ASTM D7511-12
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Total Cyanide by Segmented Flow Injection Analysis, In-Line Ultraviolet Digestion and Amperometric Detection
Standard Test Method for Total Cyanide by Segmented Flow Injection Analysis, In-Line Ultraviolet Digestion and Amperometric Detection
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
Cyanide and hydrogen cyanide are highly toxic. Regulations have been established to require the monitoring of cyanide in industrial and domestic wastewaters and surface waters.
This test method is applicable for natural water, saline waters, and wastewater effluent.
The method may be used for process control in wastewater treatment facilities.
The spot test outlined in Test Methods D2036, Annex A1 can be used to detect cyanide and thiocyanate in water or wastewater, and to approximate its concentration.
SCOPE
1.1 This method is used for determining total cyanide in drinking and surface waters, as well as domestic and industrial wastes. Cyanide ion (CN-), hydrogen cyanide in water (HCN(aq)), and the cyano-complexes of zinc, copper, cadmium, mercury, nickel, silver, and iron may be determined by this method. Cyanide ions from Au(I), Co(III), Pd(II), and Ru(II) complexes are only partially determined.
1.2 The method detection limit (MDL) is 1.0 μg/L cyanide and the minimum level (ML) is 3 μg/L. The applicable range of the method is 3 to 500 μg/L cyanide using a 200-μL sample loop. Extend the range to analyze higher concentrations by sample dilution or changing the sample loop volume.
1.3 This method can be used by analysts experienced with equipment using segmented flow analysis (SFA) and flow injection analysis (FIA) or working under the close supervision of such qualified persons.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific hazard statements are given in Note 2 and Section 9.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D7511 − 12
Standard Test Method for
Total Cyanide by Segmented Flow Injection Analysis, In-Line
1
Ultraviolet Digestion and Amperometric Detection
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7511; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope D2777 Practice for Determination of Precision and Bias of
Applicable Test Methods of Committee D19 on Water
1.1 This method is used for determining total cyanide in
D3370 Practices for Sampling Water from Closed Conduits
drinking and surface waters, as well as domestic and industrial
- D3856 Guide for Management Systems in Laboratories
wastes. Cyanide ion (CN ), hydrogen cyanide in water
Engaged in Analysis of Water
(HCN(aq)), and the cyano-complexes of zinc, copper,
D4210 Practice for Intralaboratory Quality Control Proce-
cadmium, mercury, nickel, silver, and iron may be determined
dures and a Discussion on Reporting Low-Level Data
by this method. Cyanide ions from Au(I), Co(III), Pd(II), and
3
(Withdrawn 2002)
Ru(II) complexes are only partially determined.
D5847 Practice for Writing Quality Control Specifications
1.2 The method detection limit (MDL) is 1.0 µg/L cyanide
for Standard Test Methods for Water Analysis
andtheminimumlevel(ML)is3µg/L.Theapplicablerangeof
D6696 Guide for Understanding Cyanide Species
the method is 3 to 500 µg/L cyanide using a 200-µL sample
D7365 Practice for Sampling, Preservation and Mitigating
loop. Extend the range to analyze higher concentrations by
Interferences in Water Samples for Analysis of Cyanide
sample dilution or changing the sample loop volume.
1.3 This method can be used by analysts experienced with 3. Terminology
equipment using segmented flow analysis (SFA) and flow
3.1 Definitions:
injectionanalysis(FIA)orworkingundertheclosesupervision
3.1.1 For definitions of terms used in this test method, refer
of such qualified persons.
to Terminology D1129 and Guide D6696.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
3.1.2 total cyanide—refers to all cyanide-containing com-
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
pounds in a sample, including free cyanide, WAD cyanide
standard.
compounds, and strong metal cyanide complexes.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
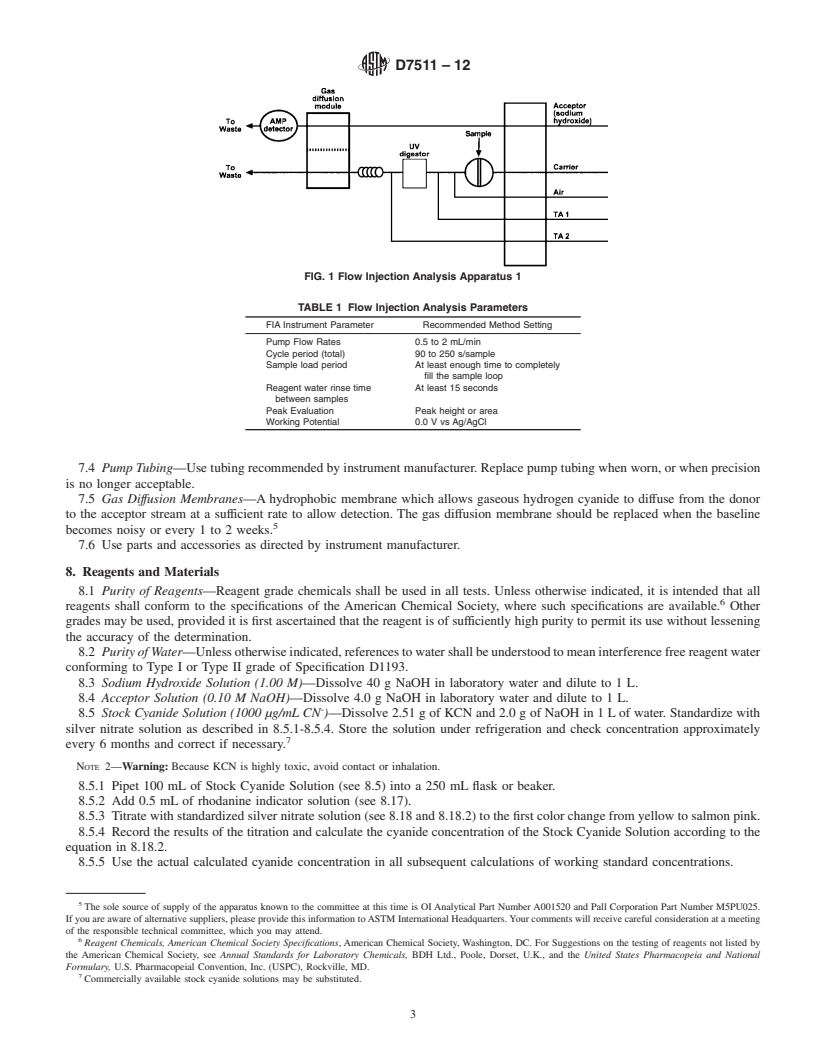
4. Summary of Test Method
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
4.1 Prior to analysis, treat the sample to remove potential
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
interferences (Sections 4 and 8). Ultraviolet (UV) digestion
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific hazard
releases cyanide from cyanide complexes. Acid addition con-
statements are given in Note 2 and Section 9.
