ASTM C1482-10
(Specification)Standard Specification for Polyimide Flexible Cellular Thermal and Sound Absorbing Insulation
Standard Specification for Polyimide Flexible Cellular Thermal and Sound Absorbing Insulation
ABSTRACT
This specification covers the composition and physical properties of lightweight, flexible open-cell polyimide foam insulation intended for use as thermal and sound-absorbing insulation for a certain temperature range in commercial and industrial environments. The insulations are classified into the following types: Types I, II, III, IV, V, and VI. Polyimide foam shall be manufactured from the appropriate monomers, and necessary compounding ingredients. Different test methods shall be performed in order to determine the following properties of the insulation: density, apparent thermal conductivity, upper temperature limit, high temperature stability, compressive strength, compression deflection, compression set, steam aging, corrosiveness, chemical resistance, surface burning characteristics, radiant panel surface flammability, vertical burn, heat release rate, specific optical smoke density, hydrogen halides in smoke, toxic gas generation, and sound absorption coefficients.
SCOPE
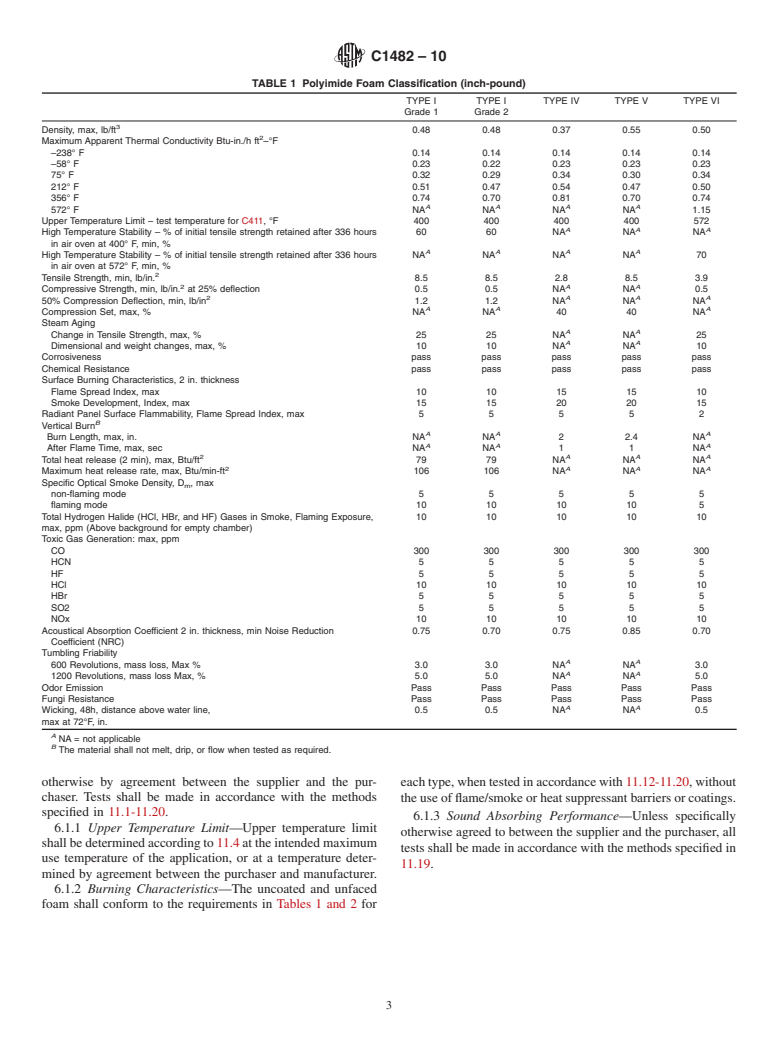
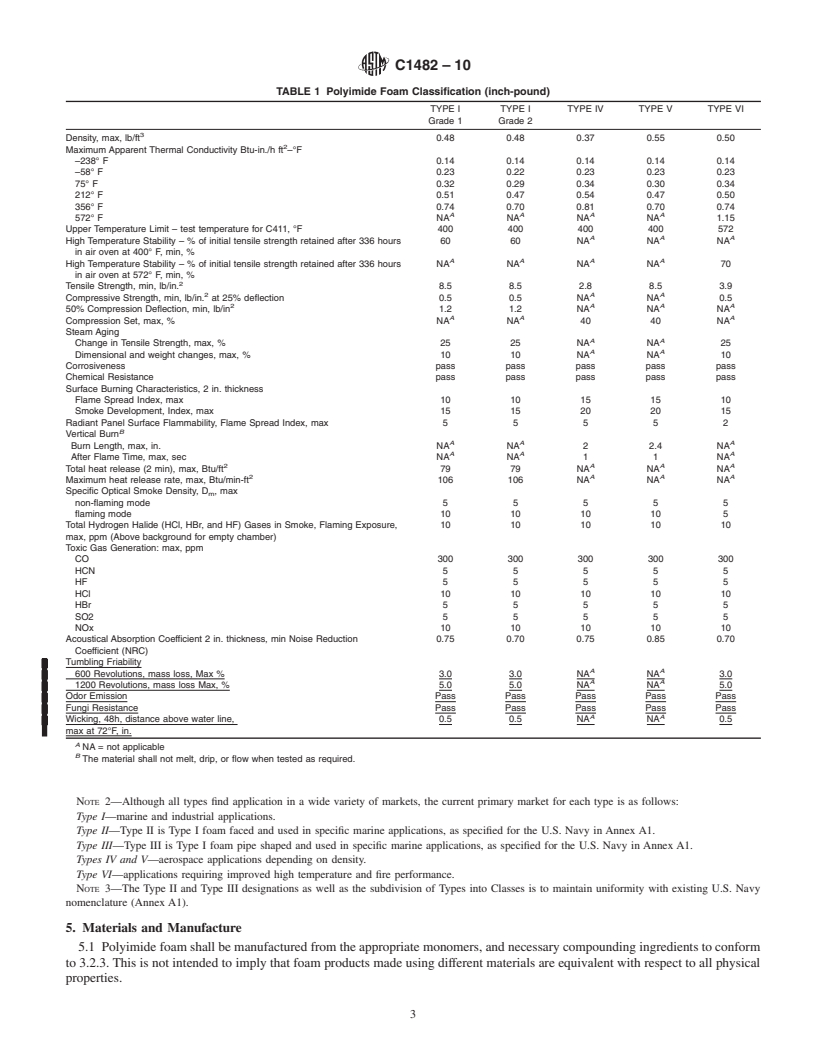
1.1 This specification covers the composition and physical properties of lightweight, flexible open-cell polyimide foam insulation intended for use as thermal and sound-absorbing insulation for temperatures from -328°F up to +572°F (-200°C and +300°C) in commercial and industrial environments.
1.1.1 Annex A1 includes faced polyimide foam as specified by the U.S. Navy for marine applications.
1.1.2 This standard is designed as a material specification and not a design document. Physical property requirements vary by application and temperature. No single test is adequate for estimating either the minimum or maximum use temperature of polyimide foam under all possible conditions. Consult the manufacturer for specific recommendations and physical properties for specific applications.
1.1.3 The use of an appropriate vapor retarder is required in all applications where condensation could occur and cause a decrease in thermal performance or affect other system properties.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.3 This standard is used to measure and describe the response of materials, products, or assemblies to heat and flame under controlled conditions, but does not by itself incorporate all factors required for fire-hazard or fire-risk assessment of the materials, products, or assemblies under actual fire conditions.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory requirements prior to use.
Note 1—The subject matter of this material specification is not covered by any other ASTM specification. There is no known ISO standard covering the subject of this standard.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: C1482 – 10
Standard Specification for
Polyimide Flexible Cellular Thermal and Sound Absorbing
1
Insulation
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C1482; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
2
1.1 This specification covers the composition and physical 2.1 ASTM Standards:
properties of lightweight, flexible open-cell polyimide foam C165 Test Method for Measuring Compressive Properties
insulation intended for use as thermal and sound-absorbing of Thermal Insulations
insulation for temperatures from -328°F up to +572°F (-200°C C168 Terminology Relating to Thermal Insulation
and +300°C) in commercial and industrial environments. C177 Test Method for Steady-State Heat Flux Measure-
1.1.1 AnnexA1 includes faced polyimide foam as specified ments and Thermal Transmission Properties by Means of
by the U.S. Navy for marine applications. the Guarded-Hot-Plate Apparatus
1.1.2 This standard is designed as a material specification C302 Test Method for Density and Dimensions of Pre-
and not a design document. Physical property requirements formed Pipe-Covering-Type Thermal Insulation
vary by application and temperature. No single test is adequate C335 Test Method for Steady-State Heat Transfer Proper-
for estimating either the minimum or maximum use tempera- ties of Pipe Insulation
ture of polyimide foam under all possible conditions. Consult C390 Practice for Sampling and Acceptance of Thermal
the manufacturer for specific recommendations and physical Insulation Lots
properties for specific applications. C411 Test Method for Hot-Surface Performance of High-
1.1.3 The use of an appropriate vapor retarder is required in Temperature Thermal Insulation
all applications where condensation could occur and cause a C421 Test Method for Tumbling Friability of Preformed
decrease in thermal performance or affect other system prop- Block-Type and Preformed Pipe-Covering-Type Thermal
erties. Insulation
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded C423 Test Method for Sound Absorption and Sound Ab-
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical sorption Coefficients by the Reverberation Room Method
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only C447 Practice for Estimating the Maximum Use Tempera-
and are not considered standard. ture of Thermal Insulations
1.3 This standard is used to measure and describe the C518 Test Method for Steady-State Thermal Transmission
responseofmaterials,products,orassembliestoheatandflame Properties by Means of the Heat Flow Meter Apparatus
under controlled conditions, but does not by itself incorporate C634 Terminology Relating to Building and Environmental
all factors required for fire-hazard or fire-risk assessment of the Acoustics
materials, products, or assemblies under actual fire conditions. C665 Specification for Mineral-Fiber Blanket Thermal In-
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the sulation for Light Frame Construction and Manufactured
safety concerns associated with its use. It is the responsibility Housing
of the user to establish appropriate safety and health practices C1045 PracticeforCalculatingThermalTransmissionProp-
and determine the applicability of regulatory requirements erties Under Steady-State Conditions
prior to use. C1058 Practice for Selecting Temperatures for Evaluating
and Reporting Thermal Properties of Thermal Insulation
NOTE 1—Thesubjectmatterofthismaterialspecificationisnotcovered
C1114 Test Method for Steady-State Thermal Transmission
by any other ASTM specification. There is no known ISO standard
Properties by Means of the Thin-Heater Apparatus
covering the subject of this standard.
