ASTM D1310-14
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Flash Point and Fire Point of Liquids by Tag Open-Cup Apparatus
Standard Test Method for Flash Point and Fire Point of Liquids by Tag Open-Cup Apparatus
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 Flash point and fire point of a liquid are physical properties that may be used to define their flammability hazards. The flash point may be used to classify materials in government regulations.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination by Tag Open-Cup Apparatus of the flash point and fire point of liquids having flash points between −18 and 165°C (0 and 325°F) and fire points up to 325°F.
1.2 This test method, when applied to paints and resin solutions that tend to skin over or that are very viscous, gives less reproducible results than when applied to solvents.
Note 1: In order to conserve time and sample, the fire point of a material may be determined by the Tag Open-Cup Method by continuing the heating of the specimen to its fire point. Fire points may also be determined by Test Method D92, which should be used for fire points beyond the scope of this test method.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.4 This standard should be used to measure and describe the properties of materials, products, or assemblies in response to heat and flame under controlled laboratory conditions and should not be used to describe or appraise the fire hazard or fire risk of materials, products, or assemblies under actual fire conditions. However, results of this test may be used as elements of a fire risk assessment which takes into account all of the factors pertinent to an assessment of the fire hazard of a particular end use
1.5 Warning—Mercury has been designated by many regulatory agencies as a hazardous material that can cause central nervous system, kidney and liver damage. Mercury, or its vapor, may be hazardous to health and corrosive to materials. Caution should be taken when handling mercury and mercury containing products. See the applicable product Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for details and EPA’s website, http://www.epa.gov/mercury/faq.htm, for additional information. Users should be aware that selling mercury and/or mercury containing products into your state or country may be prohibited by law.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address the safety problems associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D1310 − 14
Standard Test Method for
Flash Point and Fire Point of Liquids by Tag Open-Cup
1
Apparatus
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D1310; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope* aware that selling mercury and/or mercury containing prod-
ucts into your state or country may be prohibited by law.
1.1 This test method covers the determination by Tag
1.6 This standard does not purport to address the safety
Open-CupApparatusoftheflashpointandfirepointofliquids
problems associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the
having flash points between −18 and 165°C (0 and 325°F) and
user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health
fire points up to 325°F.
practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limita-
1.2 This test method, when applied to paints and resin
tions prior to use.
solutions that tend to skin over or that are very viscous, gives
less reproducible results than when applied to solvents.
2. Referenced Documents
2
NOTE 1—In order to conserve time and sample, the fire point of a
2.1 ASTM Standards:
material may be determined by the Tag Open-Cup Method by continuing
D92Test Method for Flash and Fire Points by Cleveland
the heating of the specimen to its fire point. Fire points may also be
Open Cup Tester
determined by Test Method D92, which should be used for fire points
D850Test Method for Distillation of Industrial Aromatic
beyond the scope of this test method.
Hydrocarbons and Related Materials
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
D1015Test Method for Freezing Points of High-Purity
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
Hydrocarbons
only.
D1016Test Method for Purity of Hydrocarbons from Freez-
1.4 This standard should be used to measure and describe
ing Points
thepropertiesofmaterials,products,orassembliesinresponse
D1078Test Method for Distillation Range of Volatile Or-
to heat and flame under controlled laboratory conditions and
ganic Liquids
should not be used to describe or appraise the fire hazard or
D1364Test Method for Water in Volatile Solvents (Karl
fire risk of materials, products, or assemblies under actual fire
Fischer Reagent Titration Method)
conditions. However, results of this test may be used as
D2268Test Method for Analysis of High-Purity n-Heptane
elements of a fire risk assessment which takes into account all
and Isooctane by Capillary Gas Chromatography
of the factors pertinent to an assessment of the fire hazard of a
D2699Test Method for Research Octane Number of Spark-
particular end use
Ignition Engine Fuel
D2700Test Method for Motor Octane Number of Spark-
1.5 Warning—Mercury has been designated by many regu-
Ignition Engine Fuel
latory agencies as a hazardous material that can cause central
E1Specification for ASTM Liquid-in-Glass Thermometers
nervous system, kidney and liver damage. Mercury, or its
E1137SpecificationforIndustrialPlatinumResistanceTher-
vapor, may be hazardous to health and corrosive to materials.
