ASTM D4349-96
(Classification)Standard Classification System for Polyphenylene Ether (PPE) Materials
Standard Classification System for Polyphenylene Ether (PPE) Materials
SCOPE
1.1 This classification system covers the basic polymers and copolymers known as polyphenylene ethers and polyphenylene oxides, as well as filled, modified, and reinforced versions.
Note 1-A previous specification (D2874) referred to polyphenylene oxide plastics. The term used in the title of this describes the same generic polymer species but was chosen, along with the abbreviation PPE, to avoid complications with registered trademarks.
1.2 This classification system is not intended for the selection of materials, but only as a means to call out plastic materials to be used for the manufacture of parts. The selection of these materials is to be made by personnel with expertise in the plastics field where the environment, inherent properties of the materials, performance of the parts, part design, manufacturing process, and economics are considered.
1.3 The properties included in the specification are those required to identify the compositions covered. There may be other requirements necessary to identify particular characteristics important to specific applications. These will be agreed upon between the user and the supplier by using the suffixes as given in Section 4.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard.
1.5 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the test methods portion, Section 13, of this specification: This standard does not purport to address all of the safety problems, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D 4349 – 96
Classification System for
Polyphenylene Ether (PPE) Materials
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 4349; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
TABLE 1 Testing Parameters
1. Scope
ASTM
1.1 This classification system covers the basic polymers and
Test Specimen and Testing Parameters
Test Method
copolymers known as polyphenylene ethers and polyphenylene
D 638 Type I, 3.2-mm thickness, crosshead speed of 5 mm/min for
oxides, as well as filled, modified, and reinforced versions.
reinforced materials and 50 mm/min for unreinforced
materials.
NOTE 1—Addition to the natural polymer or copolymer of pigments,
D 790 3.2 by 12.7-mm specimen, tested by Method I, Procedure A
colorants or additives may result in the final composition not meeting the
(tangent) with a crosshead speed of 1.3 mm/min and a span
requirements specified for the natural polymer or copolymer. Discussions
to depth ratio of 16 to 1.
with the supplier should take place before specifications of altered D 256 3.2 by 12.7-mm specimen, tested by Test Method A.
D 648 3.2 by 12.7-mm specimen, 102-mm support span,
compositions are established.
unannealed prior to testing.
NOTE 2—The preferred abbreviation for polyphenylene ether is PPE, as
noted in Terminology D 1600.
1.2 This classification system is not intended for the selec- 2
and Plastics and Electrical Insulating Materials
tion of materials, but only as a means to call out plastic
D 792 Test Methods for Specific Gravity (Relative Density)
materials to be used for the manufacture of parts. The selection 2
and Density of Plastics by Displacements
of these materials is to be made by personnel with expertise in
D 883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
the plastics field where the environment, inherent properties of
D 1600 Terminology for Abbreviated Terms Relating to
the materials, performance of the parts, part design, manufac-
Plastics
turing process, and economics are considered. 2
D 1898 Practice for Sampling of Plastics
1.3 There may be other requirements necessary to identify
D 3892 Practice for Packaging/Packing of Plastics
particular characteristics important to specific applications.
D 4000 Classification System for Specifying Plastic Mate-
These may be specified by using the suffixes described in
rial
Section 5.
E 29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
Determine Conformance with Specifications
standard.
2.2 Underwriters Laboratories:
UL 94 Standards for Tests for Flammability for Parts in
NOTE 3—No ISO standard exists that covers these materials.
Devices and Appliances
2. Referenced Documents
3. Terminology
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D 256 Test Methods for Impact Resistance of Plastics and 3.1 The terminology used in this classification is in accor-
Electrical Insulating Materials dance with Terminologies D 883 and D 1600.
D 618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics and Electrical 3.2 The polyphenylene ether materials will be designated
Insulating Materials for Testing PPE as specified in Terminology D 1600.
D 638 Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics
4. Classification
D 648 Test Method for Deflection Temperature of Plastics
4.1 Polyphenylene ether-based materials are classified into
Under Flexural Load
groups according to their compositions. These groups are
D 790 Test Methods for Flexural Properties of Unreinforced
subdivided into classes and grades, as shown in Table PPE.
This classification system is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D20 on
Plastics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.15 on Thermoplastic
Materials. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.02.
Current edition approved Nov. 10, 1996. Published May 1997. Originally Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.02.
published as D 4349 – 89. Last previous edition D 4349 – 93. Available from Underwriters Laboratories Inc. Publications Stock, 333 Pfing-
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.01. sten Road, Northbrook, IL 60067.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
D4349–96
TABLE PPE Requirements for Polyphenylene Ether (PPE) Materials
A
NOTE 1—Values given are for natural materials only. Other colors may be different.