C1304 Test Method for Assessing the Odor Emission of
Thermal Insulation Materials
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C16 on
Thermal Insulation and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C16.22 on
2
Organic and Nonhomogeneous Inorganic Thermal Insulations.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved Sept. 1, 2010. Published October 2010. Originally
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approved in 2000. Last previous edition approved in 2009 as C1482 – 10 DOI:
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
10.1520/C1482-10.
the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 -------------------
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:C1482–09 Designation: C1482 – 10
Standard Specification for
Polyimide Flexible Cellular Thermal and Sound Absorbing
1
Insulation
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C1482; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This specification covers the composition and physical properties of lightweight, flexible open-cell polyimide foam
insulation intended for use as thermal and sound-absorbing insulation for temperatures from -328°F up to +572°F (-200°C and
+300°C) in commercial and industrial environments.
1.1.1 Annex A1 includes faced polyimide foam as specified by the U.S. Navy for marine applications.
1.1.2 This standard is designed as a material specification and not a design document. Physical property requirements vary by
application and temperature. No single test is adequate for estimating either the minimum or maximum use temperature of
polyimide foam under all possible conditions. Consult the manufacturer for specific recommendations and physical properties for
specific applications.
1.1.3 The use of an appropriate vapor retarder is required in all applications where condensation could occur and cause a
decrease in thermal performance or affect other system properties.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.3 This standard is used to measure and describe the response of materials, products, or assemblies to heat and flame under
controlled conditions, but does not by itself incorporate all factors required for fire-hazard or fire-risk assessment of the materials,
products, or assemblies under actual fire conditions.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the
user to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory requirements prior to use.
NOTE 1—The subject matter of this material specification is not covered by any otherASTM specification. There is no known ISO standard covering
the subject of this standard.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
C165 Test Method for Measuring Compressive Properties of Thermal Insulations
C168 Terminology Relating to Thermal Insulation
C177 Test Method for Steady-State Heat Flux Measurements and Thermal Transmission Properties by Means of the
Guarded-Hot-Plate Apparatus
C302 Test Method for Density and Dimensions of Preformed Pipe-Covering-Type Thermal Insulation
C335 Test Method for Steady-State Heat Transfer Properties of Pipe Insulation
C390 Practice for Sampling and Acceptance of Thermal Insulation Lots
C411 Test Method for Hot-Surface Performance of High-Temperature Thermal Insulation
C421 Test Method for Tumbling Friability of Preformed Block-Type and Preformed Pipe-Covering-Type Thermal Insulation
C423 Test Method for Sound Absorption and Sound Absorption Coefficients by the Reverberation Room Method
C447 Practice for Estimating the Maximum Use Temperature of Thermal Insulations
C518 Test Method for Steady-State Thermal Transmission Properties by Means of the Heat Flow Meter Apparatus
C634 Terminology Relating to Building and Environmental Acoustics
C665 Specification for Mineral-Fiber Blanket Thermal Insulation for Light Frame Construction and Manufactured Housing
C1045 Practice for Calculating Thermal Transmission Properties Under Steady-State Conditions
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C16 on Thermal Insulation and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C16.22 on Organic and
Nonhomogeneous Inorganic Thermal Insulations.
Current edition approved AprilSept. 1, 2009.2010. Published May 2009.October 2010. Originally approved in 2000. Last previous edition approved in 20082009 as
C1482–08.C1482 – 10 DOI: 10.1520/C1482-109.
2
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
-----------------
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.