ASTM D3454-11
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Radium-226 in Water
Standard Test Method for Radium-226 in Water
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
The most prevalent of the five radium isotopes in ground water, having a half life greater than one day, are 226Ra and 228Ra. These two isotopes also present the greatest health risk compared to the other naturally occurring nuclides of equal concentrations if ingested via the water pathway.
Although primarily utilized on a water medium, this technique may be applicable for the measurement of the 226Ra content of any media once the medium has been completely decomposed and put into an aqueous solution.
The general methodology and basis of this technique are similar to the methodology “226Ra in Drinking Water (Radon Emanation Technique)” as described in the document EPA-600//4-80-032.
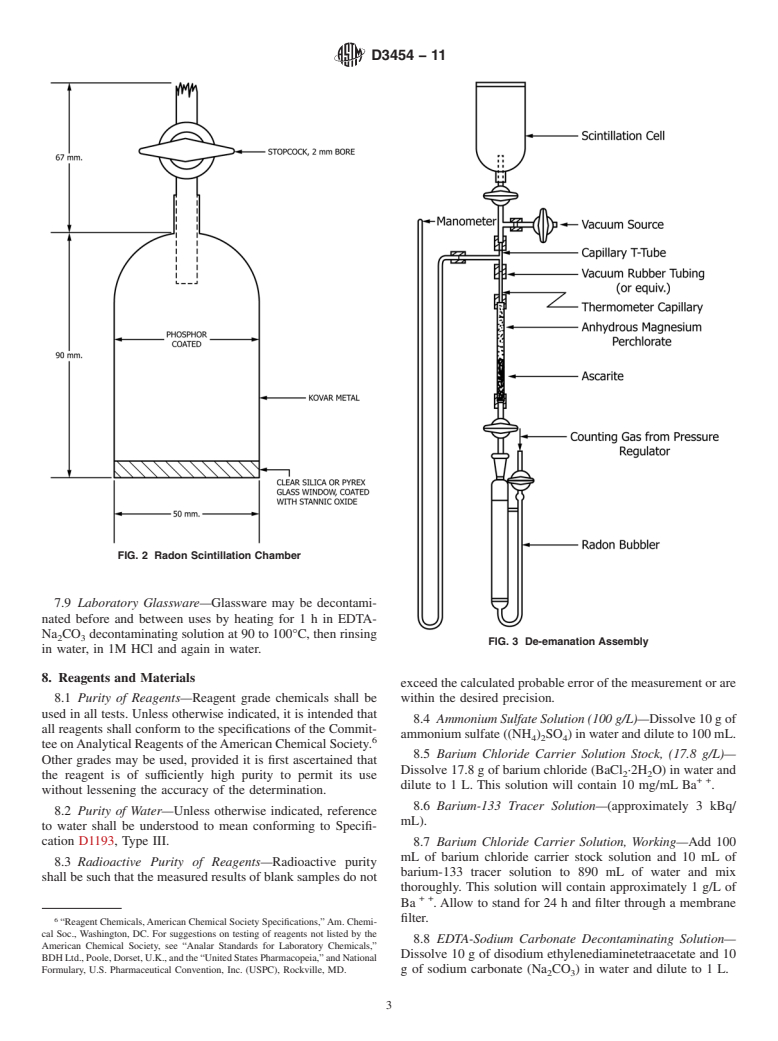
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the measurement of soluble, suspended, and total radium-226 in water in concentrations above 3.7 × 10−3 Bq/L. This test method is not applicable to the measurement of other radium isotopes.
1.2 This test method may be used for quantitative measurements by calibrating with a radium-226 standard, or for relative measurements by comparing the measurements made with each other.
1.3 This test method does not meet the current requirements of Practice D2777.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The inch-pound units given in parentheses are for information only.
1.5 Hydrofluoric acid (HF) is very hazardous and should be used in a well-ventilated hood. Wear rubber gloves, safety glasses or goggles, and a laboratory coat. Avoid breathing any HF fumes. Clean up all spills promptly and wash thoroughly after using HF.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the other safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D3454 − 11
Standard Test Method for
1
Radium-226 in Water
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D3454; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope D3648Practices for the Measurement of Radioactivity
D3649PracticeforHigh-ResolutionGamma-RaySpectrom-
1.1 This test method covers the measurement of soluble,
etry of Water
suspended, and total radium-226 in water in concentrations
−3 D3856Guide for Management Systems in Laboratories
above 3.7×10 Bq/L. This test method is not applicable to
Engaged in Analysis of Water
the measurement of other radium isotopes.
