ASTM E496-14(2022)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Measuring Neutron Fluence and Average Energy from 3H(d,n)4He Neutron Generators by Radioactivation Techniques
Standard Test Method for Measuring Neutron Fluence and Average Energy from <sup >3</sup>H(d,n)<sup>4</sup>He Neutron Generators by Radioactivation Techniques
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 Refer to Practice E261 for a general discussion of the measurement of fast-neutron fluence rates with threshold detectors.
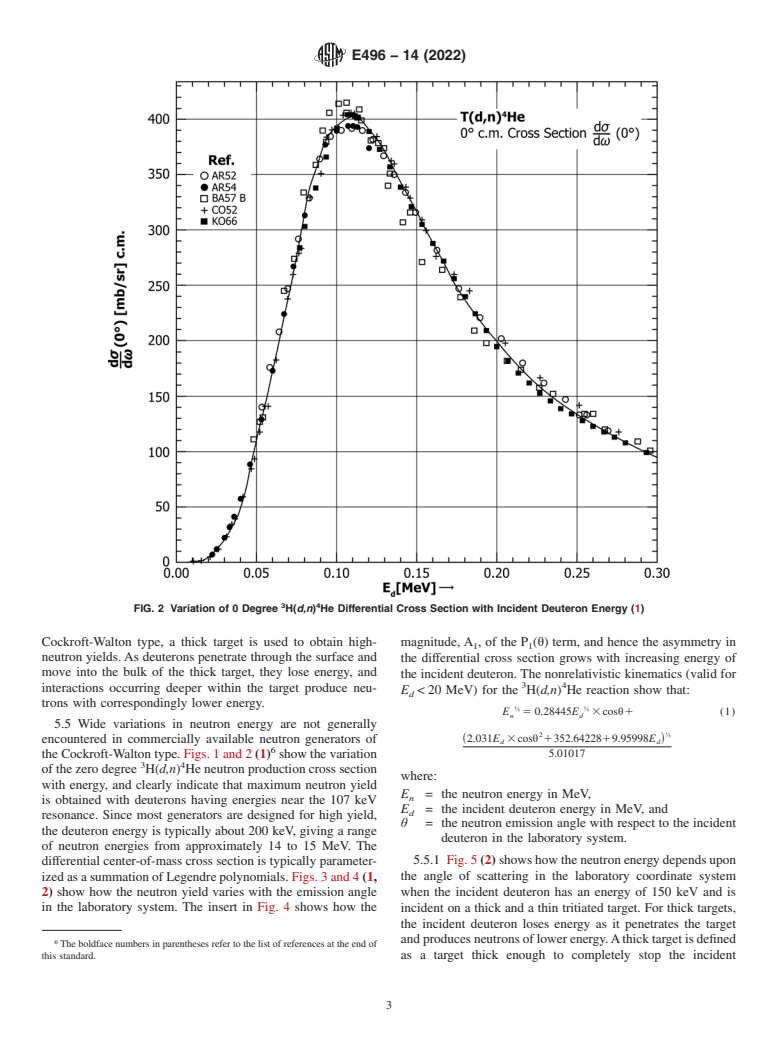
5.5.1 Fig. 5 (2) shows how the neutron energy depends upon the angle of scattering in the laboratory coordinate system when the incident deuteron has an energy of 150 keV and is incident on a thick and a thin tritiated target. For thick targets, the incident deuteron loses energy as it penetrates the target and produces neutrons of lower energy. A thick target is defined as a target thick enough to completely stop the incident deuteron. The two curves in Fig. 5, for both thick and thin targets, come from different sources. The dashed line calculations come from Ref (3); the solid curve calculations come from Ref (4); and the measured data come from Ref (5). The dash-dot curve and the right-hand axis give the difference between the calculated neutron energies for thin and thick targets. Computer codes are available to assist in calculating the expected thick and thin target yield and neutron spectrum for various incident deuteron energies (6).
FIG. 5 Dependence of 3H(d,n)4He Neutron Energy on Angle (2)
5.6 The Q-value for the primary 3H(d,n)4He reaction is +17.59 MeV. When the incident deuteron energy exceeds 3.71 MeV and 4.92 MeV, the break-up reactions 3H(d,np)3H and 3H(d,2n)3He, respectively, become energetically possible. Thus, at high deuteron energies (>3.71 MeV) this reaction is no longer monoenergetic. Monoenergetic neutron beams with energies from about 14.8 to 20.4 MeV can be produced by this reaction at forward laboratory angles (7).
