ASTM C1216-03(2008)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Adhesion and Cohesion of One-Part Elastomeric Solvent Release Sealants
Standard Test Method for Adhesion and Cohesion of One-Part Elastomeric Solvent Release Sealants
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
The failure of a building sealant in a joint that experiences movement is manifested by cohesive failure in the sealant or adhesive failure between the sealant and substrate, or both. This test method evaluates the performance of one-part elastomeric solvent release sealants in joints subjected to movement and temperature aging.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method is a laboratory procedure that determines the adhesion and cohesion performance of one-part elastomeric, solvent release sealants at high and low temperatures by the extension and compression of test specimens.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 The subcommittee with jurisdiction is not aware of any similar ISO standard.
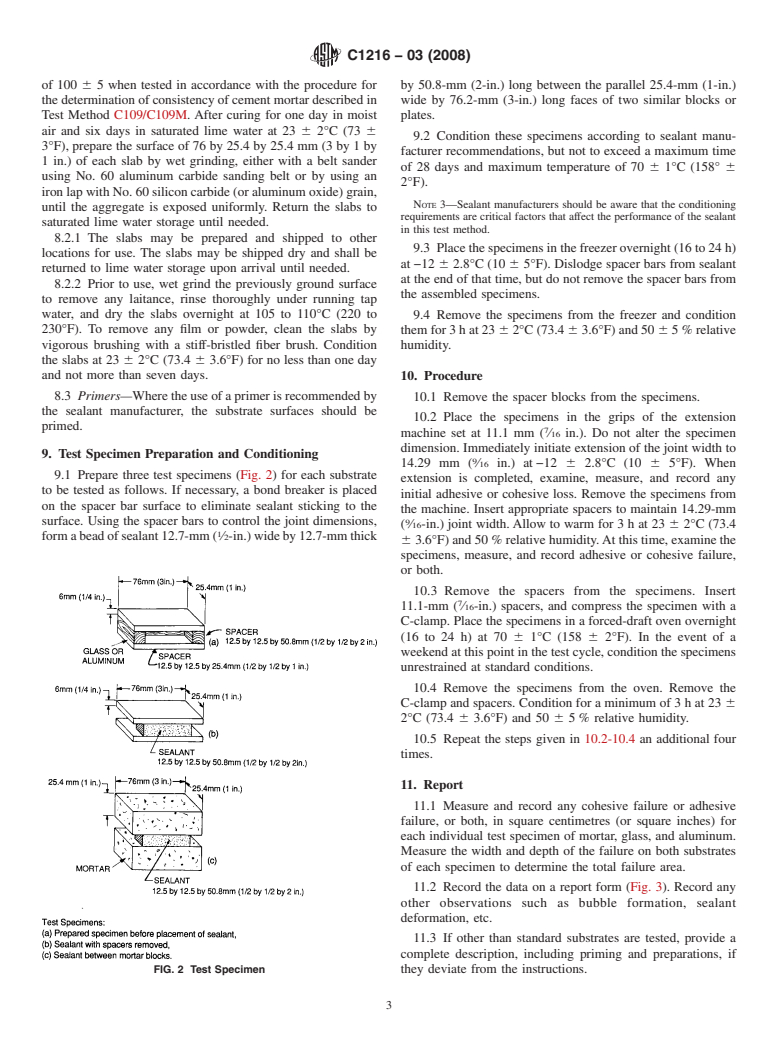
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For a specific precautionary statement, see Note 2.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: C1216 − 03(Reapproved 2008)
Standard Test Method for
Adhesion and Cohesion of One-Part Elastomeric Solvent
Release Sealants
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C1216; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope failure, bond breaker, cohesive failure, elastomeric, joint,
primer, sealant, solvent release sealant, and substrate.
1.1 This test method is a laboratory procedure that deter-
mines the adhesion and cohesion performance of one-part
4. Significance and Use
elastomeric, solvent release sealants at high and low tempera-
4.1 The failure of a building sealant in a joint that experi-
tures by the extension and compression of test specimens.
ences movement is manifested by cohesive failure in the
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
sealantoradhesivefailurebetweenthesealantandsubstrate,or
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
both. This test method evaluates the performance of one-part
only.
elastomeric solvent release sealants in joints subjected to
1.3 The subcommittee with jurisdiction is not aware of any
movement and temperature aging.
similar ISO standard.