mometers
Caution should be taken when handling mercury and mercury
E2251Specification for Liquid-in-Glass ASTM Thermom-
containing products. See the applicable product Safety Data
eters with Low-Hazard Precision Liquids
Sheet(SDS)fordetailsandEPA’swebsite,http://www.epa.gov/
E2877Guide for Digital Contact Thermometers
mercury/faq.htm, for additional information. Users should be
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D01 on Paint
and Related Coatings, Materials, andApplications and is the direct responsibility of
2
Subcommittee D01.21 on Chemical Analysis of Paints and Paint Materials. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved Dec. 15, 2014. Published January 2015. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approved in 1952. Last previous edition approved in 2007 as D1310–01 (2007). Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
DOI: 10.1520/D1310-14. the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D1310 − 14
5
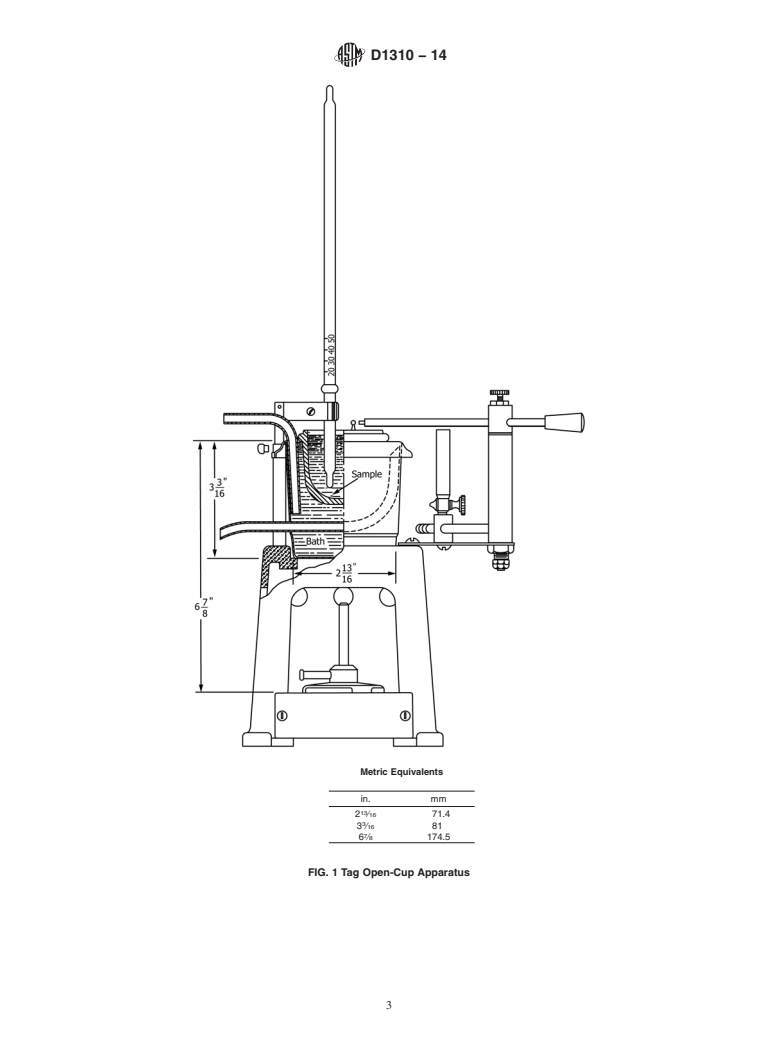
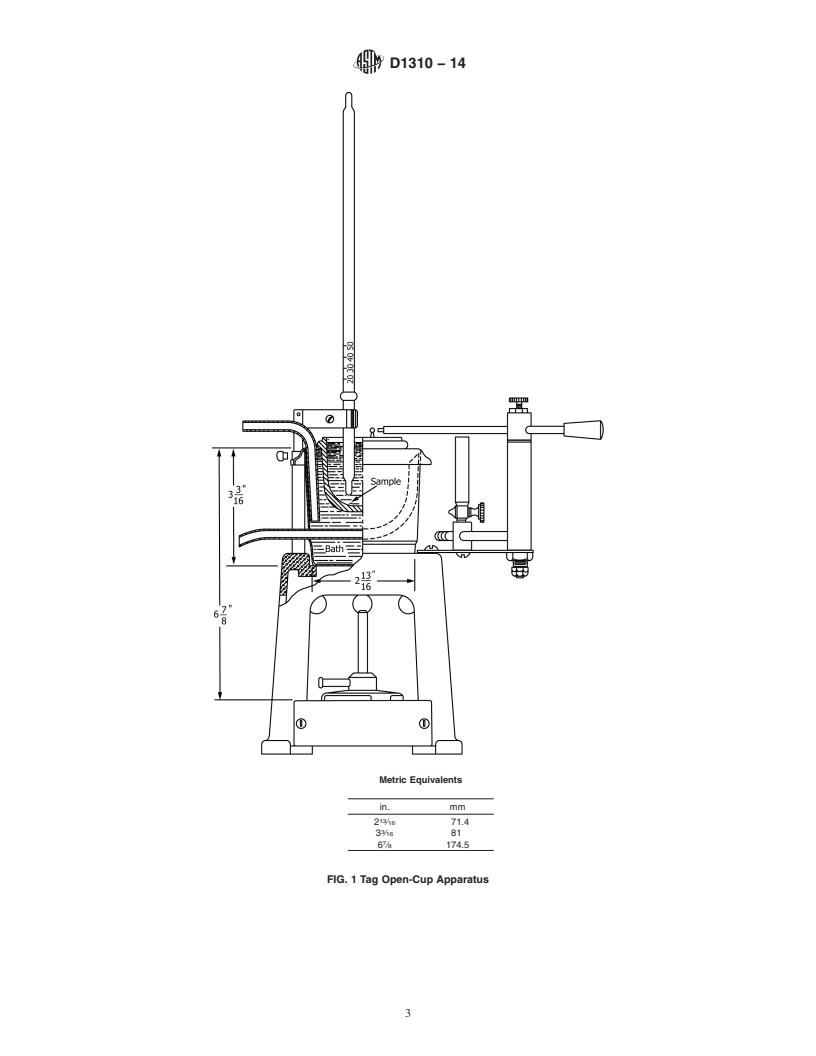
3.1.1 flash point, n—the lowest temperature, corrected to a 7.7 Diethylene Glycol, for determination of flash points
pressure of 760 mm Hg (101.3 kPa, 1013 mbar), at whi
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D1310 − 01 (Reapproved 2007) D1310 − 14
Standard Test Method for
Flash Point and Fire Point of Liquids by Tag Open-Cup
1
Apparatus
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D1310; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope Scope*
1.1 This test method covers the determination by Tag Open-Cup Apparatus of the flash point and fire point of liquids having
flash points between −18 and 165°C (0 and 325°F) and fire points up to 325°F.
1.2 This test method, when applied to paints and resin solutions that tend to skin over or that are very viscous, gives less
reproducible results than when applied to solvents.
NOTE 1—In order to conserve time and sample, the fire point of a material may be determined by the Tag Open-Cup Method by continuing the heating
of the specimen to its fire point. Fire points may also be determined by Test Method D92, which should be used for fire points beyond the scope of this
test method.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.4 This standard should be used to measure and describe the properties of materials, products, or assemblies in response to
heat and flame under controlled laboratory conditions and should not be used to describe or appraise the fire hazard or fire risk
of materials, products, or assemblies under actual fire conditions. However, results of this test may be used as elements of a fire
