ASTM D6598-00
(Guide)Standard Guide for Installing and Operating Settlement Platforms for Monitoring Vertical Deformations
Standard Guide for Installing and Operating Settlement Platforms for Monitoring Vertical Deformations
SCOPE
1.1 This guide provides recommended designs and procedures for the fabrication, installation, operation, and reading of settlement platform to determine the magnitude and rate of foundation, fill settlements, or bothgenerally under a fill or embankment load. Two types of settlement platforms are described - those be monitored by elevation surveys from an external bench mark and those that include an internal reference system supported on unyielding soil or rock beneath the compressible layer(s) of interest.
1.2 This guide does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this guide to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.3 This guide offers an organized collection of information or a series of options and does not recommend a specific course of action. This document cannot replace education or experience and should be used in conjunction with professional judgement. Not all aspects of this guide may be applicable in all circumstances. This ASTM standard is not intended to represent or replace the standard of care by which the adequacy of a given professional service must be judged, nor should this document be applied without consideration of a project's many unique aspects. The word "standard" in the title of this document means only that the document has been approved through the ASTM consensus process.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D 6598 – 00
Standard Guide for
Installing and Operating Settlement Platforms for Monitoring
Vertical Deformations
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 6598; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3. Terminology
1.1 This guide provides recommended designs and proce- 3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
dures for the fabrication, installation, operation, and reading of 3.1.1 settlement platform—a system consisting of a square
settlement platform to determine the magnitude and rate of base platform with an extendible riser pipe of known length
foundation, fill settlements, or bothgenerally under a fill or which is used to monitor vertical deformations at the elevation
embankment load. Two types of settlement platforms are of the base platform by survey measurements made of the top
described – those be monitored by elevation surveys from an of the riser pipe.
external bench mark and those that include an internal refer- 3.1.2 external and internal reference point system—with an
ence system supported on unyielding soil or rock beneath the external system, the amount of settlement is determined by
compressible layer(s) of interest. referencing the elevation of the settlement platform to an
1.2 This guide does not purport to address all of the safety outside elevation benchmark; with an internal system, the
concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility amount of settlement is determined by measuring the relative
of the user of this guide to establish appropriate safety and displacement of two co-axial riser pipes moving relative to
health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory each other, the outer riser pipe being attached to the base
limitations prior to use. platform and the inner riser pipe being fixed to an unyielding
1.3 This guide offers an organized collection of information stratum.
or a series of options and does not recommend a specific 3.1.3 anchor—an anchor system that provides an internal
course of action. This document cannot replace education or fixed reference point below the base of the settlement platform
experience and should be used in conjunction with professional system.
judgement. Not all aspects of this guide may be applicable in 3.1.4 extendible riser—a metal shaft or pipe which can be
all circumstances. This ASTM standard is not intended to incrementally lengthened using sections of the same material
represent or replace the standard of care by which the and appropriate couplings as fill is placed and compacted to
adequacy of a given professional service must be judged, nor ensure that the top of the riser remains above the level of the
should this document be applied without consideration of a surroundinggroundsurface.Dependingonwhetheranexternal
project’s many unique aspects. The word “standard” in the or internal reference point is being used, there may be one or
title of this document means only that the document has been two risers.
approved through the ASTM consensus process. 3.1.5 isolation casing—a casing of a larger diameter than
the extendible risers is used in some installations to prevent
2. Referenced Documents
down-drag of soil on the extendible riser that would otherwise
2.1 ASTM Standards:
be in contact with the soil from placing additional load on the
D 653 Terminology Relating to Soil, Rock, and Contained platform and thereby leading to overestimates of deformations.
Fluids
3.1.6 For definitions of other terms used in this guide see
D 3740 Practice for Minimum Requirements for Agencies Terminology D 653.
Engaged in the Testing and/or Inspection of Soil and Rock
4. Summary of Standard Guide
as Used in Engineering Design and Construction
D 5092 Practice for Design and Installation of Ground 4.1 The standard guide presents recommended designs for
Water Monitoring Wells in Aquifers settlement platforms along with procedures to install, operate
and monitor them. The standard guide focuses on methods that
permit (i) the effect of fill placement on underlying strata and
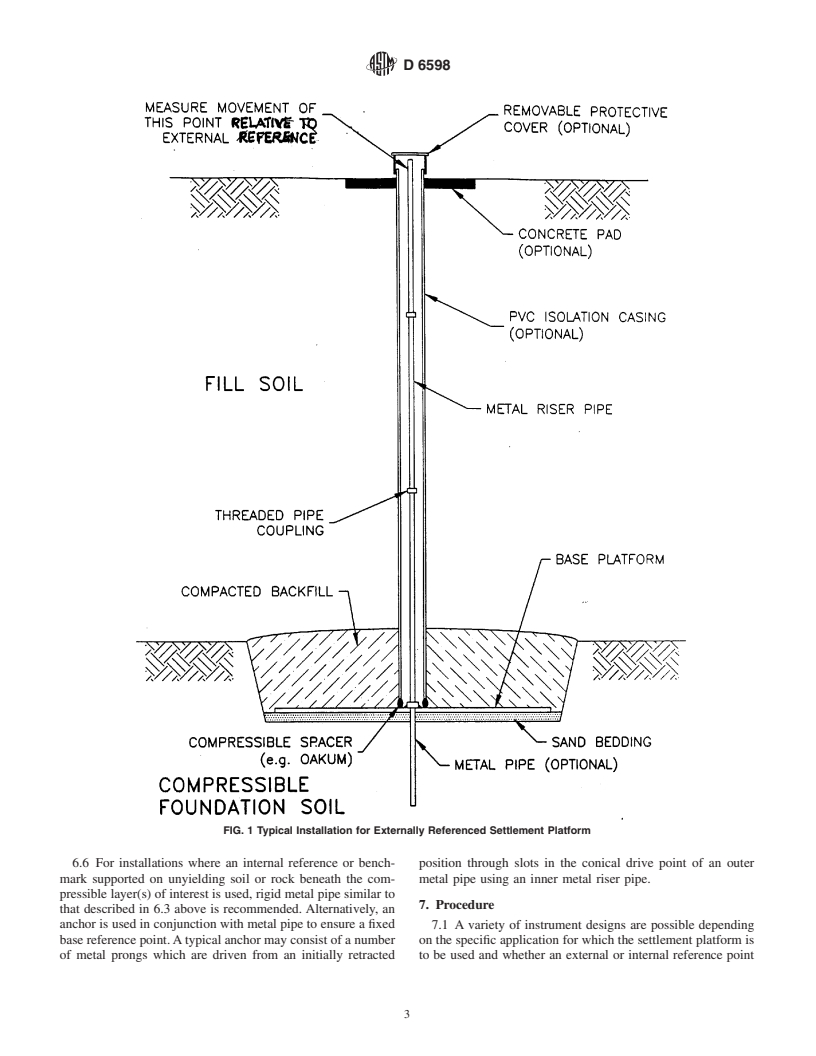
This guide is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D18 on Soil and Rock
(ii) the determination of the relative deformation within a fill.