5. Apparatus
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
5.1 Extension-Compression Machine, as shown in Fig. 1,
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro- designed to extend the test specimens automatically at a
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
constant rate of 3.20 mm ( ⁄8 in.)/h from a joint width of 11.2
7 9
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. For a specific mm ( ⁄16 in.) to 14.29 mm ( ⁄16 in.) at−12 6 2.8°C (+10 6
precautionary statement, see Note 2.
5°F).
5.2 Oven, forced-draft type, having the temperature con-
2. Referenced Documents
trolled to 70 6 1°C (158 6 2°F).
2.1 ASTM Standards:
5.3 Oven, convection type, having the temperature con-
C33Specification for Concrete Aggregates
trolled to 50 6 1°C (122 6 2°F).
C109/C109MTest Method for Compressive Strength of
Hydraulic Cement Mortars (Using 2-in. or [50-mm] Cube
5.4 Freezer Chest or Cold Box, having the temperature
Specimens)
controlled to−12 6 2.8°C (+10 6 5°F).
C150Specification for Portland Cement
5.5 C-Clamps, or other clamping devices.
C717Terminology of Building Seals and Sealants
2.2 Aluminum Association Standard:
6. Reagents
DAF-45Designation System for Aluminum Finishes
6.1 Purity of Reagents—Reagent grade chemicals shall be
3. Terminology
used in all tests. Unless otherwise indicated, it is intended that
all reagents shall conform to the specifications of the Commit-
3.1 Definitions—Refer to Definitions C717 for definitions
tee onAnalytical Reagents of theAmerican Chemical Society,
of the following terms used in this test method: adhesive
where such specifications are available. Other grades may be
used, provided it is first ascertained that the reagent is of
ThistestmethodisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeC24onBuilding
Seals and Sealants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C24.30 on
Adhesion.
Current edition approved May 1, 2008. Published June 2008. Originally Series 520 Sealant Compound Tester, manufactured by Applied Test Systems,
approved in 1992. Last previous edition approved in 2003 as C1216–03. DOI: Inc.,348NewCastleRd.,Butler,PA16001,andadurabilitytestermanufacturedby
10.1520/C1216-03R08. Ambard, Inc., 269-11 Sist Ave., New Hyde Park, NY 11040, have been found
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or suitable for this purpose.
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Reagent Chemicals, American Chemical Society Specifications ,Am.Chemical
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Soc., Washington, DC. For suggestions on the testing of reagents not listed by the
the ASTM website. American Chemical Society, see Reagent Chemicals and Standards, by Joseph
Available from Aluminum Association, 900 19th St. NW, Washington, DC Rosin, D. Van Nostrand Co., Inc., New York, NY, and the United States Pharma-
20006. copeia .
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
C1216 − 03 (2008)
NOTE 1—Three-dimensional view of compression-extension machine with automatic control units shows four specimens ready for compression-
extension cycling.
FIG. 1 Compression Extension Machine
sufficiently high purity to permit its use without lessening the epoxies are suitable as adhesives. Although the time of
accuracy of the determination. reinforcement is not critical, it has been found convenient to
applythealuminumplatestotheglassbeforepreparingthetest
6.2 Acetone or Methyl Ethyl Ketone Solvents.
specimens.
6.3 Detergent Solution.
7.2.3 Aluminum Plates,six,6063-T5or6061-T6alloyclear,
6.4 Distilled Water. 25.4-mm (1-in.) wide by 76.2-mm (3-in.) long by 6.35-mm
( ⁄4-in.) thick and anodized to AA-M32C12A31 quality as
6.5 Primer, if required.
described by DAF-45.
7. Sealants, Substrates, and Accessories 1
7.3 Rigid Spacer Bars, nine, 12.7 mm ( ⁄2 in.) by 12.7 mm
by 50.8 mm (2 in.); 18 bars 12.7 mm by 12.7 mm by 25.4 mm
7.1 The sealants shall be obtained from previously un-
9 1
(1 in.); 18 bars 14.29 mm ( ⁄16 in.) by 6.35 mm ( ⁄4 in.) by 25.4
opened containers. Precondition the unopened containers of
mm (1 in.); and 18 bars 11.1 mm ( ⁄16 in.) by 6.35 mm by 25.4
sealant at 23 6 2°C (73.4 6 3.6°F) and 50 6 5% relative
mm.
humidity for a minimum of 24 h.