risk assessment which takes into account all of the factors pertinent to an assessment of the fire hazard of a particular end use.
This standard should be used to measure and describe the properties of materials, products, or assemblies in response to heat and
flame under controlled laboratory conditions and should not be used to describe or appraise the fire hazard or fire risk of materials,
products, or assemblies under actual fire conditions. However, results of this test may be used as elements of a fire risk assessment
which takes into account all of the factors pertinent to an assessment of the fire hazard of a particular end use
1.5 Warning—Mercury has been designated by many regulatory agencies as a hazardous material that can cause central
nervous system, kidney and liver damage. Mercury, or its vapor, may be hazardous to health and corrosive to materials. Caution
should be taken when handling mercury and mercury containing products. See the applicable product Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for
details and EPA’s website, http://www.epa.gov/mercury/faq.htm, for additional information. Users should be aware that selling
mercury and/or mercury containing products into your state or country may be prohibited by law.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address the safety problems associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of
this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior
to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D92 Test Method for Flash and Fire Points by Cleveland Open Cup Tester
D850 Test Method for Distillation of Industrial Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Related Materials
D1015 Test Method for Freezing Points of High-Purity Hydrocarbons
D1016 Test Method for Purity of Hydrocarbons from Freezing Points
D1078 Test Method for Distillation Range of Volatile Organic Liquids
D1364 Test Method for Water in Volatile Solvents (Karl Fischer Reagent Titration Method)
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D01 on Paint and Related Coatings, Materials, and Applications and is the direct responsibility of
Subcommittee D01.21 on Chemical Analysis of Paints and Paint Materials.
Current edition approved June 1, 2007Dec. 15, 2014. Published August 2007January 2015. Originally approved in 1952. Last previous edition approved in 20012007 as
D1310 – 01.D1310 – 01 (2007). DOI: 10.1520/D1310-01R07.10.1520/D1310-14.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’sstandard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.