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D18.23 on Field Instrumentation.
Current edition approved Nov. 10, 2000. Published February 2001.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 04.08.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
D 6598
The guide addresses ways in which the instrument is protected configurations are shown in Figs. 1-3. Key distinctions be-
from downdrag effects from the fill soils as well as measures to tweenthesedifferentconfigurationsaresummarizedinTable1.
protect the instrument from damage by earth moving equip-
Additional considerations regarding materials for each of these
ment. Standard survey procedures are used to determine the components are provided below.
magnitude of deformations. Recommended procedures for
reporting the details of an installation and the recorded TABLE 1 Suitability and Use of Various Platform Configurations
deformations are presented.
Fill Foundation External Internal
Configuration Deformations Deformations Reference Reference
A
Fig. 1 No Yes Yes No
5. Significance and Use
A B
Fig. 2 No Yes No Yes
A B
5.1 Earthen fills are often constructed as engineered struc-
Fig. 3 No Yes No Yes
tures, for example, dams, or to support engineered structures,
A
Fill settlements could be determined with this configuration if base platform
for examples, roads or buildings. The weight of the fill may
placed at higher elevation.
B
compress or deform the supporting soil or rock foundation
External reference (control) could be used with these configurations also.
resulting in settlement of the soil throughout the embankment.
6.2 Base Platform—a square base platform typically rang-
Temporary embankments or surcharge fills are constructed to
ing between 0.3 to 1.0 m on side is placed at the elevation for
increase the strength and/or reduce the compressibility of
which the vertical deformation is required. In some cases, a
foundation soils prior to placement of the actual foundation or
steel platform 5 to 15 mm thick is used. Alternatively, a
structure. The designers often monitor the settlement of the
platform 25 to 50 mm thick fabricated from plywood is
earthstructureasafunctionoftimetodocumentthemagnitude
sometimes used. This may be particularly desirable in short
and rate of settlement, to evaluate the potential for future
term applications where degradation of the wood is not a
settlement, or to confirm the effectiveness of the surcharge and
concern. Other materials such as concrete can be used for the
the schedule for its removal. The monitoring is performed
base platform. In all cases, the thickness of the base platform
using settlement platforms installed prior to or during the
should be selected giving consideration to the area of the
embankment construction. A platform provides an accessible
platform to ensure that its rigidity is sufficient to avoid local
survey point that settles with a selected soil horizon within or
bending.
below the embankment. Careful design and installation of the
6.3 Riser Pipe—a rigid metal shaft or an assembly of a rigid
settlement platform can isolate the survey point from extrane-
metal shaft and a rigid metal pipe, typically 25 to 50 mm in
ous sources of movement such as frost-induced heave, com-
diameter, is used to reflect the vertical deformation of the
pression within the embankment, or volume changes caused by
platform at the ground surface.As layers of fill are placed, the
moisture gain or loss.
riser pipes are extended by adding additional sections of pipe.
5.2 Various settlement platform designs have been devel-
Threaded couplings are typically used. These have the advan-
oped by the agencies and practitioners that use them. This
tage that after the survey program is complete, some, if not all
standard guide provides designs and procedures that can be
theriserpipecanberecoveredbeforetheinstallationisgrouted
referred to in design guidelines, specifications and reports.
to seal off any unwanted access for water to the subsurface.
5.3 This standard guide is not meant to restrict the use of
Use of PVC or other lightweight pipe materials is not recom-
other equally appropriate designs and procedures for the
mended for reasons of survivability.
fabrication, installation, operation, and reading of settlement
platforms to monitor deformations in earthen deposits during 6.4 Riser Pipe Isolation Casing—an external pipe is some-
and after construction. times used to isolate the riser pipe from the surrounding soil.
This is done to prevent the effects of extraneous sources of
NOTE 1—Notwithstanding the statements on precision and bias con-
movement such as frost-induced heave, skin-friction due to
tained in this guide, the precision of this guide is dependent on the
compression within the fill itself, or moisture induced volume
competence of the personnel performing it and the suitability of the
equipment and facilities used. Agencies that meet the criteria of Practice changes. Given that this casing is only to isolate the riser pipe
D 3740 are generally considered capable of competent and objective
from these surrounding effects and does not constitute part of
testing. Users of this guide are cautioned that compliance with Practice
the deformation measuring system, PVC or other lightweight
D 3740 does not itself ensure reliable testing. Reliable testing de
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.