ASTM D5492-98(2003)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determination of Xylene Solubles in Propylene Plastics
Standard Test Method for Determination of Xylene Solubles in Propylene Plastics
SCOPE
1.1 This test method is to be used for determining the 25°C ortho-xylene-soluble fraction of polypropylene and propylene-ethylene copolymers.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Note 1—This standard is similar to ISO 6427-1982 in title only. The technical content is significantly different.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D 5492 – 98 (Reapproved 2003)
Standard Test Method for
1
Determination of Xylene Solubles in Propylene Plastics
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 5492; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope %. When the solution is cooled the insoluble portion precipi-
tates and is isolated by filtration. The orthoxylene is evaporated
1.1 This test method is to be used for determining the 25°C
from the filtrate, leaving the soluble fraction in the residue. The
ortho-xylene-soluble fraction of polypropylene and propylene-
percentage of this fraction in the plastic is determined gravi-
ethylene copolymers.
metrically.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
5. Significance and Use
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
5.1 The results of this test provide a relative measure of the
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
total soluble fraction of polypropylene and copolymers. The
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
soluble fraction can be approximately correlated to the amor-
NOTE 1—This standard is similar to ISO 6427-1982 in title only. The
phous fraction in the polypropylene. Xylene is widely used for
technical content is significantly different.
determining the soluble fraction in polypropylene. The concen-
tration of a soluble fraction obtained with a specific solvent has
2. Referenced Documents
been found to relate closely to the performance characteristics
2.1 ASTM Standards:
of a product in certain applications, for example film and fiber.
2
D 883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
Data obtained by one solvent and at one precipitation time
D 1600 Terminology of Abbreviated Terms Relating to
cannot be compared with data obtained by another solvent or
2
Plastics
precipitation time, respectively. Xylene is more specific to the
2.2 ISO Standard:
atactic fraction than other solvents.
ISO 6427-1982 Plastics—Determination of Matter Ex-
tracted by Organic Solvents (Conventional Methods) An-
6. Interferences
nex B Standard Method of Test for Determination of
6.1 Materials with solubilities similar to the polymer frac-
3
Polypropylene Solubility in Cold Xylene
tion, such as additives, may interfere with the measurement of
solubles. When present in concentrations that are judged to
3. Terminology
impart a significant error to the soluble-fraction data, the level
3.1 For definitions of plastic terms see Terminology D 883
of interference must be determined and corrections made.
and for abbreviations see Terminology D 1600.
6.2 Small-particle fillers and pigments that may pass
3.2 There are no terms in this test method that require new
through the filter and insoluble gels present in the polymer may
or other-than-dictionary definitions.
cause errors in the measurement.
6.3 The polymer flakes and spheres must be dried before
4. Summary of Test Method
testing to eliminate moisture that can influence the initial
4.1 A weighed amount of sample is dissolved in orthoxylene
weight of sample added to the flask.
under reflux conditions. The solution is cooled under con-
trolled conditions and maintained at a 25°C equilibrium
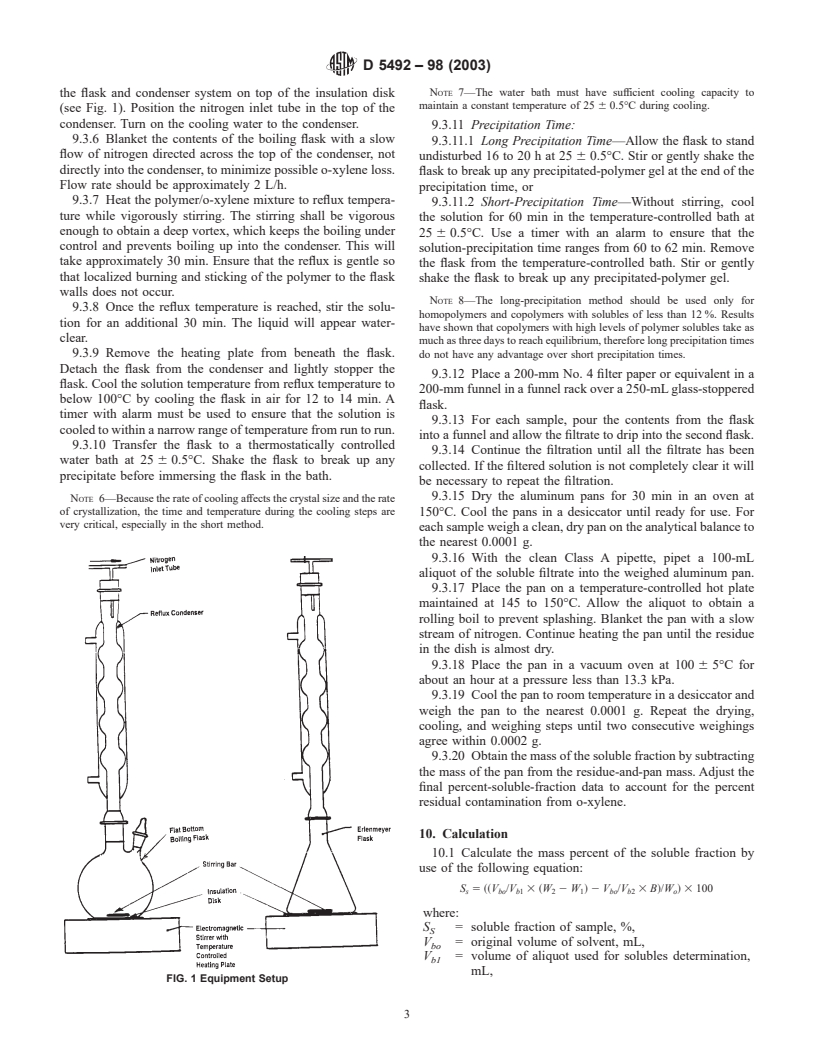
7. Apparatus
temperature so that the crystallization of the insoluble fraction
7.1 Reflux-Condenser Apparatus, 400 mm, with 24/40 glass
takes place. One of two precipitation-time periods can be used,
joint.
although the longer precipitation time should be used for
7.2 Flat-Bottom Boiling Flask, with one or two necks, 400
homopolymers and copolymers with solubles less than 12 mass
mL with 24/40 joint, Erlenmeyer flask, or cylindrical bottle.
7.3 Insulation Disk, made of fiberglass or rock wool.
1
7.4 Electromagnetic Stirrer, with temperature-controlled
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D20 on Plastics
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.12 on Olefin Plastics. heating plate, thermostated oil bath, or heater block capable of
Current edition approved July 10, 2003. Published September 2003. Originally
maintaining 145 to 150°C.
approved in 1994. Last previous edition approved in 1998 as D 5492 – 98.
7.5 Stirring Bar.
2
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.01.
3
7.6 Pipette, Class A, 200 mL.
Available from American National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
4th Floor, New York, NY 10036.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D 5492 – 98 (2003)
7.7 Pipette, Class A, 10
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.