ASTM D7545-09
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Oxidation Stability of Middle Distillate Fuels—Rapid Small Scale Oxidation Test (RSSOT)
Standard Test Method for Oxidation Stability of Middle Distillate Fuels<span class='unicode'>—</span>Rapid Small Scale Oxidation Test (RSSOT)
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
The induction period may be used as an indication of the oxidation and storage stability of middle distillate fuel.
Compared to some other oxidation and storage stability test methods, this method uses a small sample and gives a result in a short time period.
SCOPE
1.1 This laboratory test method covers a quantitative determination of the stability of middle distillate fuels such as diesel fuels and heating oils, with up to 100% biodiesel, under accelerated oxidation conditions, by an automatic instrument.
1.2 This test method is designed for products complying with Specification D 975 on Diesel Fuel, Grades No. 1D and 2D; Specification D 396 on Burner Fuel, Grades No. 1 and No. 2; Specification D 6751 on Biodiesel, B100, and Specification D 7467 on Diesel Fuel Oil, B6 to B20.
1.3 This test method measures the induction period, under specified conditions, which can be used as an indication of the oxidation and storage stability of middle distillate fuels.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D7545 − 09
StandardTest Method for
Oxidation Stability of Middle Distillate Fuels—Rapid Small
Scale Oxidation Test (RSSOT)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7545; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope D7467Specification for Diesel Fuel Oil, Biodiesel Blend
(B6 to B20)
1.1 This laboratory test method covers a quantitative deter-
minationofthestabilityofmiddledistillatefuelssuchasdiesel
3. Terminology
fuels and heating oils, with up to 100% biodiesel, under
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
accelerated oxidation conditions, by an automatic instrument.
3.1.1 break point, n—pressure in the test apparatus which is
1.2 This test method is designed for products complying
10 % below the maximum pressure of the actual test run.
with Specification D975 on Diesel Fuel, Grades No. 1D and
3.1.2 induction period, n—timeelapsedbetweenstartingthe
2D; Specification D396 on Burner Fuel, Grades No. 1 and No.
heating procedure of the sample vessel and the break point,
2; Specification D6751 on Biodiesel, B100, and Specification
measured in minutes.
D7467 on Diesel Fuel Oil, B6 to B20.
1.3 This test method measures the induction period, under
4. Summary of Test Method
specified conditions, which can be used as an indication of the
4.1 A5 mL sample is introduced into a pressure vessel
oxidation and storage stability of middle distillate fuels.
which is then charged with oxygen to 700 kPa at ambient
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
temperature. The test is initiated by starting the heater and
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
heating the pressure vessel to a temperature of 140°C.
standard.
4.2 The pressure is recorded continuously until the break-
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
pointisreached.Alternatively,thetestmaybeterminatedwhen
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
a minimum specification requirement is reached.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
5. Significance and Use
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
5.1 Theinductionperiodmaybeusedasanindicationofthe
oxidation and storage stability of middle distillate fuel.
2. Referenced Documents
5.2 Compared to some other oxidation and storage stability
2.1 ASTM Standards:
test methods, this method uses a small sample and gives a
D396Specification for Fuel Oils
result in a short time period.
D975Specification for Diesel Fuel Oils
D4057Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and
6. Apparatus
Petroleum Products
D4177Practice for Automatic Sampling of Petroleum and
6.1 General—This test method uses an automatically con-
Petroleum Products
trolled oxidation tester (see Fig. 1) comprising an oxidation
D6751Specification for Biodiesel Fuel Blend Stock (B100)
pressure vessel containing a test sample cup capable of being
for Middle Distillate Fuels
rapidly heated, fitted with a pressure sensor capable of mea-
suring pressures up to 2000 kPa and a temperature sensor
capable of reading to 0.1°C.
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
PetroleumProductsandLubricantsandisthedirectresponsibilityofSubcommittee
D02.14 on Stability and Cleanliness of Liquid Fuels.
Current edition approved July 1, 2009. Published August 2009. DOI: 10.1520/ Thesolesourceofsupplyoftheapparatusknowntothecommitteeatthistime
D7545-09. is Petrotest PetroOXY apparatus, available from Petrotest. Instruments GmbH &
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or Co, Ludwig-Erhard-Ring 13, 15827 Dahlewitz, Germany, www.petrotest.com. If
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM you are aware of alternative suppliers, please provide this information to ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on International Headquarters. Your comments will receive careful consideration at a
the ASTM website. meeting of the responsible technical committee, which you may attend.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
D7545 − 09
1. Unlocking mechanism for insulating hood
2. Safety and insulating hood
3. Screw cap for closing the test container
4. Oxygen outlet
5. Oxygen inlet
6. “O-ring” seal for test sample cup
7. Test sample cup
8. Locking mechanism for insulating hood
9. Operating panel with display
FIG. 1 Schematic of Apparatus for Rapid Small Scale Oxidation Test
6.1.1 Pressure and temperature in the oxidation vessel are 6.2 Volumetric Device—Cleanandfreefromcontaminations
recorded continuously during the test. The oxidation pressure of previous samples, capable of delivering 5.0 6 0.1 mL.