7.4 Release Paper,orothersuitablematerial,ifnecessary,to
7.2 ThestandardsubstratesusedinthetestshallbePortland
serveasabondbreakertospacerbarsforthepreparationoftest
cement mortar, float glass, and aluminum alloy.
specimens.
NOTE 1—When requested, other substrates such as brick, marble, etc.
may be specified by the purchaser in addition to the standard substrates.
8. Preparation of Substrates
7.2.1 Mortar blocks, six, prepared as described in 8.2. The
8.1 Prior to use, the glass and aluminum (and, when
blocks shall be 25.4-mm (1-in.) wide by 76.2-mm (3-in.) long
specified, other metallic substrates) shall be cleaned by wiping
by 25.4-mm (1-in.) thick.
the surface with methyl ethyl ketone or a similar solvent. Dip
7.2.2 Glass Plates, six, of clear float glass 25.4-mm (1-in.)
the surface in a 0.1% detergent solution of a clear hand
wide by 76.2-mm (3-in.) long by 6.35-mm ( ⁄4-in.) thick. The
dishwashingdetergentindistilledordeionizedwater.Rinsethe
float glass may require reinforcement to survive the rigors of
surface without touching it in distilled or deionized water and
the subsequent test procedure.This must be completed prior to
allow it to air dry.
the compression-extension cycling described in Section 10.
NOTE 2—Methyl ethyl ketone and similar solvents are toxic and
Reinforcement is provided by adhering aluminum plates,
flammable and should be handled with caution in a well-ventilated area.
25.4-mm wide by 76.2-mm long by 6.35-mm thick, to the
8.2 Mortar Slabs—Prepare cement mortar slabs, each 76 by
outside surfaces of the glass. Commercially available two-part
25.4by25.4mm(3by1by1in.)insize,usingonepartofhigh
early stre
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:C1216–92 (Reapproved 1997) Designation: C 1216 – 03 (Reapproved 2008)
Standard Test Method for
Adhesion and Cohesion of One-Part Elastomeric Solvent
Release Sealants
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C1216; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method is a laboratory procedure that determines the adhesion and cohesion performance of one-part elastomeric,
solvent release sealants at high and low temperatures by the extension and compression of test specimens.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.3
1.3 The subcommittee with jurisdiction is not aware of any similar ISO standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use. For a specific precautionary statement, see Note 2.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
C33 Specification for Concrete Aggregates
C109/C109M TestMethodforCompressiveStrengthofHydraulicCementMortars(Using2-in.or[50-mm]CubeSpecimens)
C150 Specification for Portland Cement
C717 Terminology of Building Seals and Sealants
2.2 Aluminum Association Standard:
DAF-45 Designation System for Aluminum Finishes
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions—Refer to Definitions C717 for definitions of the following terms used in this test method: adhesive failure,
bond breaker, cohesive failure, elastomeric, joint, primer, sealant, solvent release sealant, and substrate.
4. Significance and Use
4.1 The failure of a building sealant in a joint that experiences movement is manifested by cohesive failure in the sealant or
adhesive failure between the sealant and substrate, or both. This test method evaluates the performance of one-part elastomeric
solvent release sealants in joints subjected to movement and temperature aging.
5. Apparatus
5.1 Extension-Compression Machine,asshowninFig.1,designedtoextendthetestspecimensautomaticallyataconstantrate
1 7 9
of 3.20 mm ( ⁄8 in.)/h from a joint width of 11.2 mm ( ⁄16 in.) to 14.29 mm ( ⁄16 in.) at−12 6 2.8°C (+10 6 5°F).
5.2 Oven, forced-draft type, having the temperature controlled to 70 6 1°C (158 6 2°F).
5.3 Oven, convection type, having the temperature controlled to 50 6 1°C (122 6 2°F).
5.4 Freezer Chest or Cold Box, having the temperature controlled to−12 6 2.8°C (+10 6 5°F).
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee C24 on Building Seals and Sealants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C24.20 on General
Sealant Standards.
Current edition approved June 15, 1992. Published August 1992.
ThistestmethodisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeC24onBuildingSealsandSealantsandisthedirectresponsibilityofSubcommitteeC24.30onAdhesion.
Current edition approved May 1, 2008. Published June 2008. Originally approved in 1992. Last previous edition approved in 2003 as C1216–03.
ForreferencedASTMstandards,visittheASTMwebsite,www.astm.org,orcontactASTMCustomerServiceatservice@astm.org.For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
, Vol 04.02.volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 04.01.
