ASTM A1044/A1044M-16ae1
(Specification)Standard Specification for Steel Stud Assemblies for Shear Reinforcement of Concrete
Standard Specification for Steel Stud Assemblies for Shear Reinforcement of Concrete
SCOPE
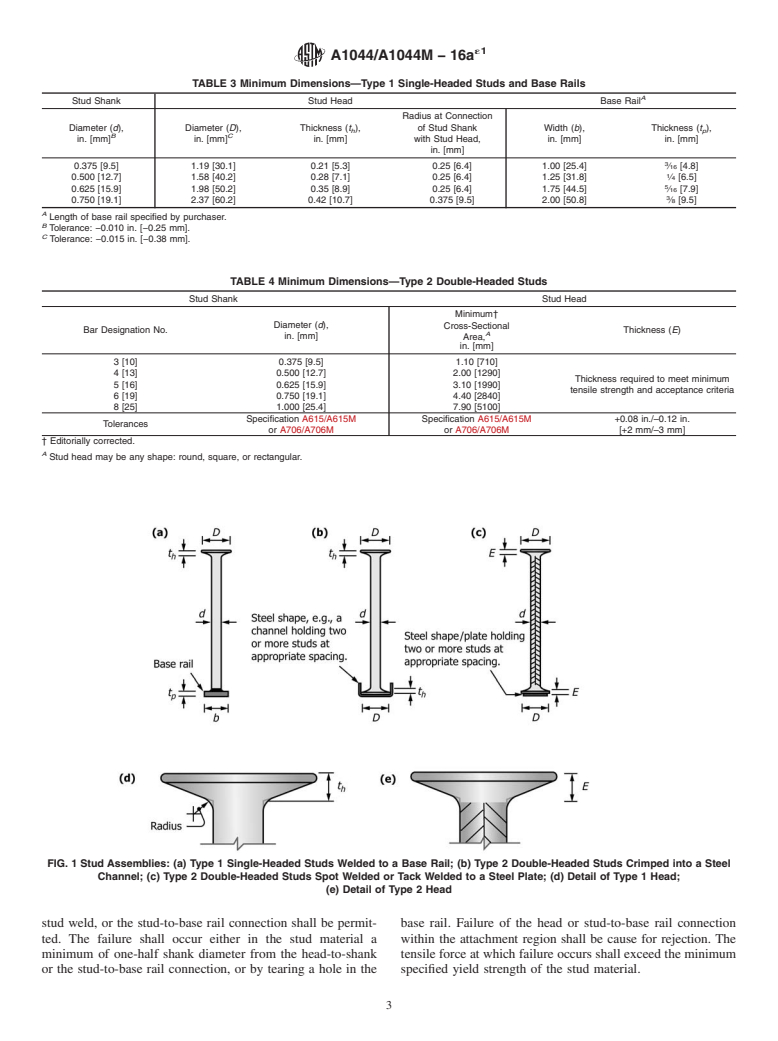
1.1 This specification covers steel stud assemblies for shear reinforcement of concrete. Stud assemblies consist of either single-headed studs (Type 1) attached to a structural steel base rail by structural welding or stud welding, or double-headed studs (Type 2) mechanically crimped into a non-structural steel shape or attached to a steel plate by spot welding or tack welding. These stud assemblies are not intended for use as shear connectors in steel-concrete composite construction.
Note 1: The configuration of the studs for stud assemblies is much different than the configuration of the headed-type studs prescribed in Section 7, Figure 7.1 of AWS D1.1/D1.1M. Ratios of the cross-sectional areas of the head-to-shank of the AWS D1.1/D1.1M studs range from about 2.5 to 4. In contrast, this specification requires the area of the head of the studs for stud assemblies to be at least 10 times the area of the shank. Thus, the standard headed-type studs in Section 7, Figure 7.1 of AWS D1.1/D1.1M do not conform to the requirements of this specification for use as stud assemblies for shear reinforcement.
1.2 This specification is applicable for orders in either inch-pound units or in SI units.
1.3 The values stated either in inch-pound or SI units are to be regarded as standard. Within the text, the SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each system must be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in nonconformance with this specification.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
´1
Designation:A1044/A1044M −16a
Standard Specification for
Steel Stud Assemblies for Shear Reinforcement of
1
Concrete
This standard is issued under the fixed designation A1044/A1044M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the
year of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last
reapproval. A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1
ε NOTE—Editorial corrections were made throughout in August 2019.
1. Scope* 2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
1.1 This specification covers steel stud assemblies for shear
A29/A29MSpecificationforGeneralRequirementsforSteel
reinforcement of concrete. Stud assemblies consist of either
Bars, Carbon and Alloy, Hot-Wrought
single-headed studs (Type 1) attached to a structural steel base
A36/A36MSpecification for Carbon Structural Steel
rail by structural welding or stud welding, or double-headed
A370Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing
studs(Type2)mechanicallycrimpedintoanon-structuralsteel
of Steel Products
shape or attached to a steel plate by spot welding or tack
A615/A615MSpecificationforDeformedandPlainCarbon-
welding. These stud assemblies are not intended for use as
Steel Bars for Concrete Reinforcement
shear connectors in steel-concrete composite construction.