vessel is fitted with filling and relief-valves and a means of
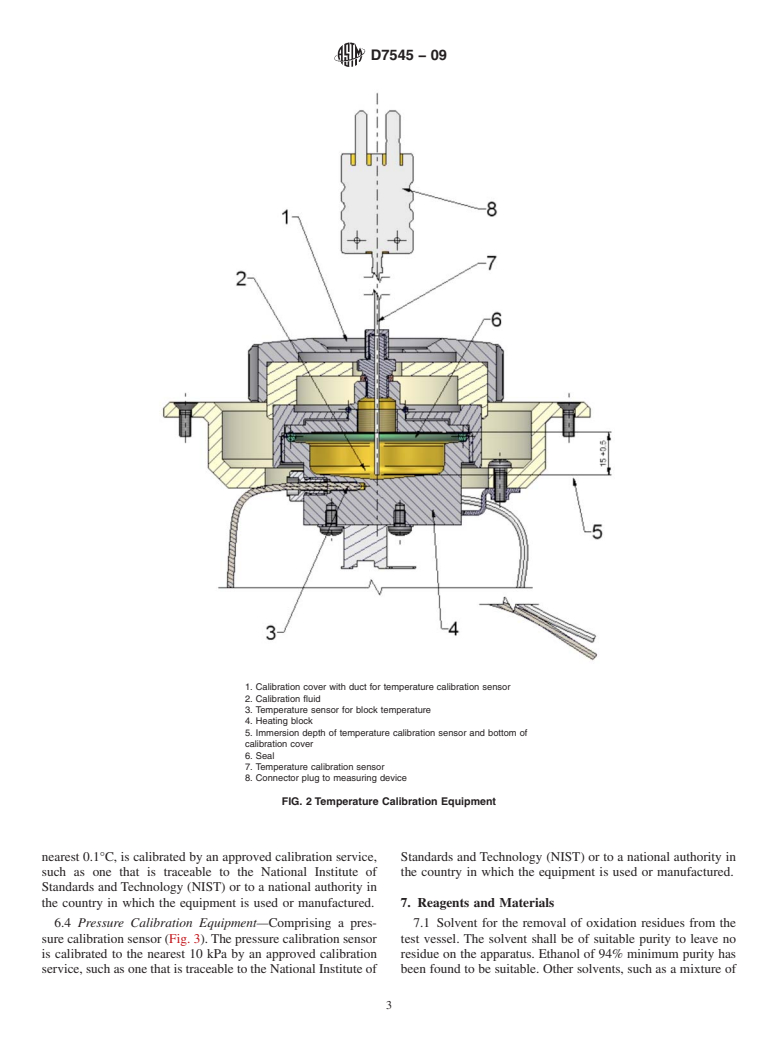
6.3 Temperature Calibration Equipment—Comprising a
automatically releasing the pressure. The integrated cooling
cover and a temperature calibration sensor (Fig. 2). The
fan cools the pressure vessel from the test temperature to
temperature calibration sensor is fixed to a depth of 15 6 0.5
ambient temperature by a flow of air. See Annex A1 for
mm. The temperature calibration sensor, calibrated to the
detailed information.
D7545 − 09
1. Calibration cover with duct for temperature calibration sensor
2. Calibration fluid
3. Temperature sensor for block temperature
4. Heating block
5. Immersion depth of temperature calibration sensor and bottom of
calibration cover
6. Seal
7. Temperature calibration sensor
8. Connector plug to measuring device
FIG. 2 Temperature Calibration Equipment
nearest 0.1°C, is calibrated by an approved calibration service, Standards and Technology (NIST) or to a national authority in
such as one that is traceable to the National Institute of the country in which the equipment is used or manufactured.
Standards and Technology (NIST) or to a national authority in
the country in which the equipment is used or manufactured. 7. Reagents and Materials
6.4 Pressure Calibration Equipment—Comprising a pres- 7.1 Solvent for the removal of oxidation residues from the
surecalibrationsensor(Fig.3).Thepressurecalibrationsensor test vessel. The solvent shall be of suitable purity to leave no
is calibrated to the nearest 10 kPa by an approved calibration residue on the apparatus. Ethanol of 94% minimum purity has
service,suchasonethatistraceabletotheNationalInstituteof been found to be suitable. Other solvents, such as a mixture of
D7545 − 09
FIG. 3 Pressure Calibration Equipment
equalvolumesoftolueneandacetone,maybeusedifshownto 8. Hazards
meet the requirements for the removal of oxidation residues
8.1 (Warning—To provide protection against possible ex-
from the test vessel without leaving any residue in the sample
plosive rupture of the pressure vessel and hazards relating to
test cup.
hotandflammablefuels,theapparatusshallbeoperatedbehind
an appropriate safety shield.)
7.2 Oxygen—Commercially available extra-dry oxygen of
not less than 99.6% purity.
9. Sampling
7.3 Lint-free Cleaning Tissue—For sensitive surfaces and
9.1 Sample in accordance with Practice D4057 or D4177.
that will not scratch the surface.
10. Preparation of Apparatus
7.4 “O -ring” Seal—See A1.2.
10.1 Remove the previous sample by means of a pipette or
7.5 Temperature Calibration Fluid—Stablemiddledistillate
similar device.
liquidwithaflashpointabove+60°Candaboilingpointabove
+150°C. 10.2 Remove the used “O-ring” seal and discard.
D7545 − 09
NOTE 1—To avoid contamination of the new test, it is necessary to
12.7.1 Undernocircumstancesmaytheleakagerateexceed
discard the used “O-ring” seal, because it might be soaked with oxidation
avalueof2kPa/h.Iftheleakagerateshowsanincrease,check
products from the previous test.
the following components: O-ring for damage or residues of
10.3 Wipethetestsamplecup,thesealgrooveandthecover
samples;surfaceofthesamplecupfordamage;samplecupfor
of the test vessel with lint-free cleaning tissue (7.3) soaked
sample residues.
with solvent until free of gum or other oxidation residues.
12.7.2 Contact the manufacturer to resolve leakage prob-
lems from other parts of the instrument.
10.4 Allow the test sample cup and cover to dry in air and
visually inspect for cleanliness.
12.8 The apparatus automati
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.