ASTM D4875-11
(Test Method)Standard Test Methods of Polyurethane Raw Materials: Determination of the Polymerized Ethylene Oxide Content of Polyether Polyols
Standard Test Methods of Polyurethane Raw Materials: Determination of the Polymerized Ethylene Oxide Content of Polyether Polyols
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
Measurements of EO content correlate with polyol reactivity (as related to primary hydroxyl content), linearity of foam rise, and the hydrophilicity of the polyol and final product.
Statistical data suggest that the 13C NMR test method is the preferred method for measuring low levels (less than 10 %) of polymerized EO in polyols.
SCOPE
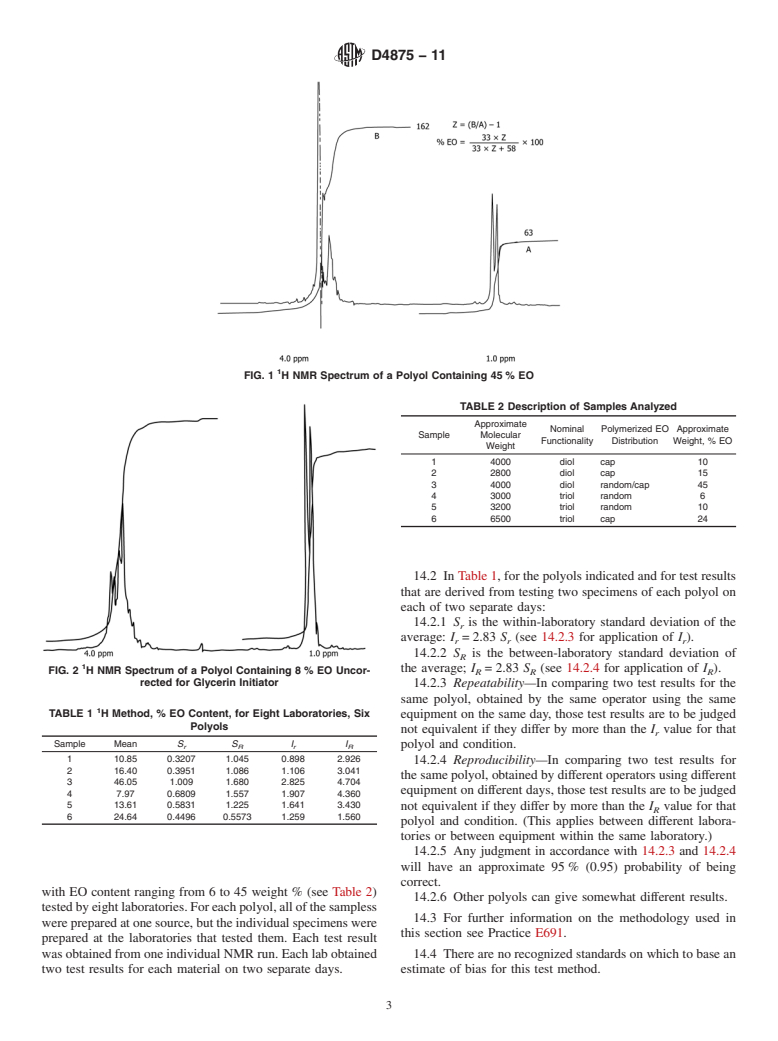
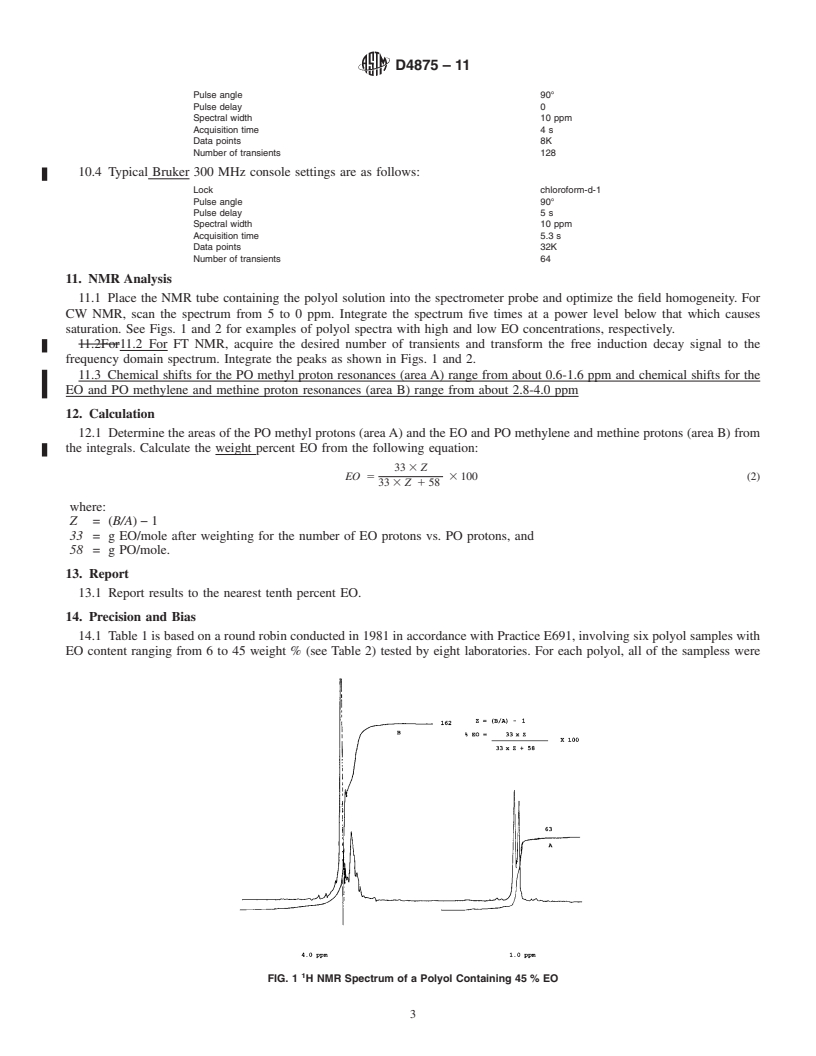
1.1 Test Method A—Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (1H NMR) measures polymerized ethylene oxide (EO) in ethylene oxide-propylene oxide polyethers used in flexible urethane foams and nonfoams. It is suitable for diols made from the commonly used initiators and containing EO percentages above five. For triols initiated with glycerin and trimethylol propane, an uncorrected EO value is obtained since both initiators have protons that contribute to the EO measurement.
1.2 Test Method B—Carbon-13 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (13C NMR) measures the polymerized EO content of ethylene oxide-propylene oxide polyethers used in flexible urethane foams and nonfoams. It is suitable for diols and triols made from the commonly used initiators and containing EO percentages above five.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Note 1—There is no known ISO equivalent to this standard.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D4875 − 11
Standard Test Methods of