5.7 It is recommended that the dosimetry sensors be fielded in the exact positions where the dosimetry results are wanted. There are a number of factors that can affect the monochromaticity or energy spread of the neutron beam (7, 8). These factors include the energy regulation of the incident deuteron energy, energy loss in retaining windows if a gas target is used or energy loss within t...
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers a general procedure for the measurement of the fast-neutron fluence rate produced by neutron generators utilizing the 3H(d,n)4He reaction. Neutrons so produced are usually referred to as 14-MeV neutrons, but range in energy depending on a number of factors. This test method does not adequately cover fusion sources where the velocity of the plasma may be an important consideration.
1.2 This test method uses threshold activation reactions to determine the average energy of the neutrons and the neutron fluence at that energy. At least three activities, chosen from an appropriate set of dosimetry reactions, are required to characterize the average energy and fluence. The required activities are typically measured by gamma-ray spectroscopy.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: E496 − 14 (Reapproved 2022)
Standard Test Method for
Measuring Neutron Fluence and Average Energy
3 4
from H(d,n) He Neutron Generators by Radioactivation
1
Techniques
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E496; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
1.1 This test method covers a general procedure for the
E170Terminology Relating to Radiation Measurements and
measurement of the fast-neutron fluence rate produced by
3 4
Dosimetry
neutron generators utilizing the H(d,n) He reaction. Neutrons
E181Test Methods for Detector Calibration andAnalysis of
so produced are usually referred to as 14-MeV neutrons, but
Radionuclides
range in energy depending on a number of factors. This test
E261Practice for Determining Neutron Fluence, Fluence
method does not adequately cover fusion sources where the
Rate, and Spectra by Radioactivation Techniques
velocity of the plasma may be an important consideration.
E265Test Method for Measuring Reaction Rates and Fast-
1.2 This test method uses threshold activation reactions to Neutron Fluences by Radioactivation of Sulfur-32
determine the average energy of the neutrons and the neutron E720Guide for Selection and Use of Neutron Sensors for
Determining Neutron Spectra Employed in Radiation-
fluence at that energy.At least three activities, chosen from an
Hardness Testing of Electronics
appropriate set of dosimetry reactions, are required to charac-
terize the average energy and fluence. The required activities 2.2 International Commission on Radiation Units and Mea-
3
are typically measured by gamma-ray spectroscopy. surements (ICRU) Reports:
ICRU Report 13Neutron Fluence, Neutron Spectra and
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
Kerma
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
ICRU Report 26Neutron Dosimetry for Biology and Medi-
standard.
cine
4
2.3 ISO Standard:
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
Guide to the Expression of Uncertainty in Measurement
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
5
2.4 NIST Document:
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
TechnicalNote1297GuidelinesforEvaluatingandExpress-
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
ing the Uncertainty of NIST Measurement Results
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accor-
3. Terminology
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
3.1 Definitions—Refer to Terminology E170.
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
4. Summary of Test Method
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
4.1 This test method describes the determination of the
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
average neutron energy and fluence by use of three activities
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website.
1 3
ThistestmethodisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeE10onNuclear Available from the International Commission on Radiation Units, 7910
Technology and Applications and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee Woodmont Ave., Washington, DC 20014.
4
E10.07 on Radiation Dosimetry for Radiation Effects on Materials and Devices. Available fromAmerican National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
CurrenteditionapprovedJuly1,2022.PublishedJuly2022.Originallyapproved 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
5
in 1973. Last previous edition approved in 2014 as E496–14. DOI: 10.1520/ Available from National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), 100
E0496-14R22. Bureau Dr., Stop 1070, Gaithersburg, MD 20899-1070, http://www.nist.gov.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E496 − 14 (2022)
from a select list of dosimetry reactions. Three dosimetry 5.2 Refer to Test Method E265 for a general discussion of
reactionsarechosenbasedonanumberoffactorsincludingthe the measurement of fast-neutron fluence rates by radioactiva-
intensity of the neutron field, the rea
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.