Summary of Practice
and impurities analysis, and determination of isotopic distribu-
tion by thermal ionization mass spectrometry as described in
3.1 UF samples intended for analysis are packaged in P-10
6
Test Methods C 761. Highly volatile impurities should be
tubes to prevent sublimation and reaction with moisture in the
determined directly on UF .
air. The P-10 tube assembly (Fig. 1) consists of a fluorothene 6
tube containing the UF , a fluorothene gasket to cover the
6
5. Apparatus
tube’s opening, and a Monel nut and plug to seal the gasket to
5.1 Steam bath, in a hood.
the tube.
5.2 Dewar flask, wide-mouth.
3.2 The UF tube is weighed, cooled in liquid nitrogen, and
6
5.3 Vise, small lab-bench model.
quickly opened and immersed in ice-cold water for dissolution.
5.4 Aluminum foil.
The pieces of the tube’s assembly are removed from the
15
5.5 Wrenches, 2.4 cm ( ⁄16 in.).
resulting solution, rinsed, dried, reassembled, and weighed.
5.6 Plastic clamping forceps, 12 to 13 cm long, with a
The solution is dried for gravimetric conversion to U O ,or
3 8
straight tip.
diluted to an appropriate concentration for dispensing into
5.7 Plastic clamping forceps, 12 to 13 cm long, with a
aliquants for subsequent analysis.
claw-like bent tip, to securely hold the cylindrical fluorothene
4. Significance and Use
tube.
4.1 Uranium hexafluoride is a basic material used to prepare
NOTE 1—These forceps are not commercially available. Bend the ends
nuclear reactor fuel. To be suitable for this purpose the material
of a straight-tip forceps by heating over a moderate flame, shaping, and
must meet criteria for uranium content, isotopic composition, maintaining the shape until cool.
metallic impurities, hydrocarbon, and partially substituted
5.8 Lint-free tissues.
halohydrocarbon content in Specification C 787. This practice
5.9 TFE-fluorocarbon-coated spatula, 0.5- to 1-cm wide at
its flat end.
5.10 Platinum rod, optional.
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C-26 on Nuclear
5.11 Watch glasses, plastic, two per sample (one to fit
Fuel Cycle and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C26.05 on Methods of
platinum dishes and one to hold tube components).
Test.
5.12 Platinum dishes, 250-mL.
Current edition approved July 10, 1996. Published September 1996.
2
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 12.01. 5.13 Funnels, plastic.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C 1346
5.14 Gloves, for use with bulk quantities of cryogenic 8.3 Perform dissolutions in a laboratory hood. Hoods should
substances. be regularly inspected for proper air flow.
5.15 Face shield or goggles. 8.4 Gaseous UF , when released to the atmosphere, reacts
6
5.16 Gloves, surgical. with moisture to form HF gas and UO F particulate (a white
2 2
5.17 Gloves, thin-cotton or equivalent, two pairs. amorphous solid that settles on all surfaces). Release of UF to
6
5.18 Copper wires, flexible and looped at one end to loosely the atmosphere is readily visible as a white cloud. The
fit around the fluorothene tube without allowing the Monel corrosive nature of HF and UF can cause skin burns and lung
6
flare nut to pass through. impairment. Medical evaluation is mandatory for all situations
5.19 Desiccator. where there may have been inhalation or contact with HF or
5.20 Graduated cylinder, 100-mL. UF . Water soluble UO F , when inhaled or ingest
...






Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.