Tensile Flexural Izod
Heat Deflection, min
Specific
Strength, Modulus, Impact,
Grade Gravity,
at 1.82 at 0.45 B,C B,C B,D
Group Description Class Description D 638, D 790, D 256,
Description ASTM
MPa, MPa,
MPa, MPa, J/m,
B B
D 792, min
D 648, °C D 648, °C
min min min
E
1 Unmodified 1 general purpose 0 other
F E
2 flame retardant 0 other
E
0 other 0 other
G
2 PS modified materials 1 general purpose 1 90 N/A 1.03 32 1750 265
G
2 100 N/A 1.03 38 1900 240
G
3 100 N/A 1.03 44 2150 185
G
4 110 N/A 1.04 55 2300 160
G
5 130 N/A 1.05 57 2300 160
0 other . . . . . .
F G
2 flame retardant 1 67 N/A 1.06 36 2200 190
G
2 80 N/A 1.07 40 2250 130
G
3 85 N/A 1.07 48 2350 100
G
4 105 N/A 1.07 55 2350 160
G
5 125 N/A 1.08 60 2500 160
0 other . . . . . .
0 other 0 other . . . . . .
G
3 PA modified materials 1 general purpose 1 N/A 145 1.05 50 2000 170
G
2 N/A 155 1.05 50 2000 160
G
3 N/A 170 1.05 50 1800 530
G
4 N/A 180 1.05 55 2000 185
G
5 N/A 195 1.05 58 2200 160
0 other . . . . . .
F E
2 flame retardant 0 other
0 other 0 other . . . . . .
4 Other 1 general purpose 0 other . . . . .
F
2 flame retardant 0 other . . . . .
0 other 0 other . . . . .
5 Rework modified 1 general purpose 0 other . . . . .
F
2 flame retardant 0 other . . . . .
0 other 0 other . . . . .
A
Use Tables A and B where necessary for colored materials.
B
See Table 1 for test parameters and conditions.
C
MPa 3 145 = psi.
D
J/m 3 0.01873 = ft·lbf/in.
E
Unfilled materials currently not available. Use Table A.
F
Flammability ratings determined in accordance with UL 94.
G
N/A—Not applicable for grade description.
TABLE A Reinforced Polyphenylene Ether Materials, Details Requirements
Designation Property Cell Limits
Order Number
0 1 23 45 6 7 8 9
A
1 Heat deflection temperature, unspecified 100 110 120 130 140 150 160 170 specify value
B
D 648, 1.82 MPa, °C, min
A
2 Heat deflection temperature, unspecified 180 190 200 210 220 230 240 250 specify value
B
D 648, 0.45 MPa, °C, min
3 Tensile strength, unspecified 45 55 65 80 100 120 140 160 specify value
B C
D 638, MPa, min
4 Flexural modulus, unspecified 2000 3000 4000 5000 6000 7500 9000 10 500 specify value
B C
D 790, MPa, min
B
5 Izod impact, D 256, unspecified 25 50 75 100 125 150 200 250 specify value
D
J/m, min
A
For specifying HDT use the “order number” corresponding to the appropriate test conditions for the material being defined. It is intended that one or the other of these
requirements be used unless specific agreement between the supplier and the user requires both.
B
SeeTable 1 for test specimen sizes.
C
MPa 3 145 = psi.
D
J/m 3 0.01873 = f·lbf/in.
