ASTM D1263-94(1999)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Leakage Tendencies of Automotive Wheel Bearing Greases
Standard Test Method for Leakage Tendencies of Automotive Wheel Bearing Greases
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the evaluation of the leakage tendencies of wheel bearing greases when tested under prescribed laboratory conditions.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety problems, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard information see Note 2 and Annex A2.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
An American National Standard
Designation:D1263–94 (Reapproved 1999)
Standard Test Method for
Leakage Tendencies of Automotive Wheel Bearing Greases
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D1263; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope 3.1.1.1 Discussion—Thedispersionofthethickenerformsa
two-phase system and immobilizes the liquid lubricant by
1.1 This test method covers the evaluation of the leakage
surfacetensionandotherphysicalforces.Otheringredientsare
tendencies of wheel bearing greases when tested under pre-
commonly included to impart special properties. D 217
scribed laboratory conditions.
3.1.2 lubricant, n—any material interposed between two
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
surfaces that reduces the friction or wear between them.
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
D 4175
only.
3.1.3 thickener, n—in lubricating grease, a substance com-
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
posed of finely-divided particles dispersed in a liquid lubricant
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
to form the product’s structure.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.1.3.1 Discussion—The solid thickener can be fibers (such
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
as various metallic soaps) or plates or spheres (such as certain
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard
non-soap thickeners) which are insoluble or, at the most, only
information see Note 2 and Annex A2.
very sightly soluble in the liquid lubricant. The general
2. Referenced Documents
requirements are that the solid particles be extremely small,
uniformlydispersed,andcapableofformingarelativelystable,
2.1 ASTM Standards:
gel-like structure with the liquid lubricant. D 217
D217 Test Methods for Cone Penetration of Lubricating
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
Grease
3.2.1 automotive wheel bearing grease, n— a lubricating
D3527 Test Method for Life Performance of Automotive
grease specifically formulated to lubricate automotive wheel
Wheel Bearing Grease
bearings at relatively high grease temperatures and bearing
D4175 Terminology Relating to Petroleum, Petroleum
speed. D 3527
Products, and Lubricants
3.2.2 leakage, n—of wheel bearing grease, separation and
D4290 Test Method for Determining the Leakage Tenden-
overflow of grease or oil from the bulk grease charge, induced
cies ofAutomotive Wheel Bearing Grease underAcceler-
by high temperature and bearing rotation. D 4290
ated Conditions
E1 Specification for ASTM Thermometers
4. Summary of Test Method
E77 Test Method for Inspection and Verification of Ther-
4 4.1 The grease is distributed in a modified front-wheel hub
mometers
and spindle assembly. The hub is rotated at a speed of 660 6
3. Terminology 30 rpm for 6 h 6 5 min, at a spindle temperature which is
raised to and then maintained at 105 6 1.2°C (220 6 2.5°F).
3.1 Definitions:
Leakage of grease or oil, or both, is measured, and the
3.1.1 lubricating grease, n—asemi-fluidtosolidproductof
condition of the bearing surface is noted at the end of the test.
a dispersion of a thickener in a liquid lubricant.
5. Significance and Use
5.1 The test method provides a screening device that per-
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D-2 on
mits differentiation among products having distinctly different
PetroleumProductsandLubricantsandisthedirectresponsibilityofSubcommittee
leakage characteristics (Note 1). It is not the equivalent of
D02.G on Lubricating Grease.
longtimeservicetests,norisitintendedtodistinguishbetween
Current edition approved Jan. 15, 1994. Published March 1994. Originally
published as D1263–53T. Last previous edition D1263–92. wheel bearing greases showing similar or borderline leakage.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 05.01.
NOTE 1—It is possible for skilled operators to observe significant
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 05.02.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.03. changes in other important grease characteristics that occurred during the
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
D1263–94 (1999)
8. Reagent
8.1 ASTM n-Heptane—99.87% purity SRM 1815.
NOTE 2—Warning:Flammable. Harmful if inhaled.
9. Procedure
9.1 Weigh 90 6 1 g of sample on a flat plate. Pack with a
spatula 2 6 0.1 g of grease in the small bearing and 36 0.1 g
in the large bearing (Note 3). Distribute the balance of the test
grease (85 g) in a uniform layer on the inside of the hub (Note
4).Apply a thin film of grease to the bearing races in the hub.
NOTE 3—A narrow, wedge-cut spatula has been found of considerable
aid in packing the bearings.
NOTE 4—Thebalanceofthetestgreasewillfillthehubpracticallyeven
with the races, and, with the exception of very fibrous greases, can be
distributed readily and uniformly by use of a spatula having a 150-mm
(6-in.) blade.
9.2 Weigh separately the leakage collector and the hub cap
to the nearest 0.1 g. Place the leakage collector and the large
(inner) bearing in the proper position on the spindle (Note 5).
Put the hub and small (outer) bearing on the spindle, followed
by the loose-fitting retainer ring (Note 6). With the torque
FIG. 1 Apparatus for Testing Leakage Tendencies of Wheel
Bearing Greases wrench, tighten the hexagonal nut which holds the hub
assembly in place, applying a torque of 6.8 6 0.1 N·m (60 6
2lbf·in.).Thenbackoffthehexagonalnut60 65°(oroneflat),
test. Such additional information can be of special interest to individual and lock it in position with a second hexagonal nut. Screw on
operators. The observations, however, are subject to differences in
thehubcap,puttheV-beltonthepulleys,andclosethecabinet
personal judgment among operators, and cannot be used effectively for
(Note 7 and Note 8).
quantitative rating.