D4448Guide for Sampling Ground-Water MonitoringWells
1.2 This test method may be used for quantitative measure-
D5847Practice for Writing Quality Control Specifications
mentsbycalibratingwitharadium-226standard,orforrelative
for Standard Test Methods for Water Analysis
measurements by comparing the measurements made with
D6001Guide for Direct-Push Groundwater Sampling for
each other.
Environmental Site Characterization
1.3 Thistestmethoddoesnotmeetthecurrentrequirements D7282Practice for Set-up, Calibration, and Quality Control
of Instruments Used for Radioactivity Measurements
of Practice D2777.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
3. Terminology
standard. The inch-pound units given in parentheses are for
3.1 Fordefinitionsoftermsusedinthistestmethod,referto
information only.
Terminology D1129. For terms not defined in this test method
1.5 Hydrofluoric acid (HF) is very hazardous and should be
or in Terminology D1129, reference may be made to other
used in a well-ventilated hood. Wear rubber gloves, safety
published glossaries.
glasses or goggles, and a laboratory coat.Avoid breathing any
HF fumes. Clean up all spills promptly and wash thoroughly
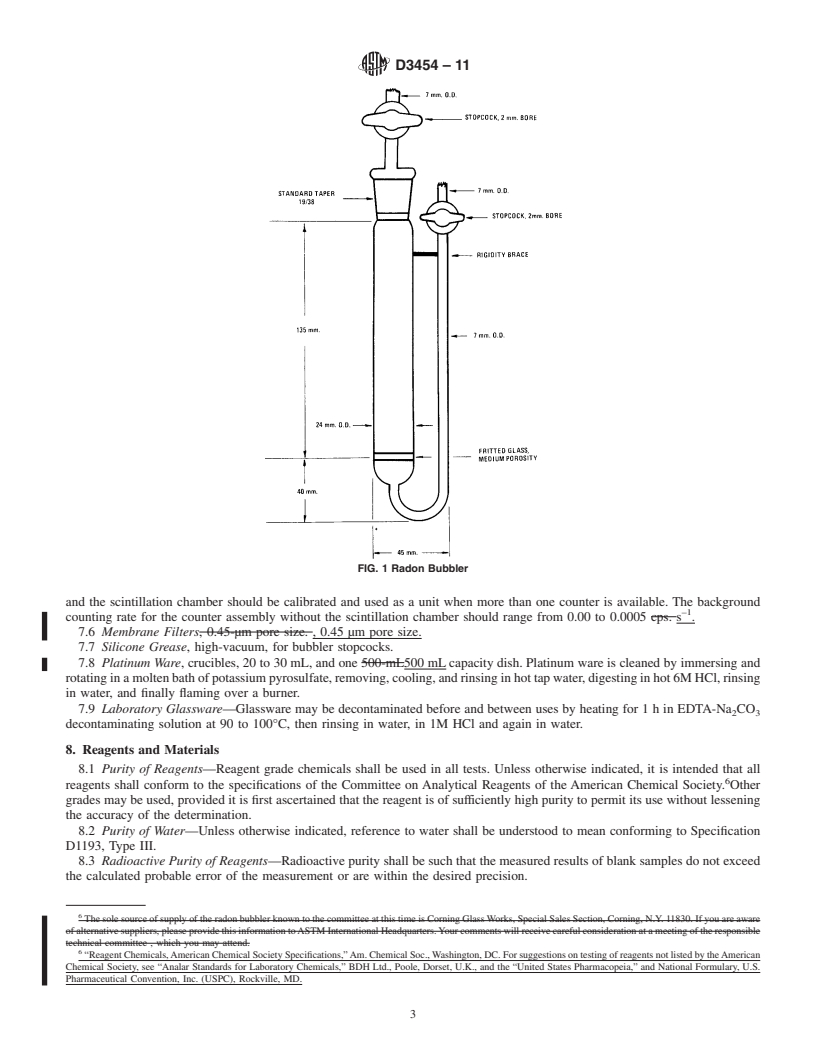
4. Summary of Test Method
after using HF.
3
4.1 This test method is based on the emanation and
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the
222
scintillation counting of Rn, a gaseous daughter product
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
226
of Ra, from a solution.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
226
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica- 4.2 Ra is collected from water by coprecipitation on a
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. relatively large amount of barium sulfate. The barium-radium
sulfateisdecomposedbyfumingwithphosphoricacid,andthe
2. Referenced Documents
resulting glassy melt is dissolved by evaporation with dilute
2
hydrochloric acid to form soluble barium-radium phosphates
2.1 ASTM Standards:
and chlorides. These salts are dissolved and the solution is
D1129Terminology Relating to Water
222
stored for ingrowth of Rn.After a suitable ingrowth period,
D1193Specification for Reagent Water
theradongasisremovedfromthesolutionbypurgingwithgas
D2777Practice for Determination of Precision and Bias of
and transferred to a scintillation counting chamber. About 4 h
Applicable Test Methods of Committee D19 on Water
222
after Rn collection, the scintillation chamber is counted for
D3370Practices for Sampling Water from Closed Conduits
226
alpha activity. The Ra concentration is calculated from the
222
alpha count rate of Rn and its immediate daughters. The
226
radioactive decay characteristics of Ra and its immediate
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D19 on Water
decay progeny are listed in Table 1.
andisthedirectresponsibilityofSubcommitteeD19.04onMethodsofRadiochemi-
cal Analysis.