Polyurethane Raw Materials: Determination of the
1
Polymerized Ethylene Oxide Content of Polyether Polyols
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4875; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* E691Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
1.1 Test Method A—Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
1
Spectroscopy( HNMR)measurespolymerizedethyleneoxide
3. Terminology
(EO) in ethylene oxide-propylene oxide polyethers used in
flexible urethane foams and nonfoams. It is suitable for diols
3.1 Definitions—Terminology in these test methods follows
made from the commonly used initiators and containing EO
the standard terminology defined in Terminology D883 and
percentages above five. For triols initiated with glycerin and
Practice E386.
trimethylolpropane,anuncorrectedEOvalueisobtainedsince
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
both initiators have protons that contribute to the EO measure-
ment.
3.2.1 heteric polyol, n—a polyether polyol in which ethyl-
ene oxide and propylene oxide units are randomly arranged.
1.2 Test Method B—Carbon-13 Nuclear Magnetic Reso-
13
nance Spectroscopy ( C NMR) measures the polymerized EO
3.2.2 initiator, n—a substance with which ethylene oxide or
content of ethylene oxide-propylene oxide polyethers used in
propylene oxide reacts to form a polyether polyol.
flexible urethane foams and nonfoams. It is suitable for diols
3.2.2.1 Discussion—One initiator unit is incorporated into
and triols made from the commonly used initiators and
each polymer or oligomer molecule.
containing EO percentages above five.
3.2.3 EO capped polyol—a polyol that contains a terminal
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
block of ethylene oxide units
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
standard.