NOTE 5—Caution:All grease collectors should be inspected carefully
6. Apparatus to make sure that the inner lip is flush with the sealing face. Otherwise,
this lip will interfere with the correct seating of the inner bearing.
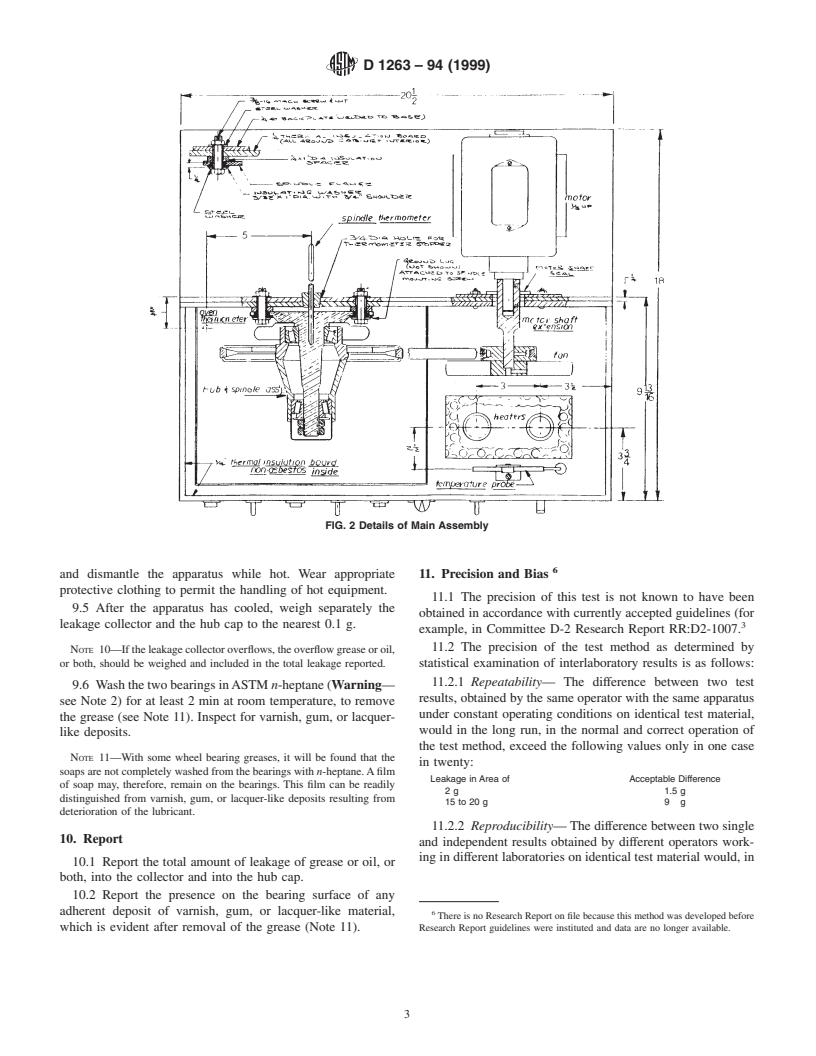
6.1 TheapparatusshowninFig.1andFig.2hasbeenfound
NOTE 6—Caution:In assembling the packed hub on the spindle, care
suitable and is described in detail in Annex A1. The tester
should be taken to prevent contact between grease pack and spindle.
consists of a special front wheel hub and spindle assembly, the
NOTE 7—Caution:From time to time, the drive pulley and the driven
hub being rotated by an electric motor through a V-belt drive.
pulley should be checked for alignment. Misalignment can introduce
The assembly is encased in a thermostatically controlled air
leakage variations.
bath. Means of measuring both ambient (cabinet) and spindle
NOTE 8—Excessive end play of the hub assembly is sometimes due to
temperaturesareprovided.Atorquewrench,suitableforuseon
worn bearings. Therefore new bearings, both cups and cones, should be
31.75-mm (1 ⁄4-in.) hexagonal nuts, is also required.
installed after each 250 tests, or sooner if inspection indicates wear or
other damage to the bearings.
6.2 The apparatus (spindle, case, and motor) must be
electrically grounded, otherwise the thermocouples will not
9.3 After closing the cabinet turn on the motor and both
function due to accumulated static charges. Provision is made
heaters (Note 9). Operate at a speed of 660 6 30 rpm for 6 h
for this, as shown in Fig. 2.
6 5 min, the spindle temperature being raised to 1056 1.4°C
6.3 Machines furnished with 660-W heaters have been
(220 6 2.5°F) then maintained for the balance of the test
found suitable, and these will usually provide the proper heat
period.Thespindletemperatureof105 61.4°Cisobtainedby
input to attain the temperatures in the specified time intervals.
maintaining an ambient temperature of 115 6 3°C (235 6
However, if it is found that proper balance cannot be obtained,
5°F). Leave the auxiliary heater on only until an ambient or
heaters of the required wattage can be substituted.
oven temperature of 115°C is attained. It is desirable to have
the thermoregulator previously adjusted to maintain a 115°C
7. Test Bearings
oven temperature, or to have a reproducible setting for this
7.1 The inner bearing (tapered roller) isTimken 15118.The
temperature. The ambient temperature of 115 6 3°C shall be
corresponding cup is No. 15250.The smaller, outer bearing, is
attained within 15 6 5 min. The spindle temperature of 1056
Timken 09074, with corresponding cup No. 09196.
1.4°C shall be attained within 60 6 10 min. This combination
results in the spindle holding 105 6 1.4°C for 5 h 6 15 min.
NOTE 9—Caution:Drafts can affect the rate of heating. Care should
therefore be exercised in the location of the tester.
Wrenches meeting these requirements are
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.