Current edition approved June 15, 2011. Published July 2011. Originally
approved in 1975. Last previous edition approved in 2005 as D3454–05. DOI:
3
10.1520/D3454-11. This test method is based on a previously published method by Rushing, D.E.,
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or Garcia, W.J., and Clark, D.A. “The Analysis of Effluents and Environmental
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Samples from Uranium Mills and of Biological Samples for Radium, Polonium and
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Uranium,” Radiological Health and Safety in Mining and Milling of Nuclear
the ASTM website. Materials, Vol. II, IAEA, Vienna, Austria, 1964), p. 187.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D3454 − 11
TABLE 1 Radioactive Decay Characteristics of Radium-226 and
Its Daughters
Radionuclide Half-life Mode o
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:D3454–05 Designation:D3454–11
Standard Test Method for
1
Radium-226 in Water
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D3454; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1This1.1 This test method covers the measurement of soluble, suspended, and total radium-226 in water in concentrations
−3
above 3.7 310 Bq/L. This test method is not applicable to the measurement of other radium isotopes.
1.2 This test method may be used for quantitative measurements by calibrating with a radium-226 standard, or for relative
measurements by comparing the measurements made with each other.
1.3 This test method does not meet the current requirements of Practice D2777.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The inch-pound units given in parentheses are for
information only.
1.5 Hydrofluoric acid (HF) is very hazardous and should be used in a well-ventilated hood. Wear rubber gloves, safety glasses
or goggles, and a laboratory coat. Avoid breathing any HF fumes. Clean up all spills promptly and wash thoroughly after using
HF.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the other safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of
regulatory limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D1129 Terminology Relating to Water
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
D2777 Practice for Determination of Precision and Bias of Applicable Test Methods of Committee D19 on Water
D3370 Practices for Sampling Water from Closed Conduits
D3648 Practices for the Measurement of Radioactivity
D3649 Practice for High-Resolution Gamma-Ray Spectrometry of Water
D3856 Guide for Good Laboratory Practices in Laboratories Engaged in Sampling and Analysis of Water
D4448 Guide for Sampling Ground-Water Monitoring Wells
D5847 Practice for Writing Quality Control Specifications for Standard Test Methods for WaterAnalysis Practice for Writing
Quality Control Specifications for Standard Test Methods for Water Analysis
D6001 Guide for Direct-Push Ground Water Sampling for Environmental Site Characterization
D7282 Practice for Set-up, Calibration, and Quality Control of Instruments Used for Radioactivity Measurements
3. Terminology
3.1Definitions—For3.1 For definitions of terms used in this test method, refer to Terminology D1129, and to other published
glossaries. . For terms not defined in this test method or in Terminology D1129, reference may be made to other published
glossaries.
4. Summary of Test Method
222 226
3
4.1 This test method is based on the emanation and scintillation counting of Rn, a gaseous daughter product of Ra, from
a solution.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D19 on Water and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D19.04 on Methods of Radiochemical
Analysis.
CurrenteditionapprovedFeb.1,2005.PublishedFebruary2005.Originallyapprovedin1975.Lastpreviouseditionapprovedin1997asD3454–97.DOI:10.1520/D3454-05.
CurrenteditionapprovedJune15,2011.PublishedJuly2011.Originallyapprovedin1975.Lastpreviouseditionapprovedin2005asD3454–05.DOI:10.1520/D3454-11.
2
ForreferencedASTMstandards,visittheASTMwebsite,www.astm.org,orcontactASTMCustomerServiceatservice@astm.org.For Annual Book ofASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
American National Standard Glossary of Terms in Nuclear Science and Technology, N1.1-1967.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D3454–11
226
4.2 Ra is collected from water by coprecipitation on a relatively large amount of barium sulfate. The barium-radium sulfate
is decomposed by fuming with phosphoric acid, and the resulting glassy melt is dissolved by evaporation with dilute hydrochloric
acid to form soluble barium-radium phosphates and chlorides. These salts are dissolved and the solution is stored for ingrowth
222
of Rn. After a suitable ingrowth period, the radon gas is removed from the solution by purging with gas and transferred to a
222 226
scintillation counting chamber.About 4 h after
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.