A706/A706MSpecification for Deformed and Plain Low-
NOTE 1—The configuration of the studs for stud assemblies is much
Alloy Steel Bars for Concrete Reinforcement
different than the configuration of the headed-type studs prescribed in
3
2.2 AWS Standard:
Section 7, Figure 7.1 of AWS D1.1/D1.1M. Ratios of the cross-sectional
AWS D1.1/D1.1M-2004Structural Welding Code—Steel
areas of the head-to-shank of the AWS D1.1/D1.1M studs range from
4
about 2.5 to 4. In contrast, this specification requires the area of the head
2.3 U.S. Military Standards:
of the studs for stud assemblies to be at least 10 times the area of the
MIL-STD-129Marking for Shipment and Storage
shank. Thus, the standard headed-type studs in Section 7, Figure 7.1 of
MIL-STD-163SteelMillProductsPreparationforShipment
AWS D1.1/D1.1M do not conform to the requirements of this specifica-
and Storage
tion for use as stud assemblies for shear reinforcement.
4
2.4 U.S. Federal Standard:
1.2 This specification is applicable for orders in either
Fed. Std. No. 123Marking for Shipment (Civil Agencies)
inch-pound units or in SI units.
3. Terminology
1.3 The values stated either in inch-pound or SI units are to
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
beregardedasstandard.Withinthetext,theSIunitsareshown
3.1.1 base rail, n—the steel shape or plate that a group of
in brackets. The values stated in each system are not exact
headed studs is attached to by welding or other means.
equivalents; therefore, each system must be used indepen-
3.1.1.1 Discussion—Stud assemblies comprised of single-
dently of the other. Combining values from the two systems
headed studs (Type 1) require a base rail; the base rail acts as
may result in nonconformance with this specification.
a structural element to provide anchorage to the concrete. For
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
stud assemblies in which double-headed studs (Type 2) are
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
mechanically crimped into a steel shape, for example, into a
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
steelchannel,thebaserailisnotrequiredtoprovideanchorage
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
to the concrete; the purpose of the base rail is to hold the studs
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
in the appropriate location, direction, and spacing until the
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee A01 on Steel, Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Stainless Steel and RelatedAlloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee the ASTM website.
3
A01.05 on Steel Reinforcement. Available from American Welding Society (AWS), 8669 NW 36 St., #130,
Current edition approved March 1, 2016. Published May 2016. Originally Miami, FL 33166-6672, http://www.aws.org.
4
approved in 2005. Last previous edition approved in 2016 as A1044/A1044M–16. Available from DLA Document Services, Building 4/D, 700 Robbins Ave.,
DOI: 10.1520/A1044_A1044M-16AE01. Philadelphia, PA 19111-5094, http://quicksearch.dla.mil.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohock
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
´1
Designation: A1044/A1044M − 16a A1044/A1044M − 16a
Standard Specification for
Steel Stud Assemblies for Shear Reinforcement of
1
Concrete
This standard is issued under the fixed designation A1044/A1044M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the
year of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last
reapproval. A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1
ε NOTE—Editorial corrections were made throughout in August 2019.
1. Scope*
1.1 This specification covers steel stud assemblies for shear reinforcement of concrete. Stud assemblies consist of either
single-headed studs (Type 1) attached to a structural steel base rail by structural welding or stud welding, or double-headed studs
(Type 2) mechanically crimped into a non-structural steel shape or attached to a steel plate by spot welding or tack welding. These
stud assemblies are not intended for use as shear connectors in steel-concrete composite construction.
NOTE 1—The configuration of the studs for stud assemblies is much different than the configuration of the headed-type studs prescribed in Section 7,
Figure 7.1 of AWS D1.1/D1.1M. Ratios of the cross-sectional areas of the head-to-shank of the AWS D1.1/D1.1M studs range from about 2.5 to 4. In
contrast, this specification requires the area of the head of the studs for stud assemblies to be at least 10 times the area of the shank. Thus, the standard
headed-type studs in Section 7, Figure 7.1 of AWS D1.1/D1.1M do not conform to the requirements of this specification for use as stud assemblies for
shear reinforcement.
1.2 This specification is applicable for orders in either inch-pound units or in SI units.
1.3 The values stated either in inch-pound or SI units are to be regarded as standard. Within the text, the SI units are shown
in brackets. The values stated in each system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each system must be used independently of the
other. Combining values from the two systems may result in nonconformance with this specification.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
A29/A29M Specification for General Requirements for Steel Bars, Carbon and Alloy, Hot-Wrought
A36/A36M Specification for Carbon Structural Steel
A370 Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing of Steel Products
A615/A615M Specification for Deformed and Plain Carbon-Steel Bars for Concrete Reinforcement
A706/A706M Specification for Deformed and Plain Low-Alloy Steel Bars for Concrete Reinforcement
3
2.2 AWS Standard:
AWS D1.1/D1.1M-2004 Structural Welding Code—Steel
4
2.3 U.S. Military Standards:
MIL-STD-129 Marking for Shipment and Storage
MIL-STD-163 Steel Mill Products Preparation for Shipment and Storage
4
2.4 U.S. Federal Standard:
Fed. Std. No. 123 Marking for Shipment (Civil Agencies)
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A01 on Steel, Stainless Steel and Related Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee A01.05
on Steel Reinforcement.
Current edition approved March 1, 2016. Published May 2016. Originally approved in 2005. Last previous edition approved in 2016 as A1044/A1044M – 16. DOI:
10.1520/A1044_A1044M-16A.10.1520/A1044_A1044M-16AE01.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’sstandard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Available from American Welding Society (AWS), 8669 NW 36 Street,St., #130, Miami, FL 33166-6672, http://www.aws.org.
4
Available from Standardization Documents Order Desk, DODSSP, Bldg. 4, Section D, DLA Document Services, Building 4/D, 700 Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA
19111-5098, http://dodssp.daps.dla.mil.19111-5094, http://quicksearch.dla.mil.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
´1
A1044/A1044M − 16a
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.1.1
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.