D4349–96
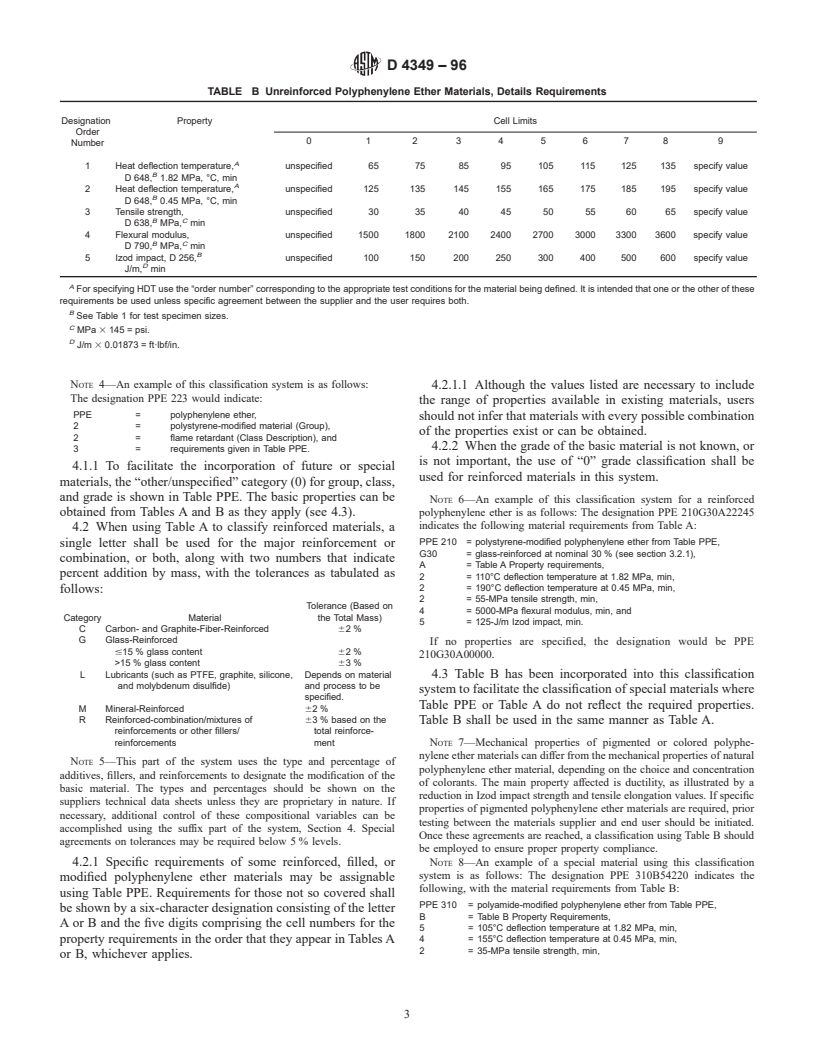
TABLE B Unreinforced Polyphenylene Ether Materials, Details Requirements
Designation Property Cell Limits
Order
0 1 2 3456 7 8 9
Number
A
1 Heat deflection temperature, unspecified 65 75 85 95 105 115 125 135 specify value
B
D 648, 1.82 MPa, °C, min
A
2 Heat deflection temperature, unspecified 125 135 145 155 165 175 185 195 specify value
B
D 648, 0.45 MPa, °C, min
3 Tensile strength, unspecified 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 specify value
B C
D 638, MPa, min
4 Flexural modulus, unspecified 1500 1800 2100 2400 2700 3000 3300 3600 specify value
B C
D 790, MPa, min
B
5 Izod impact, D 256, unspecified 100 150 200 250 300 400 500 600 specify value
D
J/m, min
A
For specifying HDT use the “order number” corresponding to the appropriate test conditions for the material being defined. It is intended that one or the other of these
requirements be used unless specific agreement between the supplier and the user requires both.
B
See Table 1 for test specimen sizes.
C
MPa 3 145 = psi.
D
J/m 3 0.01873 = ft·lbf/in.
NOTE 4—An example of this classification system is as follows:
4.2.1.1 Although the values listed are necessary to include
The designation PPE 223 would indicate:
the range of properties available in existing materials, users
PPE = polyphenylene ether,
should not infer that materials with every possible combination
2 = polystyrene-modified material (Group),
of the properties exist or can be obtained.
2 = flame retardant (Class Description), and
4.2.2 When the grade of the basic material is not known, or
3 = requirements given in Table PPE.
is not important, the use of “0” grade classification shall be
4.1.1 To facilitate the incorporation of future or special
used for reinforced materials in this system.
materials, the “other/unspecified” category (0) for group, class,
and grade is shown in Table PPE. The basic properties can be
NOTE 6—An example of this classification system for a reinforced
obtained from Tables A and B as they apply (see 4.3). polyphenylene ether is as follows: The designation PPE 210G30A22245
indicates the following material requirements from Table A:
4.2 When using Table A to classify reinforced materials, a
PPE 210 = polystyrene-modified polyphenylene ether from Table PPE,
single letter shall be used for the major reinforcement or
G30 = glass-reinforced at nominal 30 % (see section 3.2.1),
combination, or both, along with two numbers that indicate
A = Table A Property requirements,
percent addition by mass, with the tolerances as tabulated as
2 = 110°C deflection temperature at 1.82 MPa, min,
2 = 190°C deflection temperature at 0.45 MPa, min,
follows:
2 = 55-MPa tensile strength, min,
Tolerance (Based on
4 = 5000-MPa flexural modulus, min, and
Category Material the Total Mass)
5 = 125-J/m Izod impact, min.
C Ca
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.