ASTM C405-82(1997)
(Practice)Standard Practice for Estimating Consistency of Wet-Mixed Thermal Insulating Cement (Withdrawn 2006)
Standard Practice for Estimating Consistency of Wet-Mixed Thermal Insulating Cement (Withdrawn 2006)
SCOPE
1.1 This practice covers estimating the consistency of thermal insulating cements, after mixing with a known amount of water. The consistency of a wet cement affects such properties as ease of toweling, wet adhesion, drying shrinkage, dry density, and thermal conductivity.
1.2 This practice estimates consistency of thermal insulating cements in terms of either percentage of deformation as described in Method A or inches of penetration as described in Method B.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety problems, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
WITHDRAWN RATIONALE
This practice covers estimating the consistency of thermal insulating cements, after mixing with a known amount of water. The consistency of a wet cement affects such properties as ease of toweling, wet adhesion, drying shrinkage, dry density, and thermal conductivity.
Formerly under the jurisdiction of Committee C16 on Thermal Insulation, this practice was withdrawn in February 2006 in accordance with section 10.5.3.1 of the Regulations Governing ASTM Technical Committees, which requires that standards shall be updated by the end of the eighth year since the last approval date.
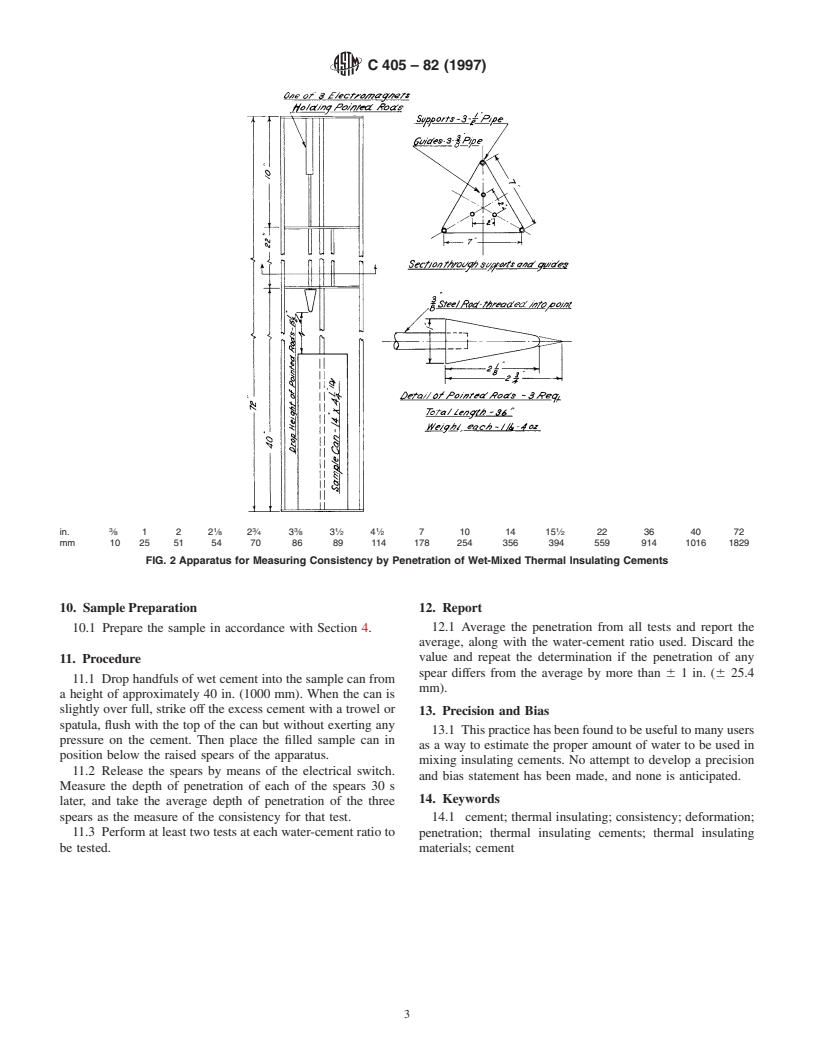
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:C405–82 (Reapproved 1997)
Standard Practice for
Estimating Consistency of Wet-Mixed Thermal Insulating
Cement
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C 405; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope METHOD A—DEFORMATION METHOD
1.1 This practice covers estimating the consistency of ther-
4. Apparatus
mal insulating cements, after mixing with a known amount of
4.1 Dead Load Tester (Fig. 1), equipped with two clamps,
water. The consistency of a wet cement affects such properties
one of which permits the loading member arm to swivel out of
as ease of trowelling, wet adhesion, drying shrinkage, dry
the way while the sample is put in position, while the other
density, and thermal conductivity.
keeps the loading member from sliding until it is released. The
1.2 Thispracticeestimatesconsistencyofthermalinsulating
total weight of the loading member (sliding vertical bar plus
cements in terms of either percentage of deformation as
8-in. (203-mm) diameter disk) is adjusted to exactly 5 lb (2.27
described in MethodAor inches of penetration as described in
kg) by adding weights as necessary at the top of the bar. A
Method B.
cylindrical brass mold, 3 in. (76.2 mm) in inside diameter by 6
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
in. (152.4 mm) in height, is used to prepare the sample.
as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for
information only.
5. Sample Preparation
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
5.1 Sample at least 3 lb (1.4 kg) of dry cement and mix with
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
a weighed amount of water at a temperature of 70 to 75°F (21
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
to 24°C) in accordance with Practice C 163. When thoroughly
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
mixed, smooth the cement into a circular mound 3 to 4 in. high
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
(75 to 100 mm) and allowed to sit for 1 h.Then mix once again
before testing (hydraulic setting cements shall be tested 15 min
2. Referenced Documents
after mixing).
2.1 ASTM Standards:
C 163 Practice for Mixing Thermal Insulating Cement
NOTE 1—All the water to be mixed with the dry cement shall be added
Samples at one time: tests at other water-cement ratios shall be performed using
entirely new batches of cement mixed in accordance with 5.1.
C 168 Terminology Relating to Thermal Insulating Materi-
als
6. Procedure
3. Terminology
6.1 Oil the inside of the cylindrical mold lightly. Fill the
mold by throwing 25 to 30 small pieces of wet cement into it
3.1 Definitions—Except for 3.2, Terminology C 168 shall
with just enough force to eliminate voids. When the mold is
apply to the terms used in this standard.
slightlyoverfull,strikeofftheexcesscementlevelwiththetop
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
of the mold, with a trowel or spatula; take care not to compress
3.2.1 consistency—the degree to which wet-mixed thermal
the cement when this is done.
insulating cement resists deformation due to the application of
6.2 Center the filled mold under the load member of the
outside forces such as trowel pressure.
apparatus, remove the mold, and place the load member flush
on the sample. If the sample deforms (sags) when it is free
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C-16 on Thermal
standing, still place the load member flush on the sample, and
Insulation and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C16.31 on Chemical and
include the amount of sag as part of the measured deformation.
Physical Properties.
Release the load member, and measure the deformation 30 s
Current edition approved June 25, 1982. Published August 1982. Originally
published as C 405 – 58 T. Last previous edition C 405 – 60 (1979). later.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 04.06.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
----------------------
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.