verts cyanide ion to hydrogen cyanide gas (HCN), which
passes under a gas diffusion membrane. The hydrogen cyanide
2. Referenced Documents
gas diffuses through the membrane into an alkaline receiving
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
solution, where it converts back to cyanide ion. A silver
D1129 Terminology Relating to Water
working electrode, silver/silver chloride reference electrode,
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
and platinum/stainless steel counter electrode at an applied
D2036 Test Methods for Cyanides in Water
potential of zero volt amperometrically monitor the cyanide
ion. The current generated is proportional to the cyanide
concentration present in the original sample.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D19 on Water
andisthedirectresponsibilityofSubcommitteeD19.06onMethodsforAnalysisfor
4.2 Calibrations and data are processed with the instru-
Organic Substances in Water.
ment’s data acquisition software.
Current edition approved Jan. 1, 2012. Published January 2012. Last previous
edition published 2009 as D7511–09E01. DOI: 10.1520/D7511-12.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
3
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
the ASTM website. www.astm.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D7511 − 12
5. Significance and Use dioxide diffuses across the gas diffusion membrane into the
alkaline receiving solution, reducing its pH. Treat effluents
5.1 Cyanide and hydrogen cyanide are highly toxic. Regu-
from high carbonate
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
´2
Designation:D7511–09 Designation: D7511 – 12
Standard Test Method for
Total Cyanide by Segmented Flow Injection Analysis, In-Line
1
Ultraviolet Digestion and Amperometric Detection
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7511; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1
´ NOTE—A typographical error was editorially corrected in Section 8.13 in March 2010.
2
´ NOTE—Research report information was editorially added in March 2010.
1. Scope
1.1 This method is used for determining total cyanide in drinking and surface waters, as well as domestic and industrial wastes.
-
Cyanide ion (CN ), hydrogen cyanide in water (HCN(aq)), and the cyano-complexes of zinc, copper, cadmium, mercury, nickel,
silver, and iron may be determined by this method. Cyanide ions from Au(I), Co(III), Pd(II), and Ru(II) complexes are only
partially determined.
1.2 The method detection limit (MDL) is 1.0 µg/Lcyanide and the minimum level (ML) is 3 µg/L. The applicable range of the
methodis3to500µg/Lcyanideusinga200-µLsampleloop.Extendtherangetoanalyzehigherconcentrationsbysampledilution
or changing the sample loop volume.
1.3 This method can be used by analysts experienced with equipment using segmented flow analysis (SFA) and flow injection
analysis (FIA) or working under the close supervision of such qualified persons.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use. Specific hazard statements are given in Note 2 and Section 9.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D1129 Terminology Relating to Water
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
D2036 Test Methods for Cyanides in Water
D2777 Practice for Determination of Precision and Bias of Applicable Test Methods of Committee D19 on Water
D3370 Practices for Sampling Water from Closed Conduits
D3856 Guide for Management Systems in Laboratories Engaged in Analysis of Water
D4210 Practice for Intralaboratory Quality Control Procedures and a Discussion on Reporting Low-Level Data
D5847 Practice for Writing Quality Control Specifications for Standard Test Methods for Water Analysis
D6696 Guide for Understanding Cyanide Species
D7365 Practice for Sampling, Preservation and Mitigating Interferences in Water Samples for Analysis of Cyanide
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 For definitions of terms used in this test method, refer to Terminology D1129 and Guide D6696.
3.1.2 total cyanide—referstoallcyanide-containingcompoundsinasample,includingfreecyanide,WADcyanidecompounds,
and strong metal cyanide complexes.
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 Prior to analysis, treat the sample to remove potential interferences (Sections 4 and 8). Ultraviolet (UV) digestion releases
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D19 on Water and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D19.06 on Methods for Analysis for
Organic Substances in Water.
Current edition approved Feb. 15, 2009. Published March 2009. DOI: 10.1520/D7511-09.
Current edition approved Jan. 1, 2012. Published January 2012. Last previous edition published 2009 as D7511–09E01. DOI: 10.1520/D7511-12.
2
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book ofASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D7511 – 12
cyanide from cyanide complexes. Acid addition converts cyanide ion to hydrogen cyanide gas (HCN), which passes under a gas
diffusion membrane. The hydrogen cyanide gas diffuses through the membrane into an alkaline receiving solution, where it
converts back to cyanide ion. A silver working electrode, silver/silver chloride reference electrode, and platinum/stainless steel
counter electrode at an applied potential of zero volt amperometrically monitor the
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.