Available from Aluminum Association, 900 19th St. NW, Washington, DC 20006.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 04.07.
Series 520 Sealant Compound Tester, manufactured by Applied Test Systems, Inc., 348 New Castle Rd., Butler, PA 16001, and a durability tester manufactured by
Ambard, Inc., 269-11 Sist Ave., New Hyde Park, NY 11040, have been found suitable for this purpose.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
C 1216 – 03 (2008)
NOTE 1—Three-dimensional view of compression-extension machine with automatic control units shows four specimens ready for compression-
extension cycling.
FIG. 1 Compression Extension Machine
5.5 C-Clamps, or other clamping devices.
6. Reagents
6.1 Purity of Reagents—Reagent grade chemicals shall be used in all tests. Unless otherwise indicated, it is intended that all
reagents shall conform to the specifications of the Committee on Analytical Reagents of the American Chemical Society, where
such specifications are available. Other grades may be used, provided it is first ascertained that the reagent is of sufficiently high
purity to permit its use without lessening the accuracy of the determination.
6.2 Acetone or Methyl Ethyl Ketone Solvents.
6.3 Detergent Solution.
6.4 Distilled Water.
6.5 Primer, if required.
7. Sealants, Substrates, and Accessories
7.1 The sealants shall be obtained from previously unopened containers. Precondition the unopened containers of sealant at 23
6 2°C (73.4 6 3.6°F) and 50 6 5% relative humidity for a minimum of 24 h.
7.2 The standard substrates used in the test shall be Portland cement mortar, float glass, and aluminum alloy.
NOTE 1—When requested, other substrates such as brick, marble, etc. may be specified by the purchaser in addition to the standard substrates.
7.2.1 Mortar blocks, six, prepared as described in 8.2. The blocks shall be 25.4-mm (1-in.) wide by 76.2-mm (3-in.) long by
25.4-mm (1-in.) thick.
7.2.2 Glass Plates, six, of clear float glass 25.4-mm (1-in.) wide by 76.2-mm (3-in.) long by 6.35-mm ( ⁄4-in.) thick. The float
glass may require reinforcement to survive the rigors of the subsequent test procedure. This must be completed prior to the
compression-extension cycling described in Section 10. Reinforcement is provided by adhering aluminum plates, 25.4-mm wide
by 76.2-mm long by 6.35-mm thick, to the outside surfaces of the glass. Commercially available two-part epoxies are suitable as
adhesives.Althoughthetimeofreinforcementisnotcritical,ithasbeenfoundconvenienttoapplythealuminumplatestotheglass
before preparing the test specimens.
Available from Aluminum Association, 818 Connecticut Ave. NW, Washington, DC 20006.
Reagent Chemicals, American Chemical Society Specifications , Am. Chemical Soc., Washington, DC. For suggestions on the testing of reagents not listed by the
American Chemical Society, see Reagent Chemicals and Standards, by Joseph Rosin, D. Van Nostrand Co., Inc., New York, NY, and the United States Pharmacopeia .
Series 520 Sealant Compound Tester, manufactured by Applied Test Systems, Inc., 348 New Castle Rd., Butler, PA 16001, and a durability tester manufactured by
Ambard, Inc., 269-11 Sist Ave., New Hyde Park, NY 11040, have been found suitable for this purpose.
Dawn, a registered trademark of Proctor and Gamble, Co., P.O. Box 599, Cincinnati, OH 54201, or Palmolive Green, a registered trademark of Colgate Palmolive Co.,
300-T Park Ave., New York, NY 10022, have been found suitable for this purpose.
C 1216 – 03 (2008)
7.2.3 Aluminum Plates,six,6063-T5or6061-T6alloyclear,25.4-mm(1-in.)wideby76.2-mm(3-in.)longby6.35-mm( ⁄4-in.)
thick and anodized to AA-M32C12A31 quality as described by DAF-45.
7.3 Rigid Spacer Bars, nine, 12.7 mm ( ⁄2 in.) by 12.7 mm by 50.8 mm (2 in.); 18 bars 12.7 mm by 12.7 mm by 25.4 mm (1
9 1 7
in.); 18 bars 14.29 mm ( ⁄16 in.) by 6.35 mm ( ⁄4 in.) by 25.4 mm (1 in.); and 18 bars 11.1 mm ( ⁄16 in.) by 6.35 mm by 25.4 mm.
7.4 Release Paper
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.