4. Summary of Test Methods
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
1
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
4.1 Test Method A—The H NMR spectra of polyether
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
polyols show two groups of resonance peaks corresponding to
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
the methyl protons of propylene oxide (PO) and to the
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
methylene and methine protons of EO and PO. The EO peak
areaisobtainedbysubtractingtheareaofthePOmethylpeaks
NOTE 1—There is no known ISO equivalent to this standard.
from the area of the methylene and methine peaks. Initiators
2. Referenced Documents
other than glycols of EO and PO give systematic errors (see
2
2.1 ASTM Standards: Note 2).
D883Terminology Relating to Plastics
NOTE 2—The initiator error can be estimated by calculating the
E386Practice for Data Presentation Relating to High-
theoretical contribution of initiator protons to the EO and PO peak areas.
Resolution Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spec-
13
4.2 Test Method B—The C NMR spectra of polyether
troscopy
polyols contain multiple resonances arising from initiator, EO,
1 PO, EO/PO, sequencing, and end-group distribution. EO con-
These test methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D20 on
Plastics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.22 on Cellular
tentcanbedeterminedrelativetoPOorrelativetoPOandtriol
Materials - Plastics and Elastomers.
initiator.Intheformer,theareaoftheEOpeaksisratioedtothe
Current edition approved April 1, 2011. Published April 2011. Originally
total area of PO methylene and methine carbons. In the latter,
approved in 1988. Last previous edition approved in 2005 as D4875-05. DOI:
10.1520/D4875-11.
the area of the EO peaks is ratioed to the total area of PO
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
methyleneandmethinecarbonsandtwoinitiatorcarbons.This
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
test method describes the determination of EO relative to PO
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. only.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D4875 − 11
5. Significance and Use
Lock optional, TMS
Offset 0
5.1 Measurements of EO content correlate with polyol
Sweep width 5 ppm
reactivity (as related to primary hydroxyl content), linearity of Sweep time
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:D4875–05 Designation:D4875–11
Standard Test Methods of
Polyurethane Raw Materials: Determination of the
1
Polymerized Ethylene Oxide Content of Polyether Polyols
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4875; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1
1.1 Test Method A—Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy ( H NMR) measures polymerized ethylene oxide (EO)
in ethylene oxide-propylene oxide polyethers used in flexible urethane foams and nonfoams. It is suitable for diols made from the
commonly used initiators and containing EO percentages above five. For triols initiated with glycerin and trimethylol propane, an
uncorrected EO value is obtained since both initiators have protons that contribute to the EO measurement.
13
1.2 Test Method B—Carbon-13 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy ( C NMR) measures the polymerized EO content
ofethyleneoxide-propyleneoxidepolyethersusedinflexibleurethanefoamsandnonfoams.Itissuitablefordiolsandtriolsmade
from the commonly used initiators and containing EO percentages above five. C NMR) measures the polymerized EO content of
ethylene oxide-propylene oxide polyethers used in flexible urethane foams and nonfoams. It is suitable for diols and triols made
from the commonly used initiators and containing EO percentages above five.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
NOTE1—There are no equivalent ISO standards.
1.3This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use. 1—There is no known ISO equivalent to this standard.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
E386 Practice for Data Presentation Relating to High-Resolution Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to Determine the Precision of a Test Method
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions—TerminologyinthesetestmethodsfollowsthestandardterminologydefinedinTerminologyD883andPractice
E386.
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.2.1 heteric polyol, n—a polyether polyol in which ethylene oxide and propylene oxide units are randomly arranged.
3.2.2 initiator, n—a substance with which ethylene oxide or propylene oxide reacts to form a polyether polyol.
3.2.2.1 Discussion—One initiator unit is incorporated into each polymer or oligomer molecule.
3.2.3 EO capped polyol—a polyol that contains a terminal block of ethylene oxide units
4. Summary of Test Methods
1
4.1 Test MethodA—The HNMRspectraofpolyetherpolyolsshowtwogroupsofresonancepeakscorrespondingtothemethyl
protons of propylene oxide (PO) and to the methylene and methine protons of EO and PO. The EO peak area is obtained by
1
These test methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D20 on Plastics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.22 on Cellular Plastics.
Current edition approved July 1, 2005. Published August 2005. Originally approved in 1988. Last previous edition approved in 1999 as D4875-99. DOI:
10.1520/D4875-05.on Cellular Materials - Plastics and Elastomers.
Current edition approved April 1, 2011. Published April 2011. Originally approved in 1988. Last previous edition approved in 2005 as D4875-05. DOI:
10.1520/D4875-11.
2
ForreferencedASTMstandards,visittheASTMwebsite,www.astm.org,orcontactASTMCustomerServiceatservice@astm.org.For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D4875–11
subtracting the area of the PO met
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.